| [1] Preston CD, Pearman DA, Dines TD. The New Atlas of the British and Irish Flora. Oxford University Press.2002.[2] Chrubasik JE, Roufogalis BD, Wagner H, et al. A comprehensive review on the stinging nettle effect and efficacy profiles. Part II: urticae radix. Phytomedicine. 2007; 14:568-579[3] Chrubasik JE, Roufogalis BD, Wagner H, et al. A comprehensive review on nettle effect and efficacy profiles, Part I: herba urticae. Phytomedicine.2007;14:423-435.[4] Koch E. Extracts from fruits of saw palmetto (Sabal serrulata) and roots of stinging nettle (Urtica dioica): viable alternatives in the medical treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia and associated lower urinary tracts symptoms. Planta Med.2001; 67:489-500.[5] Wang M, Zhang Y, Zhang H, et al.The active glycosides from Urtica fissa rhizome decoction.J Nat Med. 2018. doi: 10.1007/s11418-018-1172-3. [6] Abu-Darwish MS, Efferth T. Medicinal Plants from Near East for Cancer Therapy.Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:56.[7] Yatoo MI, Gopalakrishnan A, Saxena A, et al. Anti-inflammatory drugs and herbs with special emphasis on herbal medicines for countering inflammatory diseases and disorders - a Review.Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2018. doi: 10.2174/1872213X12666180115153635.8.[8] Zouari BK, Bardaa S, Khimiri M, et al.Exploring the <i>Urtica dioica</i> Leaves Hemostatic and Wound-Healing Potential. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:1047523.[9] Akkouh O, Ng TB, Singh SS, et al.Lectins with anti-HIV activity: a review.Molecules. 2015 ;20(1):648-68.[10] Cui D, Li H, Xu X, et al.mesenchymal stem cells for cartilage regeneration of TMJ Osteoarthritis.Stem Cells Int. 2017;2017: 5979741.[11] Park HC, Son YB, Lee SL, et al. Effects of osteogenic-conditioned medium from human periosteum-derived cells on osteoclast differentiation.Int J Med Sci. 2017 Nov 2;14(13):1389-1401.[12] Park JH, Park BW, Kang YH, et al.Lin28a enhances in vitro osteoblastic differentiation of human periosteum-derived cells.Cell Biochem Funct. 2017;35(8):497-509.[13] Luo H, Zhang Y, Li G, et al. Sacrificial template method for the synthesis of three-dimensional nanofibrous 58S bioglass scaffold and its in vitro bioactivity and cell responses.J Biomater Appl. 2017;32(2):265-275.[14] Almeida HV, Sathy BN, Dudurych I, et al. Anisotropic shape-memory alginate scaffolds functionalized with either type I or type II collagen for cartilage tissue Engineering.Tissue Eng Part A. 2017;23(1-2):55-68.[15] Cecen B, Kozaci LD, Yuksel M, et al. Biocompatibility and biomechanical characteristics of loofah based scaffolds combined with hydroxyapatite, cellulose, poly-l-lactic acid with chondrocyte-like cells.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016; 69:437-446.[16] Hernandez I, Kumar A, Joddar B. A Bioactive hydrogel and 3D printed polycaprolactone system for bone tissue engineering.Gels.2017;3(3):26.[17] Wozney JM. The bone morphogenetic protein family : multifunctional cellular regulators in the embryo and adult. EurJ Oral Sci.1998;106(Suppl1):160-166.[18] 张晓,王啸,张鹏,等.丹参对小鼠前成骨细胞的增殖分化的影响及其与细胞外信号调节激酶1/2信号通路的关系[J].中华实验外科杂志,2017,34(1):86-89.[19] Antunes-Ricardo M, Gutierrez-Uribe J, Serna-Saldivar SO. Anti-inflammatory glycosylated flavonoids as therapeutic agents for treatment of diabetes-impaired wounds. Curr Top Med Chem. 2015; 15:2456-2463.[20] Nguyen TY, To DC, Tran MH, et al. Anti-inflammatory Flavonoids Isolated from Passiflora foetida. Nat Prod Commun. 2015;10:929-931.[21] Al Mamun MA, Hosen MJ, Islam K, et al. Tridax procumbens flavonoids promote osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Biol Res.2015;48:65[22] Leotoing L, Davicco MJ, Lebecque P, et al. The flavonoid fisetin promotes osteoblasts differentiation through Runx2 transcriptional activity. Mol Nutr Food Res.2014;58: 1239-1248.[23] Nash LA, Sullivan PJ, Peters SJ, et al. Rooibos flavonoids, orientin and luteolin, stimulate mineralization in human osteoblasts through the Wnt pathway. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2015;59:443-453.[24] Al Mamun MA, Islam K, Alam MJ, et al. Flavonoids isolated from Tridax procumbens (TPF) inhibit osteoclasts differentiation and bone resorption. Biol Res. 2015;48:51.[25] Lee J, Noh AL, Zheng T, et al. Eriodicyol inhibits osteoclast differentiation and ovariectomy-induced bone loss in vivo. Exp Cell Res. 2015;339:380-388.[26] Ming LG, Chen KM, Xian CJ. Functions and action mechanisms of flavonoids genistein and icariin in regulating bone remodeling. J Cell Physiol. 2013; 228:513-521.[27] Lappe J, Kunz I, Bendik I, et al. Effect of a combination of genistein, polyunsaturated fatty acids and vitamins D3 and K1 on bone mineral density in postmenopausal women: a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind pilot study. Eur J Nutr. 2013;52:203-215[28] Behloul N, Wu G. Genistein: a promising therapeutic agent for obesity and diabetes treatment. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013; 698: 31-38.[29] Yang L, Yu Z, Qu H, et al. Comparative effects of hispidulin, genistein, and icariin with estrogen on bone tissue in ovariectomized rats. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2014; 70: 485-490.[30] 陆海涛,袁峰,张峻玮,等.低氧环境下共培养的骨膜细胞和髓核细胞骨向分化能力的研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2016,24: 839-844.[31] 张国营,方加虎,李翔,等.周期性流体静压对骨膜细胞血管内皮生长因子表达的影响及其机制[J]. 江苏医药, 2015, 41:999-1001.[32] 张峻玮,陆海涛,杨宇明,等.低氧培养对骨膜细胞成软骨分化的影响[J].中华实验外科杂志,2016,33:1281-1283.[33] Kessler S, Koepp HE, Mayr-Wohlfart U, et al. Bone morphogeneric protein2 accelerates osteointegration and remodelling of sovent-dehydrated bone substitutes. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2004;2124(2006):2410-2414.[34] Zhang X, Aubin JE, Inman RD. Molecular and cellular biology of new bone formation: insights into the ankylosis of ankylosing spondylitis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2003;2015 (2004):2387-2393. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
碱性磷酸酶:分布于人体骨骼、肾脏、肝脏等各个组织,这种酶可作用于核酸分子使其脱掉5’磷酸基团,其同工酶有6种,其中一种来源于骨细胞,有研究表明骨形成中必不可少的酶是碱性磷酸酶,也是成骨细胞前体细胞分化为成熟的成骨细胞的重要检测指标,也是评估其功能的重要标志,其表达和成骨细胞分化成熟度和活跃度密切相关。同时它也密切参与到骨的矿化中去,可调控细胞间质中无机磷酸的浓度和电解质比例,启动和促进矿化。
荨麻:是荨麻科多年生草本植物,是传统的中草药,分布广泛,在中国多地均有产出,全草可入药,有祛风除湿和止咳等功效,其提取物主要成分包括硝酸钾、异鼠李素和山奈酚等多种成分,荨麻提取物中包含多种植物类雌激素。
文题释义:
碱性磷酸酶:分布于人体骨骼、肾脏、肝脏等各个组织,这种酶可作用于核酸分子使其脱掉5’磷酸基团,其同工酶有6种,其中一种来源于骨细胞,有研究表明骨形成中必不可少的酶是碱性磷酸酶,也是成骨细胞前体细胞分化为成熟的成骨细胞的重要检测指标,也是评估其功能的重要标志,其表达和成骨细胞分化成熟度和活跃度密切相关。同时它也密切参与到骨的矿化中去,可调控细胞间质中无机磷酸的浓度和电解质比例,启动和促进矿化。
荨麻:是荨麻科多年生草本植物,是传统的中草药,分布广泛,在中国多地均有产出,全草可入药,有祛风除湿和止咳等功效,其提取物主要成分包括硝酸钾、异鼠李素和山奈酚等多种成分,荨麻提取物中包含多种植物类雌激素。.jpg) 文题释义:
碱性磷酸酶:分布于人体骨骼、肾脏、肝脏等各个组织,这种酶可作用于核酸分子使其脱掉5’磷酸基团,其同工酶有6种,其中一种来源于骨细胞,有研究表明骨形成中必不可少的酶是碱性磷酸酶,也是成骨细胞前体细胞分化为成熟的成骨细胞的重要检测指标,也是评估其功能的重要标志,其表达和成骨细胞分化成熟度和活跃度密切相关。同时它也密切参与到骨的矿化中去,可调控细胞间质中无机磷酸的浓度和电解质比例,启动和促进矿化。
荨麻:是荨麻科多年生草本植物,是传统的中草药,分布广泛,在中国多地均有产出,全草可入药,有祛风除湿和止咳等功效,其提取物主要成分包括硝酸钾、异鼠李素和山奈酚等多种成分,荨麻提取物中包含多种植物类雌激素。
文题释义:
碱性磷酸酶:分布于人体骨骼、肾脏、肝脏等各个组织,这种酶可作用于核酸分子使其脱掉5’磷酸基团,其同工酶有6种,其中一种来源于骨细胞,有研究表明骨形成中必不可少的酶是碱性磷酸酶,也是成骨细胞前体细胞分化为成熟的成骨细胞的重要检测指标,也是评估其功能的重要标志,其表达和成骨细胞分化成熟度和活跃度密切相关。同时它也密切参与到骨的矿化中去,可调控细胞间质中无机磷酸的浓度和电解质比例,启动和促进矿化。
荨麻:是荨麻科多年生草本植物,是传统的中草药,分布广泛,在中国多地均有产出,全草可入药,有祛风除湿和止咳等功效,其提取物主要成分包括硝酸钾、异鼠李素和山奈酚等多种成分,荨麻提取物中包含多种植物类雌激素。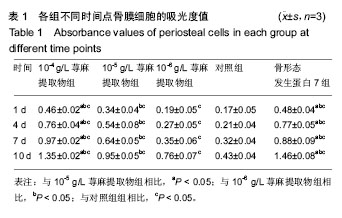
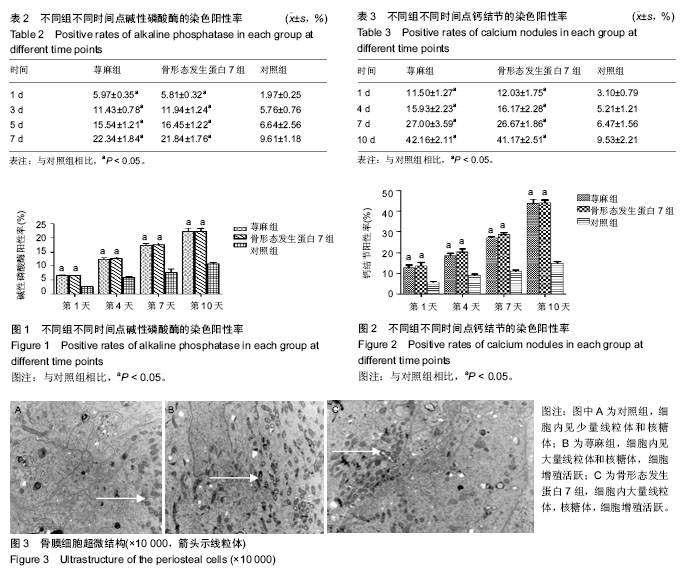
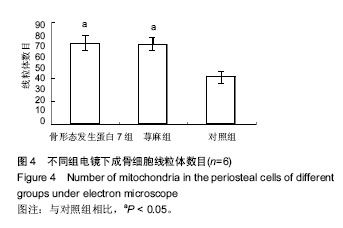
.jpg) 文题释义:
碱性磷酸酶:分布于人体骨骼、肾脏、肝脏等各个组织,这种酶可作用于核酸分子使其脱掉5’磷酸基团,其同工酶有6种,其中一种来源于骨细胞,有研究表明骨形成中必不可少的酶是碱性磷酸酶,也是成骨细胞前体细胞分化为成熟的成骨细胞的重要检测指标,也是评估其功能的重要标志,其表达和成骨细胞分化成熟度和活跃度密切相关。同时它也密切参与到骨的矿化中去,可调控细胞间质中无机磷酸的浓度和电解质比例,启动和促进矿化。
荨麻:是荨麻科多年生草本植物,是传统的中草药,分布广泛,在中国多地均有产出,全草可入药,有祛风除湿和止咳等功效,其提取物主要成分包括硝酸钾、异鼠李素和山奈酚等多种成分,荨麻提取物中包含多种植物类雌激素。
文题释义:
碱性磷酸酶:分布于人体骨骼、肾脏、肝脏等各个组织,这种酶可作用于核酸分子使其脱掉5’磷酸基团,其同工酶有6种,其中一种来源于骨细胞,有研究表明骨形成中必不可少的酶是碱性磷酸酶,也是成骨细胞前体细胞分化为成熟的成骨细胞的重要检测指标,也是评估其功能的重要标志,其表达和成骨细胞分化成熟度和活跃度密切相关。同时它也密切参与到骨的矿化中去,可调控细胞间质中无机磷酸的浓度和电解质比例,启动和促进矿化。
荨麻:是荨麻科多年生草本植物,是传统的中草药,分布广泛,在中国多地均有产出,全草可入药,有祛风除湿和止咳等功效,其提取物主要成分包括硝酸钾、异鼠李素和山奈酚等多种成分,荨麻提取物中包含多种植物类雌激素。