| [1] Bolli R, Chugh AR, D'Amario D, et al. Cardiac stem cells in patients with ischaemic cardiomyopathy (SCIPIO): initial results of a randomised phase 1 trial. Lancet. 2011;378(9806):1847-1857.[2] Makkar RR, Smith RR, Cheng K, et al. Intracoronary cardiosphere-derived cells for heart regeneration after myocardial infarction (CADUCEUS): a prospective, randomised phase 1 trial. Lancet. 2012;379(9819): 895-904.[3] Doppler SA, Deutsch MA, Lange R, et al. Cardiac regeneration: current therapies-future concepts. J Thorac Dis. 2013;5(5):683-697.[4] 陆东风,吴昊,黄璟,等.新生SD大鼠心肌干细胞的体外分离培养与鉴定[J].南方医科大学学报, 2006,26(11):1629- 1632.[5] 郝军荣,张丽,秦正红.神经干细胞球和单层贴壁神经干细胞的培养及鉴定[J].神经药理学报,2011(1):51-55.[6] 李梅,王湘臻,徐铁军.海马神经干细胞不同传代方法的比较[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(6):985- 989.[7] Golden HB, Gollapudi D, Gerilechaogetu F, et al. Isolation of cardiac myocytes and fibroblasts from neonatal rat pups. Methods Mol Biol. 2012;843: 205-214.[8] 胡圣大,马根山,姚玉宇,等.人心肌干细胞的体外改良培养[J].中国病理生理杂志,2013,29(2):381-384.[9] 何璐.大鼠心肌干细胞的分离培养与鉴定及鹿茸多肽对其分化的诱导作用研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2016.[10] 姬婷婷,徐岩,张建华,等.新生SD大鼠心肌细胞的原代培养及荧光鉴定[J].安徽医科大学学报,2014(1):120-122.[11] Leri A, Kajstura J, Anversa P. Cardiac stem cells and mechanisms of myocardial regeneration. Physiol Rev. 2005;85(4):1373-1416.[12] Nam YJ, Song K, Olson EN. Heart repair by cardiac reprogramming. Nat Med. 2013;19(4):413-415.[13] Beltrami AP, Barlucchi L, Torella D, et al. Adult cardiac stem cells are multipotent and support myocardial regeneration. Cell. 2003;114(6):763-776.[14] Wang X, Hu Q, Nakamura Y, et al. The role of the sca-1+/CD31- cardiac progenitor cell population in postinfarction left ventricular remodeling. Stem Cells. 2006;24(7):1779-1788.[15] Matsuura K, Nagai T, Nishigaki N, et al. Adult cardiac Sca-1-positive cells differentiate into beating cardiomyocytes. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(12):11384- 11391.[16] Mouquet F, Pfister O, Jain M, et al. Restoration of cardiac progenitor cells after myocardial infarction by self-proliferation and selective homing of bone marrow-derived stem cells. Circ Res. 2005;97(11): 1090-1092.[17] Xaymardan M, Tang L, Zagreda L, et al. Platelet-derived growth factor-AB promotes the generation of adult bone marrow-derived cardiac myocytes. Circ Res. 2004;94(5):E39-45.[18] Pfister O, Mouquet F, Jain M, et al. CD31- but Not CD31+ cardiac side population cells exhibit functional cardiomyogenic differentiation. Circ Res. 2005;97(1): 52-61.[19] Yamada Y, Yokoyama S, Wang XD, et al. Cardiac stem cells in brown adipose tissue express CD133 and induce bone marrow nonhematopoietic cells to differentiate into cardiomyocytes. Stem Cells. 2007; 25(5):1326-1333.[20] Moretti A, Caron L, Nakano A, et al. Multipotent embryonic isl1+ progenitor cells lead to cardiac, smooth muscle, and endothelial cell diversification. Cell. 2006;127(6):1151-1165. [21] Bu L, Jiang X, Martin-Puig S, et al. Human ISL1 heart progenitors generate diverse multipotent cardiovascular cell lineages. Nature. 2009;460(7251): 113-117. [22] Wu SM, Fujiwara Y, Cibulsky SM, et al. Developmental origin of a bipotential myocardial and smooth muscle cell precursor in the mammalian heart. Cell. 2006;127(6):1137-1150. [23] Moretti A, Bellin M, Jung CB, et al. Mouse and human induced pluripotent stem cells as a source for multipotent Isl1+ cardiovascular progenitors. FASEB J. 2010;24(3):700-711.[24] Cai CL, Liang X, Shi Y, et al. Isl1 identifies a cardiac progenitor population that proliferates prior to differentiation and contributes a majority of cells to the heart. Dev Cell. 2003;5(6):877-889.[25] Kattman SJ, Huber TL, Keller GM. Multipotent flk-1+ cardiovascular progenitor cells give rise to the cardiomyocyte, endothelial, and vascular smooth muscle lineages. Dev Cell. 2006;11(5):723-732.[26] 徐富翠,邹礼乐,梅欣明,等.神经干细胞培养及其影响因素[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(10):1835-1840.[27] Barat D, Benazzi G, Mowlem MC, et al. Design, simulation and characterisation of integrated optics for a microfabricated flow cytometer. Opt Commun. 2010; 283(9):1987-1992.[28] Joo S, Kim KH, Kim HC, et al. A portable microfluidic flow cytometer based on simultaneous detection of impedance and fluorescence. Biosens Bioelectron. 2010;25(6):1509-1515. [29] Kamei T. Miniaturized and integrated fluorescence detectors for microfluidic capillary electrophoresis devices. Methods Mol Biol. 2009;503:361-374. [30] Irawan R, Tjin SC. Detection of fluorescence generated in microfluidic channel using in-fiber grooves and in-fiber microchannel sensors. Methods Mol Biol. 2009;503:403-422. [31] Narakathu BB, Atashbar MZ, Bejcek BE. Improved detection limits of toxic biochemical species based on impedance measurements in electrochemical biosensors. Biosens Bioelectron. 2010;26(2):923-928. [32] Segerink LI, Sprenkels AJ, ter Braak PM, et al. On-chip determination of spermatozoa concentration using electrical impedance measurements. Lab Chip. 2010; 10(8):1018-1024. [33] Schultz E, Galland R, Du Bouëtiez D, et al. A novel fluorescence-based array biosensor: principle and application to DNA hybridization assays. Biosens Bioelectron. 2008;23(7):987-994. [34] Mishra NN, Retterer S, Zieziulewicz TJ, et al. On-chip micro-biosensor for the detection of human CD4(+) cells based on AC impedance and optical analysis. Biosens Bioelectron. 2005;21(5):696-704.[35] 赵书涛,武晓东,王策,等.流式细胞仪的原理?应用及最新进展[J].现代生物医学进展,2011,11(22):4378-4381. |
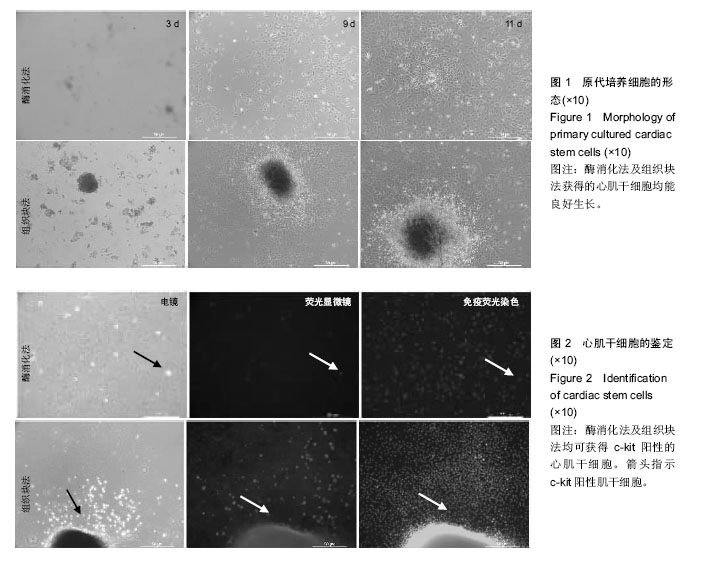
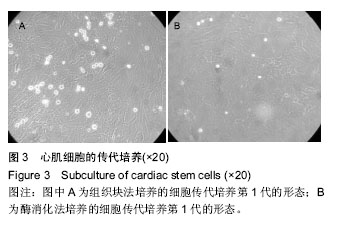
.jpg)
.jpg)