| [1] Society Of Cariology And Endodontology CS. Guidelines for Root Canal Therapy. Chin J Dent Res. 2015;18(4):213-216. [2] Jordan RA, Holzner AL, Markovic L, et al. Clinical effectiveness of basic root canal treatment after 24 months: a randomized controlled trial. J Endod. 2014;40(4):465-470. [3] Kang SH, Kim BS, Kim Y. Cracked Teeth: Distribution, Characteristics, and Survival after Root Canal Treatment. J Endod. 2016;42(4):557-562.[4] Galler KM, Brandl FP, Kirchhof S, et al. Suitability of Different Natural and Synthetic Biomaterials for Dental Pulp Tissue Engineering. Tissue Eng Part A. 2017 Jul 20. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEA.2016.0555. [Epub ahead of print][5] 杜暘,高秀秋,金鼎. 丝素胶原支架与人牙周膜成纤维细胞相容性研究[J]. 中国实用口腔科杂志, 2009, 2(9):534-536.[6] Wang SD, Ma Q, Wang K, et al. Strong and biocompatible three-dimensional porous silk fibroin/graphene oxide scaffold prepared by phase separation. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;111: 237-246.[7] Harumi Miyagi SP, Kerkis I, da Costa Maranduba CM, et al. Expression of extracellular matrix proteins in human dental pulp stem cells depends on the donor tooth conditions. J Endod. 2010;36(5): 826-831. [8] Jafary F, Hanachi P, Gorjipour K. Osteoblast Differentiation on Collagen Scaffold with Immobilized Alkaline Phosphatase. Int J Organ Transplant Med. 2017;8(4):195-202.[9] Shekhter AB, Guller AE, Istranov LP, et al. Morphology of collagen matrices for tissue engineering (biocompatibility, biodegradation, tissue response). Arkh Patol. 2015;77(6):29-38. [10] Hou G, Zhou F, Guo Y, et al. In vivo study of a bioactive nanoparticle-gelatin composite scaffold for bone defect repair in rabbits. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2017;28(11):181.[11] Fayyazbakhsh F, Solati-Hashjin M, Keshtkar A, et al. Release behavior and signaling effect of vitamin D3 in layered double hydroxides-hydroxyapatite/gelatin bone tissue engineering scaffold: An in vitro evaluation. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2017;158:697-708.[12] Ishihara T, Miyazaki M, Notani N, et al. Locally Applied Simvastatin Promotes Bone Formation in a Rat Model of Spinal Fusion. J Orthop Res. 2017;35(9):1942-1948.[13] Oryan A, Sharifi P, Moshiri A, et al. The role of three-dimensional pure bovine gelatin scaffolds in tendon healing, modeling, and remodeling: an in vivo investigation with potential clinical value. Connect Tissue Res. 2017;58(5):424-437.[14] Duan W, Haque M, Kearney MT, et al. Collagen and Hydroxyapatite Scaffolds Activate Distinct Osteogenesis Signaling Pathways in Adult Adipose-Derived Multipotent Stromal Cells. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2017;23(10):592-603.[15] Yang F, Miao Y, Wang Y, et al. Electrospun Zein/Gelatin Scaffold- Enhanced Cell Attachment and Growth of Human Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells. Materials (Basel). 2017;10(10): E1168.[16] Kucinska-Lipka J, Gubanska I, Janik H, et al. Fabrication of polyurethane and polyurethane based composite fibres by the electrospinning technique for soft tissue engineering of cardiovascular system. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2015;46: 166-176.[17] Huang L, Zhu L, Shi X, et al. A compound scaffold with uniform longitudinally oriented guidance cues and a porous sheath promotes peripheral nerve regeneration in vivo.Acta Biomater. 2017. pii: S1742-7061(17)30766-3. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2017.12.010. [Epub ahead of print][18] Ghaderi Gandomani M, Sahebghadam Lotfi A, Kordi Tamandani D, et al. The enhancement of differentiating adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells toward hepatocyte like cells using gelatin cryogel scaffold. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;491(4):1000-1006.[19] Hess SC, Stark WJ, Mohn D, et al. Gene expression in human adipose-derived stem cells: comparison of 2D films, 3D electrospun meshes or co-cultured scaffolds with two-way paracrine effects. Eur Cell Mater. 2017;34:232-248.[20] Guo W, Qiu J, Liu J, et al. Graphene microfiber as a scaffold for regulation of neural stem cells differentiation. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1): 5678. [21] Que RA, Arulmoli J, Da Silva NA, et al. Recombinant collagen scaffolds as substrates for human neural stem/progenitor cells. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2018 Jan 17. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.36343. [Epub ahead of print][22] Lee J, Yoo JJ, Atala A, et al. Controlled heparin conjugation on electrospun poly(ε-caprolactone)/gelatin fibers for morphology- dependent protein delivery and enhanced cellular affinity. Acta Biomater. 2012;8(7):2549-2558.[23] Yang L, Tanabe K, Miura T, et al. Influence of lyophilization factors and gelatin concentration on pore structures of atelocollagen/gelatin sponge biomaterial. Dent Mater J. 2017;36(4):429-437.[24] Zhu J, Yang F, He F, et al. A tubular gelatin scaffold capable of the time-dependent controlled release of epidermal growth factor and mitomycin C. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2015;135:416-424.[25] Alidadi S, Oryan A, Bigham-Sadegh A, et al. Role of platelet gel embedded within gelatin scaffold on healing of experimentally induced critical-sized radial bone defects in rats. Int Orthop. 2017; 41(4):805-812. [26] Elsayed Y, Lekakou C, Labeed F, et al. Fabrication and characterisation of biomimetic, electrospun gelatin fibre scaffolds for tunica media-equivalent, tissue engineered vascular grafts. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;61:473-483.[27] Sisson K, Zhang C, Farach-Carson MC, et al. Evaluation of cross-linking methods for electrospun gelatin on cell growth and viability. Biomacromolecules. 2009;10(7):1675-1680. [28] Wissink MJ, Beernink R, Pieper JS, et al. Immobilization of heparin to EDC/NHS-crosslinked collagen. Characterization and in vitro evaluation. Biomaterials. 2001;22(2):151-163.[29] Barnes CP, Pemble CW, Brand DD, et al. Cross-linking electrospun type II collagen tissue engineering scaffolds with carbodiimide in ethanol. Tissue Eng. 2007;13(7):1593-1605.[30] Kwon IK, Kidoaki S, Matsuda T. Electrospun nano- to microfiber fabrics made of biodegradable copolyesters: structural characteristics, mechanical properties and cell adhesion potential. Biomaterials. 2005;26(18):3929-3939.[31] Van Nieuwenhove I, Salamon A, Adam S, et al. Gelatin- and starch-based hydrogels. Part B: In vitro mesenchymal stem cell behavior on the hydrogels. Carbohydr Polym. 2017;161:295-305.[32] Menicanin D, Hynes K, Han J, et al. Cementum and Periodontal Ligament Regeneration. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015;881:207-236.[33] Hilkens P, Bronckaers A, Ratajczak J, et al. The Angiogenic Potential of DPSCs and SCAPs in an In Vivo Model of Dental Pulp Regeneration. Stem Cells Int. 2017;2017:2582080.[34] Lambrichts I, Driesen RB, Dillen Y, et al. Dental Pulp Stem Cells: Their Potential in Reinnervation and Angiogenesis by Using Scaffolds. J Endod. 2017;43(9S):S12-S16..[35] Zhang X, Li H, Sun J, et al. Cell-derived micro-environment helps dental pulp stem cells promote dental pulp regeneration. Cell Prolif. 2017;50(5). doi: 10.1111/cpr.12361. |
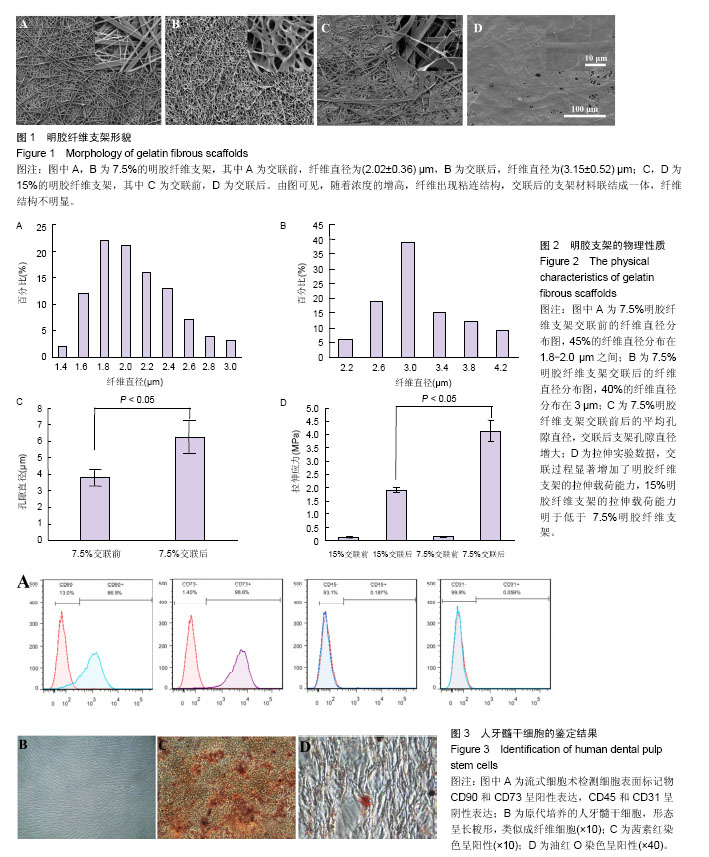
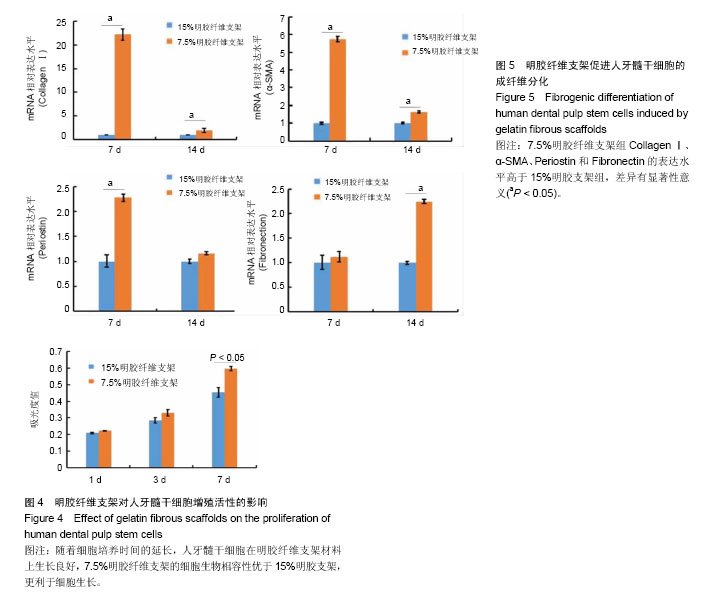
.jpg)
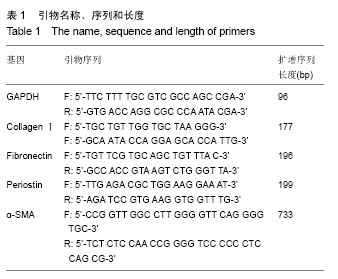
.jpg)