| [1] White AP,Hashimoto R,Norvell DC,et al.Morbidity and mottality related to odontoid fracture surgery in the elderly population.Spine. 2010;35(9):146-157.[2] Lee MJ,Cassinelli E,Riew KD. The feasibility of inserting atlas lateral mass screws via the posterior arch. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(24):2798-2801.[3] Resuick DK,Lpsiwala S,Trost GR.Anatomic suitability of the C1-C2 complex for pedicle screw fixation. Spine. 2002;27(14): 1494-1498.[4] 罗飞,许建中,王序全,等.三种颈椎前路内固定装置对术后脊柱稳定性的作用[J].中国临床康复,2003,7(20):2830-2831.[5] Liu GY,Xu RM,Ma WH,et al.Biomechaincal comparision of cervical transfacet pedicle screws versus pedicle screws.Chin Med J(Engl). 2008;121(15):1390-1393.[6] Abumi K,Ito M,Sudo H.Reconstruction of the subaxial cervical spine using pedicle screw instrumenta tion.Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2010;37(5):E349-E356.[7] 谭明生,张光铂,李子荣,等. 寰椎测量及其经后弓侧块螺钉固定通道的研究[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2002,12(1):5-8.[8] Yeom JS,Kafle D,Nguyen NQ,et al. Routine insertion of the lateral mass screw via the posterior arch for C1 fixation: feasibility and related complications. Spine J. 2012;12(6): 476-483.[9] 姚小涛,程斌,丁真奇. 寰枢椎椎弓根钉系统内固定治疗Ⅱc型齿状突骨折[J].临床骨科杂志,2015,18(1):13-14.[10] 马向阳,尹庆水,夏虹,等. 新鲜Ⅱ型齿状突骨折的术式选择及治疗效果[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2011,21(7):550-553.[11] 郝定均,许正伟,贺宝荣,等.寰枢椎椎弓根螺钉技术治疗陈旧性齿状突骨折并寰枢椎失稳[J].中华创伤杂志, 2011,27(2): 121-124.[12] 陈卫,丁真奇,康两期,等. 寰枢椎椎弓根螺钉固定治疗Jefferson骨折合并齿状突骨折[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2008, 18(1):50-54.[13] 尹庆水,万磊,夏虹,等.计算机辅助设计寰枢椎椎弓根内固定数字化导向模板精确置钉[J]中华骨科杂志, 2009,29(12):1089-1092.[14] 张少杰, 王星, 史君, 等. 数字化导航模板辅助儿童胸椎椎弓根螺钉置钉的准确性[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(35):5660-5665.[15] 师继红,陆声,张元智,等.数字化脊柱椎弓根导航模板在胸腰椎骨折中的应用[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2008,10(2):138-141.[16] 高方友,王曲,刘窗溪,等.个体化3D打印模型辅助后路螺钉内固定治疗颅颈交界区畸形[J].中华神经外科杂志, 2013,29(9):896-901.[17] Wasinpongwanich K, Paholpak P, Tuamsuk P, et al. Morphological study of subaxial cervical pedicles by using three-dimensional computed tomography reconstructionimage. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo).2014; 54 (9):736-745.[18] Lee JY, Lee JW, Pang KM, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of magnesium-based resorbable metallic screw system in a bilateral sagittal split ramus osteotomy model using three-dimensional finite element analysis. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2014;72(2):402.[19] Yang M, Zeng C, Guo S, et al. Digitalized design of extraforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a computer based simulation and cadaveric study. PLoS One. 2014;9(8): e105646.[20] Dankowski R, Baszko A, Sutherland M, et al. 3D heart model printing for preparation fo peructaneous structural interventions: descripiton of the technology and case report. Kardiol pol. 2014; 72: 546-551.[21] 严斌,张国栋,吴章林,等. 3D打印导航模块辅助腰椎椎弓根螺钉精确植入的实验研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2014,32(3): 252-255.[22] Illés T, Somoskeöy S. Comparison of scoliosis measurements based on three-dimensional vertebra vectors and conventional two- dimensional measurements: advantages in evaluation of prognosis and surgical results. Eur Spine J. 2013;22(6):1255-1263.[23] 马立敏,张余,周烨, 等.3D打印技术在股骨远端骨肿瘤的应用[J].中国数字医学,2013, 8(8): 70-72.[24] Kawaguchi Y,Nakano M,Yasuda T,et al. Development of a new technique for pedicle screw and Magerl screw insertion using a 3-dimensional image guide. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2012;37(23):1983-1988.[25] Lu S,Xu YQ,Chen GP,et al. Efficacy and accuracy of a novel rapid prototyping drill template for cervical pedicle screw placement. Comput Aided Surg. 2011;16(5):240-248.[26] 左睿,孙永建,吴毅,等.3D打印与虚拟手术设计在复杂胫骨平台骨折手术治疗中的应用[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2016 , 31(4):369-372.[27] 李涛,陈卓夫,龚辉,等.3D打印技术在复杂髋臼骨折术中的初步临床应用[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2016,31(4):387-388.[28] 吴爱悯,金海明,车灿文,等.上颈椎3D打印模型的精确性验证及在前路枕-寰-枢螺钉内固定术中的可行性[J].中华创伤杂志, 2016,32(1):41-46.[29] Ferrari V, Parchi P, Condino S, et al. An optimal design for patient-specific templates for pedicle spine screws placement. Int J Med Robot. 2013;9(3):298-304.[30] Kaneyama S, Sugawara T, Sumi M, et al. A novel screw guiding method with a screw guide template system for posterior C-2 fixation:clinical article. J Neurosurg Spine. 2014;21(2):231-238.[31] Yang JC,Ma XY,Xia H,et al. Clinical application of computer-aided design-rapid prototyping in C 1--C2 operation techniques for complex atlantoaxial instability. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2014;27(4):E143-150.[32] Merc M,Drstvensek I,Vogrin M,et al.Error rate of multi-level rapid prototyping trajeetories for pedicle screw placement in lumbar and sacral spine.Chin J Traumatol. 2014;17(5) : 261-266.[33] Hu Y,Yuan ZS,Kepler CK,et a1.Deviation analysis of C1-C2 transarticular screw placement assisted by a novel rapid prototyping drill template:a cadaveric study.J Spinal Disord Tech. 2014;27(5):E181-186.[34] 姜良海,谭明生,董亮,等.3D打印导板在脊柱置钉中的应用研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2015,23(10):908-911.[35] Wu AM, Shao ZX, Wang JS, et al. The accuracy of a method for printing three-dimensional spinal models. PloS One. 2015; 10(4): 1-11.[36] Bredow J, Oppermann J, Kraus B, et al. The accuracy of 3D fluoroscopy-navigated screw insertion in the upper and subaxial cervical spine. Eur Spine J. 2015;24(12): 2967-2976.[37] Lu S, Xu YQ, Zhang YZ, et al. Rapid prototyping drill guide template for lumbar pedicle screw placement. Chin J Traumatol. 2009;12(3): 177-180.[38] Richter M,Mattes T,Cakir B.Computer-assisted posterier instrumentation of the cervical and cervico thoracic spine.Eur Spine J. 2004;13(1):50-59.[39] Grauer JN,Shaft B,Hilibrand AS,et a1.Proposal of a modified,treatment-oriented classification of odontoid fractures. Spine J. 2005;5(2):123-129.[40] 姜良海,谭明生,董亮,等. 标杆型 3D打印导板辅助寰枢椎椎弓根置钉准确度分析[J].脊柱外科杂志,2016,14(4):205-210. |
.jpg)
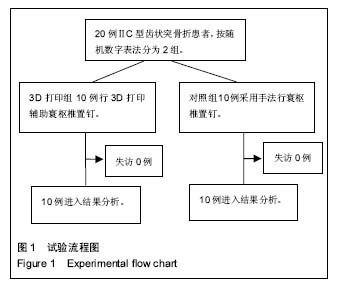

.jpg)