| [1] Hwang CM, Lee BK, Green D, et al. Auricular reconstruction using tissue-engineered alloplastic implants for improved clinical outcomes. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2014;133(3):360e-369e. [2] Murphy EH, Szeto WY, Herdrich BJ, et al. The management of endograft J Vasc Surg. 2013;58(5):1179-1185.[3] Darouiche RO. Treatment of infections associated with surgical implants. N Engl J Med. 2004;350(14):1422-1429.[4] Narayanan KB, Han SS. Dual-crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol)/sodium alginate/silver nanocomposite beads - A promising antimicrobial material. Food Chem. 2017;234:103-110. [5] Jeon HJ, Yi SC, Oh SG. Preparation and antibacterial effects of Ag-SiO2 thin films by sol-gel method. Biomaterials. 2003;24(27): 4921-4928.[6] 冯宇,曹聪,董宇启,等.载银纳米氧化钛涂层抗菌性能的初步研究[J].中华医学杂志,2008,88(29):2077-2080.[7] Rautray TR, Narayanan R, Kwon TY, et al. Surface modification of titanium and titanium alloys by ion implantation. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2010;93(2):581-591. [8] Goderecci SS, Kaiser E, Yanakas M, et al. Silver Oxide Coatings with High Silver-Ion Elution Rates and Characterization of Bactericidal Activity. Molecules. 2017;22(9):E1487.[9] Kose N, Otuzbir A, Pek?en C, et al. A silver ion-doped calcium phosphate-based ceramic nanopowder-coated prosthesis increased infection resistance. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(8):2532-2539. [10] 徐连春,尚剑,孙晔,等.银纳米颗粒及载银抗菌涂层的研究与进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(25):3793-3800.[11] 李庆艳,郑新颖,吕俏,等.无机载银抗菌剂在口腔修复中的研究应用现状[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(29):5460-5464.[12] 王家琦,尚剑,孙晔,等.钛合金表面抗菌涂层:抗菌能力及生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(25):4069-4075.[13] 李建新,王进,沈丽如,等.银离子注入表面改性涤纶材料的抗菌性能研究[J].真空科学与技术学报,2006,26(5):408-411.[14] 周鑫,陈兴,石小花,等.银离子表面注入改性硅橡胶抗菌性能及生物相容性的初步研究[J].第三军医大学学报, 2015,37(19):1914-1920.[15] 向友来,覃礼钊,李崇,等.Ag/Cu离子双注入ABS树脂抗菌性能研究[J].塑料科技,2014,42(10):25-29.[16] 李金华.医用钛合金表面微纳结构/组分调控及其生物学性能研究[D].北京:中国科学院大学,2016.[17] 张薇.材料的表面改性对细菌粘附的影响[D].无锡:江南大学, 2016.[18] 侯兴刚,闫广青,马慧艳,等.Ag+注入对TiO2薄膜光催化、抗菌和亲水性能的影响[J].天津师范大学学报(自然版), 2015,35(4):30-36.[19] 赵永彬,王永,赵亚群.银离子对卡介苗菌株黏附硅胶管表面特性的影响[J].实用医学杂志,2016,32(4):535-538.[20] Kumar R, Münstedt H. Silver ion release from antimicrobial polyamide/silver composites. Biomaterials. 2005;26(14):2081-2088.[21] Xiu ZM, Zhang QB, Puppala HL, et al. Negligible particle-specific antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2012;12(8): 4271-4275. [22] Rochford ET, Richards RG, Moriarty TF. Influence of material on the development of device-associated infections. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2012;18(12):1162-1167. [23] 邹国友,沈灏,蒋垚.材料表面发热范围温度升高对于内植物相关感染的预防[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2010,3(3):183-185.[24] 张巍.纳米抑菌与抗菌内植物的研发[D].北京:解放军军医进修学院,2009.[25] 王光超.负载万古霉素具贯通孔图案结构钛涂层的制备及在骨科应用基础研究[D].上海:第二军医大学,2017.[26] 邹国友.表面温度发热范围升高预防和治疗内植物金黄色葡萄球菌感染的实验[D].上海:上海交通大学,2010.[27] Zimmerli W. Clinical presentation and treatment of orthopaedic implant-associated infection. J Intern Med. 2014;276(2):111-119. [28] 周炎,刘世清,瞿新丛,等.保留内植物结合负压封闭引流技术治疗四肢骨折术后早期感染[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究, 2015,12(6):54-57. [29] 闫廷飞,孙晨曦,杨勇,等.腰椎内固定术后感染的临床研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2016,36(22):1463-1468.[30] 姚海,刘涛,王信,等.血清IL-6水平在小鼠术后早期内植物感染中的筛查作用[J].中国抗生素杂志,2013,38(4):275-279. |
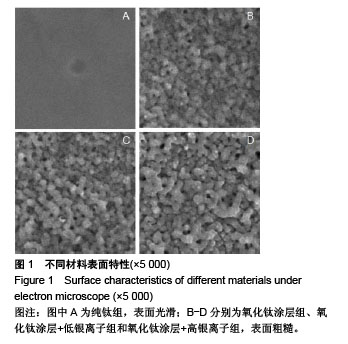
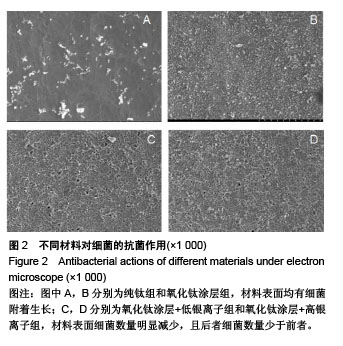
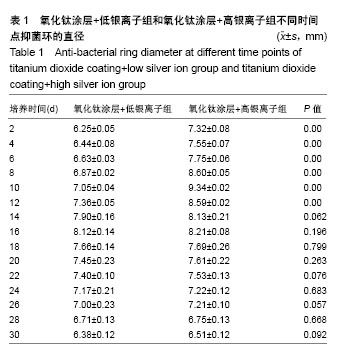
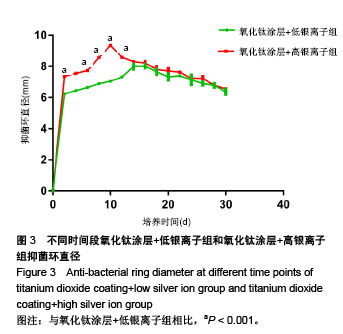
.jpg)
.jpg)