| [1] Yousefi AM, James PF, Akbarzadeh R,et al. Prospect of Stem Cells in Bone Tissue Engineering: A Review. Stem Cells Int.2016;2016:6180487.
[2] Rao RR, Stegemann JP. Cell-based approaches to the engineering of vascularized bone tissue.Cytotherapy. 2013;15(11):1309-1322.
[3] Pina S,Oliveira JM,Reis RL.Natural-based nanocomposites for bone tissue engineering and regenerativemedicine: a review. Adv Mater. 2015; 27(7): 1143-1169.
[4] Shi Y,Hu G,Su J,et al.Mesenchymal stem cells: a new strategy for immunosuppression and tissue repair. Cell Res.2010;20(5):510-518.
[5] Burlacu A,Grigorescu G, Rosca AM,et al.Factors secreted by mesenchymal stem cells and endothelial progenitor cells have complementary effects on angiogenesis in vitro. Stem Cells Dev.2013;22(4):643-653.
[6] 曾晶晶,周诺,黄旋平等.犬骨髓间质干细胞体外培养和鉴定[J].实用医学杂志,2013,29(16):2649-2651.
[7] 吴尉,梁芳,宋小琴,等.人脂肪干细胞的提取和鉴定[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(28):4498-4502.
[8] 卢遥,王静成,顾加祥,等.兔胎盘来源间充质干细胞修复兔桡骨骨缺损的实验研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2011, 13(11):1060-1065.
[9] 杜晶春,朱蕊,徐霞,等.人羊水来源间质干细胞的鉴定及其免疫调节功能和相关机制研究[J].实用医学杂志, 2013, 29(4):529-532.
[10] Vishnubalaji R, Al-Nbaheen M, Kadalmani B, et al.Comparative investigation of the differentiation capability of bone-marrow- andadipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells by qualitative and quantitative analysis.Cell Tissue Res. 2012;347(2):419-427.
[11] Zhang W, Zhang X, Wang S,et al. Comparison of the use of adipose tissue-derived and bone marrow-derived stemcells for rapid bone regeneration. J Dent Res. 2013;92(12):1136-1141.
[12] Wen Y,Jiang B,Cui J,et al.Superior osteogenic capacity of different mesenchymal stem cells for bone tissue engineering.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2013;116(5):e324-332.
[13] Hass R,Kasper C,BöhmS,et al.Different populations and sources of human mesenchymal stem cells (MSC): A comparison of adult and neonatal tissue-derived MSC. Cell Commun Signal.2011;9:12.
[14] Li X,Bai J,JiX,et al.Comprehensive characterization of four different populations of human mesenchymal stem cells as regards their immune properties, proliferation and differentiation. Int J Mol Med.2014;34(3):695-704.
[15] De Francesco F, Ricci G, D'AndreaF,et al. Human Adipose Stem Cells: From Bench to Bedside. Tissue Eng Part B Rev.2015;21(6):572-584.
[16] Ren G, Zhang L, Zhao X,et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-mediated immunosuppression occurs via concerted action ofchemokines and nitric oxide.Cell Stem Cell. 2008;2(2):141-150.
[17] Ren G, Su J, Zhang L,et al. Species variation in the mechanisms of mesenchymal stem cell- mediatedimmunosuppression. Stem Cells. 2009; 27(8):1954-1962.
[18] Li W,RenG,Huang Y, et al.Mesenchymal stem cells:a double-edged sword in regulating immune response. Cell Death Differ 2012;19:1505-1513
[19] Montespan F,Deschaseaux F, Sensébé L,et al.Osteodifferentiated mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow and adipose tissueexpress HLA-G and display immunomodulatory properties in HLA-mismatched settings:implications in bone repair therapy.JImmunol Res. 2014;2014:230346.
[20] Melief SM, Zwaginga JJ, FibbeWE,et al.Adipose tissue-derived multipotent stromal cells have a higher immunomodulatorycapacity than their bone marrow-derived counterparts. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2013;2(6):455-463.
[21] Ribeiro A, Laranjeira P, Mendes S,et al.Mesenchymal stem cells from umbilical cord matrix, adipose tissue and bone marrowexhibit different capability to suppress peripheral blood B, natural killer and Tcells.Stem Cell Res Ther.2013;4(5):125.
[22] Najar M, Raicevic G, BoufkerHI,et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells use PGE2 to modulate activation and proliferation oflymphocyte subsets: Combined comparison of adipose tissue, Wharton's Jelly andbone marrow sources.Cell Immunol. 2010;264(2):171-179.
[23] Boukhechba F,Balaguer T,Bouvet-Gerbettaz S,et al.Fate of bone marrow stromal cells in a syngenic model of bone formation.TissueEng Part A 2011;17:2267-2278.
[24] Mendez JJ, Ghaedi M, Sivarapatna A,et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells form vascular tubes when placed in fibrin sealant andaccelerate wound healing in vivo. Biomaterials.2015;40:61-71.
[25] Correia C,Grayson WL,Park M,et al.In vitro model of vascularized bone:synergizing vascular development and osteogenesis.PLoS One.2011;6(12),e28352.
[26] Verseijden F, Posthumus-van Sluijs SJ, Pavljasevic P,et al. Adult human bone marrow- and adipose tissue-derived stromal cells support theformation of prevascular-like structures from endothelial cells in vitro. Tissue Eng Part A. 2010;16(1):101-114.
[27] Edwards SS, Zavala G, Prieto CP,et al. Functional analysis reveals angiogenic potential of human mesenchymal stem cells from Wharton's jelly in dermal regeneration.Angiogenesis. 2014;17(4):851-866.
[28] Rubina K,Kalinina N,Efimenko A,et al.Adipose stromal cells stimulate angiogenesis via promoting progenitor celldifferentiation, secretion of angiogenic factors, and enhancing vesselmaturation. Tissue Eng Part A. 2009; 15(8):2039-2050.
[29] Watt SM, Gullo F, van der Garde M,et al.The angiogenic properties of mesenchymal stem/stromal cells and their therapeuticpotential. Br Med Bull. 2013; 108:25-53.
[30] Kim KI, Park S, Im GI.Osteogenic differentiation and angiogenesis with cocultured adipose-derivedstromal cells and bone marrow stromal cells. Biomaterials. 2014;35(17):4792-4804.
[31] Freiman A, Shandalov Y, Rozenfeld D,et al. Adipose-derived endothelial and mesenchymal stem cells enhance vascular network formation on three-dimensional constructs in vitro.Stem Cell Res Ther.2016;7(1):5.
[32] Niemeyer P, Fechner K, Milz S,et al.Comparison of mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow and adipose tissue for bone regeneration in a critical size defect of the sheep tibia and the influence of platelet-rich plasma. Biomaterials. 2010;31(13):3572-3579.
[33] Hung BP, Hutton DL, Kozielski KL,et al. Platelet-Derived Growth Factor BB Enhances Osteogenesis of Adipose-Derived But Not Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells. Stem Cells. 2015;33(9):2773-2784.
[34] Yang Y, Wu J, Jin G,et al. Research of osteoblastic induced rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells cultured on β-TCP/PLLA porous scaffold. Int J ClinExp Med. 2015;8(3):3202-3209.
[35] Duan S, Yang X, Mei F,et al. Enhanced osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells on poly(L-lactide) nanofibrous scaffolds containing carbon nanomaterials. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2015;103(4):1424-1435.
[36] 王立勋,吕飞舟,马晓生,等.慢病毒介导骨形成蛋白-2基因转染骨髓间质干细胞修复大鼠颅骨骨缺损[J].中华实验外科杂志,2008,25(6):705-706.
[37] 王庆,陈光兴,郭林,等.骨形态发生蛋白-2和7联合基因修饰构建组织工程骨的实验研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2013,15(11):984-989.
[38] Pak J, Chang JJ, Lee JH,et al. Safety reporting on implantation of autologous adipose tissue-derived stem cells with platelet-rich plasma into human articular joints. BMC MusculoskeletDisord. 2013;14:337.
[39] Pak J, Lee JH, Lee SH. Regenerative repair of damaged meniscus with autologous adipose tissue-derived stem cells. Biomed Res Int.2014;2014:436029.
[40] Ra JC, Shin IS, Kim SH,et al. Safety of intravenous infusion of human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells in animals and humans.Stem Cells Dev. 2011;20(8):1297-1308.
[41] Rhee KJ, Lee JI, Eom YW. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Mediated Effects of Tumor Support or Suppression.Int J Mol Sci.2015;16(12):30015-30033 |
.jpg) 文题释义:
免疫调节:是指免疫系统中的免疫细胞和免疫分子之间,以及与其他系统如神经内分泌系统之间的相互作用,使得免疫应答以最恰当的形式维持在最适当的水平。
成骨细胞:是骨形成的主要功能细胞,负责骨基质的合成、分泌和矿化。骨不断地进行着重建,骨重建过程包括破骨细胞贴附在旧骨区域,分泌酸性物质溶解矿物质,分泌蛋白酶消化骨基质,形成骨吸收陷窝;其后,成骨细胞移行至被吸收部位,分泌骨基质,骨基质矿化而形成新骨。破骨与成骨过程的平衡是维持正常骨量的关键。
文题释义:
免疫调节:是指免疫系统中的免疫细胞和免疫分子之间,以及与其他系统如神经内分泌系统之间的相互作用,使得免疫应答以最恰当的形式维持在最适当的水平。
成骨细胞:是骨形成的主要功能细胞,负责骨基质的合成、分泌和矿化。骨不断地进行着重建,骨重建过程包括破骨细胞贴附在旧骨区域,分泌酸性物质溶解矿物质,分泌蛋白酶消化骨基质,形成骨吸收陷窝;其后,成骨细胞移行至被吸收部位,分泌骨基质,骨基质矿化而形成新骨。破骨与成骨过程的平衡是维持正常骨量的关键。.jpg) 文题释义:
免疫调节:是指免疫系统中的免疫细胞和免疫分子之间,以及与其他系统如神经内分泌系统之间的相互作用,使得免疫应答以最恰当的形式维持在最适当的水平。
成骨细胞:是骨形成的主要功能细胞,负责骨基质的合成、分泌和矿化。骨不断地进行着重建,骨重建过程包括破骨细胞贴附在旧骨区域,分泌酸性物质溶解矿物质,分泌蛋白酶消化骨基质,形成骨吸收陷窝;其后,成骨细胞移行至被吸收部位,分泌骨基质,骨基质矿化而形成新骨。破骨与成骨过程的平衡是维持正常骨量的关键。
文题释义:
免疫调节:是指免疫系统中的免疫细胞和免疫分子之间,以及与其他系统如神经内分泌系统之间的相互作用,使得免疫应答以最恰当的形式维持在最适当的水平。
成骨细胞:是骨形成的主要功能细胞,负责骨基质的合成、分泌和矿化。骨不断地进行着重建,骨重建过程包括破骨细胞贴附在旧骨区域,分泌酸性物质溶解矿物质,分泌蛋白酶消化骨基质,形成骨吸收陷窝;其后,成骨细胞移行至被吸收部位,分泌骨基质,骨基质矿化而形成新骨。破骨与成骨过程的平衡是维持正常骨量的关键。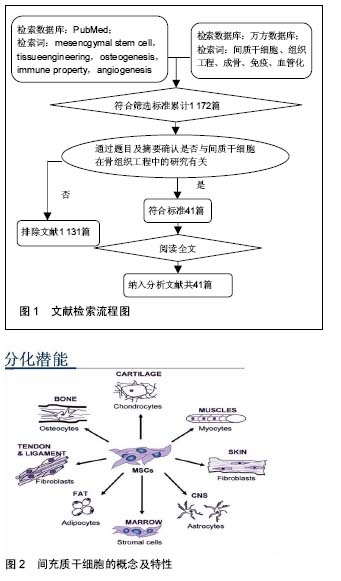
.jpg) 文题释义:
免疫调节:是指免疫系统中的免疫细胞和免疫分子之间,以及与其他系统如神经内分泌系统之间的相互作用,使得免疫应答以最恰当的形式维持在最适当的水平。
成骨细胞:是骨形成的主要功能细胞,负责骨基质的合成、分泌和矿化。骨不断地进行着重建,骨重建过程包括破骨细胞贴附在旧骨区域,分泌酸性物质溶解矿物质,分泌蛋白酶消化骨基质,形成骨吸收陷窝;其后,成骨细胞移行至被吸收部位,分泌骨基质,骨基质矿化而形成新骨。破骨与成骨过程的平衡是维持正常骨量的关键。
文题释义:
免疫调节:是指免疫系统中的免疫细胞和免疫分子之间,以及与其他系统如神经内分泌系统之间的相互作用,使得免疫应答以最恰当的形式维持在最适当的水平。
成骨细胞:是骨形成的主要功能细胞,负责骨基质的合成、分泌和矿化。骨不断地进行着重建,骨重建过程包括破骨细胞贴附在旧骨区域,分泌酸性物质溶解矿物质,分泌蛋白酶消化骨基质,形成骨吸收陷窝;其后,成骨细胞移行至被吸收部位,分泌骨基质,骨基质矿化而形成新骨。破骨与成骨过程的平衡是维持正常骨量的关键。