中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (36): 5440-5449.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.36.018
• 干细胞综述 stem cell review • 上一篇 下一篇
诱导性多能干细胞与心血管疾病
詹 琪,张 静,王晓青,陈晓芳,黄 艳
- 北京航空航天大学生物与医学工程学院,生物力学与力生物学教育部重点实验室,北京市 100191
-
修回日期:2016-07-29出版日期:2016-09-02发布日期:2016-09-02 -
通讯作者:黄艳,博士,讲师,硕士生导师,北京航空航天大学生物与医学工程学院,生物力学与力生物学教育部重点实验室,北京市 100191 -
作者简介:詹琪,女,1991年生,黑龙江省大庆市人,汉族,北京航空航天大学生物与医学工程学院在读硕士,主要从事组织工程基础研究。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(11302020)
Induced pluripotent stem cells and cardiovascular disease
Zhan Qi, Zhang Jing, Wang Xiao-qing, Chen Xiao-fang, Huang Yan
- Key Laboratory for Biomechanics and Mechanobiology of Ministry of Education, School of Biological Science and Medical Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
-
Revised:2016-07-29Online:2016-09-02Published:2016-09-02 -
Contact:Huang Yan, Ph.D., Lecturer, Master’s supervisor, Key Laboratory for Biomechanics and Mechanobiology of Ministry of Education, School of Biological Science and Medical Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China -
About author:Zhan Qi, Studying for master’s degree, Key Laboratory for Biomechanics and Mechanobiology of Ministry of Education, School of Biological Science and Medical Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 11302020
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义: 诱导性多能干细胞源心血管细胞:诱导性多能干细胞是指生物体已经完全分化的体细胞经过基因改造,重新编码,使其成为具有类似胚胎干细胞的多能性细胞,理论上可以向任意细胞分化。心血管细胞包括心肌细胞、内皮细胞、血管平滑肌细胞等,诱导性多能干细胞可以经过一定的诱导方式来实现向这些细胞的分化,并可在心脏病治疗等领域有应用的潜能。 细胞疾病模型:文章中的细胞模型是由诱导性多能干细胞来源的细胞所构建的。例如,某患者带有基因缺陷性疾病,为研究其致病机制便于治疗,可以取其体细胞重编程为可无限增殖的诱导性多能干细胞,再分化为相应体细胞用于研究,并且仍然携带其基因缺陷。
摘要 背景:诱导性多能干细胞具有自我更新和多向分化能力的同时,又避免了胚胎干细胞的免疫排斥、伦理学争议等问题,因此在组织修复领域有着巨大的应用前景。 目的:综述诱导性多能干细胞向心肌细胞、内皮细胞方向的分化以及其在心血管疾病领域的研究进展。 方法:由第一作者检索2000至2015年PubMed 数据库以及中国知网数据库有关诱导性多能干细胞向心肌细胞和内皮细胞方向分化的文献,并进行系统整理、总结和分析,最终保留78篇文献进行分析。 结果与结论:诱导性多能干细胞可以通过多种方法分化为心血管细胞。环孢菌素A、维生素C等因子可促进诱导性多能干细胞向心肌细胞方向分化,血管内皮细胞生长因子、成纤维细胞生长因子等可促进诱导性多能干细胞向内皮细胞方向分化。诱导性多能干细胞源心血管细胞可用于建立体外疾病模型、体内移植、药物筛选等方面。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程 ORCID: 0000-0002-1616-9156(黄艳)
中图分类号:
引用本文
詹 琪,张 静,王晓青,陈晓芳,黄 艳. 诱导性多能干细胞与心血管疾病[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2016, 20(36): 5440-5449.
Zhan Qi, Zhang Jing, Wang Xiao-qing, Chen Xiao-fang, Huang Yan. Induced pluripotent stem cells and cardiovascular disease[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(36): 5440-5449.
总之,诱导性多能干细胞源内皮细胞除具有特异性基因和表达物外,在分化成熟后可在适当条件下形成血管样结构,这也是观察内皮细胞特性的重要指标。血管内皮生长因子信号通路在干细胞内皮向分化的过程中并非必要,但是在内皮细胞的存活方面可能具有重要作用。骨形成蛋白执行Hedgehog信号通路的下游功能,对血管发生具有重要的调控作用,骨形态发生蛋白4可以促进胚胎中胚层发育和内皮祖细胞的形成,通过SMAD1/5信号通路诱导胚胎干细胞转化为KDR阳性细胞[49]。
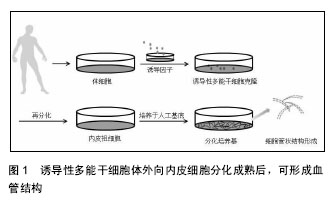
由于诱导性多能干细胞源心血管细胞的转化效率有限,并不能满足研究需求,在分化和纯化方式上正在不断地发现、创新。以高速录像显微镜观察诱导性多能干细胞源心肌细胞,检测到细胞的运动与场电位存在着线性关系,对于运动动力学的深入理解来说比较新颖,并且利于研究细胞的电生理和机械运动之间的关系[71]。在弹性微柱阵列上培养诱导性多能干细胞源心肌细胞可用来研究细胞的收缩强度和动力学[77]。Josowitz等[78]发现诱导性多能干细胞源心房样心肌细胞通过细菌人工染色体使得心房特异性基因肌脂蛋白的表达以红色荧光显示出来,以流式细胞仪纯化荧光强表达的细胞,证实了肌脂蛋白是监测和分离心房样细胞的标志物,开创了新的纯化方法。Uosaki等[18]研究发现,CD106可以作为诱导性多能干细胞源心肌细胞的标志物用于纯化心肌细胞,这也是一种新的纯化方式。
| [1] Takahashi K, Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell. 2006;126(4):663-676. [2] Itskovitz-Eldor J, Schuldiner M, Karsenti D, et al. Differentiation of human embryonic stem cells into embryoid bodies compromising the three embryonic germ layers. Mol Med. 2000;6(2):88-95. [3] 李晴,刘靖,徐秀琴.人类多能干细胞源心肌细胞的研究进展与应用前景[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2013,35(3): 251-261. [4] Honda M, Kiyokawa J, Tabo M, et al. Electrophysiological characterization of cardiomyocytes derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells. J Pharmacol Sci. 2011;117(3):149-159. [5] Kawamura M, Miyagawa S, Miki K, et al. Feasibility, safety, and therapeutic efficacy of human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocyte sheets in a porcine ischemic cardiomyopathy model. Circulation. 2012;126(11 Suppl 1):S29-37. [6] Tanaka A, Yuasa S, Mearini G, et al. Endothelin-1 induces myofibrillar disarray and contractile vector variability in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. J Am Heart Assoc. 2014;3(6):e001263. [7] Dambrot C, Braam SR, Tertoolen LG, et al. Serum supplemented culture medium masks hypertrophic phenotypes in human pluripotent stem cell derived cardiomyocytes. J Cell Mol Med. 2014;18(8):1509-1518. [8] Mauritz C, Schwanke K, Reppel M, et al. Generation of functional murine cardiac myocytes from induced pluripotent stem cells. Circulation. 2008;118(5): 507-517. [9] Burridge PW, Thompson S, Millrod MA, et al. A universal system for highly efficient cardiac differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells that eliminates interline variability. PLoS One. 2011 8;6(4):e18293. [10] Zwi-Dantsis L, Mizrahi I, Arbel G, et al. Scalable production of cardiomyocytes derived from c-Myc free induced pluripotent stem cells. Tissue Eng Part A. 2011;17(7-8):1027-1037. [11] Fujiwara M, Yan P, Otsuji TG, et al. Induction and enhancement of cardiac cell differentiation from mouse and human induced pluripotent stem cells with cyclosporin-A. PLoS One. 2011;6(2):e16734. [12] Cao N, Liu Z, Chen Z, et al. Ascorbic acid enhances the cardiac differentiation of induced pluripotent stem cells through promoting the proliferation of cardiac progenitor cells. Cell Res. 2012;22(1):219-236. [13] Ye L, Zhang S, Greder L, et al. Effective cardiac myocyte differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells requires VEGF. PLoS One. 2013;8(1): e53764. [14] Lee YK, Ng KM, Lai WH, et al. Calcium homeostasis in human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes.Stem Cell Rev. 2011;7(4):976-986. [15] Shinozawa T, Furukawa H, Sato E, et al. A novel purification method of murine embryonic stem cell- and human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes by simple manual dissociation. J Biomol Screen. 2012;17(5):683-691. [16] Lan F, Lee AS, Liang P, et al. Abnormal calcium handling properties underlie familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy pathology in patient-specific induced pluripotent stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2013;12(1): 101-113. [17] Shinozawa T, Imahashi K, Sawada H, et al. Determination of appropriate stage of human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes for drug screening and pharmacological evaluation in vitro. J Biomol Screen. 2012;17(9):1192-1203. [18] Uosaki H, Fukushima H, Takeuchi A, et al. Efficient and scalable purification of cardiomyocytes from human embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cells by VCAM1 surface expression. PLoS One. 2011;6(8): e23657. [19] Correia C, Serra M, Espinha N, et al. Combining hypoxia and bioreactor hydrodynamics boosts induced pluripotent stem cell differentiation towards cardiomyocytes. Stem Cell Rev. 2014;10(6):786-801. [20] Ohno Y, Yuasa S, Egashira T, et al. Distinct iPS Cells Show Different Cardiac Differentiation Efficiency. Stem Cells Int. 2013;2013:659739. [21] Fujita J, Fukuda K. Future prospects for regenerated heart using induced pluripotent stem cells. J Pharmacol Sci. 2014;125(1):1-5. [22] Földes G, Matsa E, Kriston-Vizi J, et al. Aberrant α-adrenergic hypertrophic response in cardiomyocytes from human induced pluripotent cells. Stem Cell Reports. 2014;3(5):905-914. [23] Zhang GQ, Wei H, Lu J, et al. Identification and characterization of calcium sparks in cardiomyocytes derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells. PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e55266. [24] Iglesias-García O, Baumgartner S, Macrí-Pellizzeri L, et al. Neuregulin-1β induces mature ventricular cardiac differentiation from induced pluripotent stem cells contributing to cardiac tissue repair. Stem Cells Dev. 2015;24(4):484-496. [25] Yang X, Rodriguez M, Pabon L, et al. Tri-iodo-l-thyronine promotes the maturation of human cardiomyocytes-derived from induced pluripotent stem cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014;72:296-304. [26] Kuzmenkin A, Liang H, Xu G, et al. Functional characterization of cardiomyocytes derived from murine induced pluripotent stem cells in vitro. FASEB J. 2009;23(12):4168-4180. [27] Kim JJ, Yang L, Lin B, et al. Mechanism of automaticity in cardiomyocytes derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2015;81: 81-93. [28] Germanguz I, Sedan O, Zeevi-Levin N, et al. Molecular characterization and functional properties of cardiomyocytes derived from human inducible pluripotent stem cells. J Cell Mol Med. 2011;15(1):38-51. [29] Kawamura T, Miyagawa S, Fukushima S, et al. N-glycans: phenotypic homology and structural differences between myocardial cells and induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. PLoS One. 2014;9(10):e111064. [30] Kaichi S, Hasegawa K, Takaya T, et al. Cell line-dependent differentiation of induced pluripotent stem cells into cardiomyocytes in mice. Cardiovasc Res. 2010;88(2):314-323. [31] Itzhaki I, Maizels L, Huber I, et al. Modelling the long QT syndrome with induced pluripotent stem cells. Nature. 2011;471(7337):225-229. [32] Tan KS, Tamura K, Lai MI, et al. Molecular pathways governing development of vascular endothelial cells from ES/iPS cells. Stem Cell Rev. 2013;9(5):586-598. [33] Sivarapatna A, Ghaedi M, Le AV, et al. Arterial specification of endothelial cells derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells in a biomimetic flow bioreactor. Biomaterials. 2015;53:621-633. [34] Yoo CH, Na HJ, Lee DS, et al. Endothelial progenitor cells from human dental pulp-derived iPS cells as a therapeutic target for ischemic vascular diseases. Biomaterials. 2013;34(33):8149-8160. [35] Samuel R, Daheron L, Liao S, et al. Generation of functionally competent and durable engineered blood vessels from human induced pluripotent stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(31):12774-12779. [36] Choi KD, Yu J, Smuga-Otto K, et al. Hematopoietic and endothelial differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells. 2009;27(3): 559-567. [37] Homma K, Sone M, Taura D, et al. Sirt1 plays an important role in mediating greater functionality of human ES/iPS-derived vascular endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis. 2010;212(1):42-47. [38] White MP, Rufaihah AJ, Liu L, et al. Limited gene expression variation in human embryonic stem cell and induced pluripotent stem cell-derived endothelial cells. Stem Cells. 2013;31(1):92-103. [39] Narazaki G, Uosaki H, Teranishi M, et al. Directed and systematic differentiation of cardiovascular cells from mouse induced pluripotent stem cells. Circulation. 2008;118(5):498-506. [40] Du C, Narayanan K, Leong MF, et al. Induced pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocytes and endothelial cells in multi-component hydrogel fibers for liver tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2014;35(23): 6006-6014. [41] Joo HJ, Kim H, Park SW, et al. Angiopoietin-1 promotes endothelial differentiation from embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells. Blood. 2011;118(8):2094-2104. [42] Lee JB, Werbowetski-Ogilvie TE, Lee JH, et al. Notch-HES1 signaling axis controls hemato-endothelial fate decisions of human embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cells. Blood. 2013;122(7):1162-1173. [43] Di Bernardini E, Campagnolo P, Margariti A, et al. Endothelial lineage differentiation from induced pluripotent stem cells is regulated by microRNA-21 and transforming growth factor β2 (TGF-β2) pathways. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(6):3383-3393. [44] Adams WJ, Zhang Y, Cloutier J, et al. Functional vascular endothelium derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cell Reports. 2013; 1(2):105-113. [45] Margariti A, Winkler B, Karamariti E, et al. Direct reprogramming of fibroblasts into endothelial cells capable of angiogenesis and reendothelialization in tissue-engineered vessels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109(34):13793-13798. [46] Xu Y, Liu L, Zhang L, et al. Efficient commitment to functional CD34+ progenitor cells from human bone marrow mesenchymal stem-cell-derived induced pluripotent stem cells. PLoS One. 2012;7(4): e34321. [47] Suzuki H, Shibata R, Kito T, et al. Comparative angiogenic activities of induced pluripotent stem cells derived from young and old mice. PLoS One. 2012; 7(6): e39562. [48] Belair DG, Whisler JA, Valdez J, et al. Human vascular tissue models formed from human induced pluripotent stem cell derived endothelial cells. Stem Cell Rev. 2015;11(3):511-525. [49] Zhou Y, Yang F, Chen T, et al. An updated view on the differentiation of stem cells into endothelial cells. Sci China Life Sci. 2014;57(8):763-773. [50] Gu M, Nguyen PK, Lee AS, et al. Microfluidic single-cell analysis shows that porcine induced pluripotent stem cell-derived endothelial cells improve myocardial function by paracrine activation. Circ Res. 2012;111(7):882-893. [51] Mauritz C, Martens A, Rojas SV, et al. Induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived Flk-1 progenitor cells engraft, differentiate, and improve heart function in a mouse model of acute myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J. 2011;32(21):2634-2641. [52] Suzuki H, Shibata R, Kito T, et al. Therapeutic angiogenesis by transplantation of induced pluripotent stem cell-derived Flk-1 positive cells. BMC Cell Biol. 2010;11:72. [53] Prasain N, Lee MR, Vemula S, et al. Differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells to cells similar to cord-blood endothelial colony-forming cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2014;32(11):1151-1157. [54] Morita R, Suzuki M, Kasahara H, et al. ETS transcription factor ETV2 directly converts human fibroblasts into functional endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112(1):160-165. [55] Kim KL, Song SH, Choi KS, et al. Cooperation of endothelial and smooth muscle cells derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells enhances neovascularization in dermal wounds. Tissue Eng Part A. 2013;19(21-22):2478-2485. [56] Templin C, Zweigerdt R, Schwanke K, et al. Transplantation and tracking of human-induced pluripotent stem cells in a pig model of myocardial infarction: assessment of cell survival, engraftment, and distribution by hybrid single photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography of sodium iodide symporter transgene expression. Circulation. 2012;126(4):430-439. [57] Citro L, Naidu S, Hassan F, et al. Comparison of human induced pluripotent stem-cell derived cardiomyocytes with human mesenchymal stem cells following acute myocardial infarction. PLoS One. 2014; 9(12):e116281. [58] Masumoto H, Ikuno T, Takeda M, et al. Human iPS cell-engineered cardiac tissue sheets with cardiomyocytes and vascular cells for cardiac regeneration. Sci Rep. 2014;4:6716. [59] Wang Y, Huang W, Liang J, et al. Suicide gene-mediated sequencing ablation revealed the potential therapeutic mechanism of induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiovascular cell patch post-myocardial infarction. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014;21(16):2177-2191. [60] Carpenter L, Carr C, Yang CT, et al. Efficient differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells generates cardiac cells that provide protection following myocardial infarction in the rat. Stem Cells Dev. 2012;21(6):977-986. [61] Miki K, Uenaka H, Saito A, et al. Bioengineered myocardium derived from induced pluripotent stem cells improves cardiac function and attenuates cardiac remodeling following chronic myocardial infarction in rats. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2012;1(5):430-437. [62] Matsa E, Dixon JE, Medway C, et al. Allele-specific RNA interference rescues the long-QT syndrome phenotype in human-induced pluripotency stem cell cardiomyocytes. Eur Heart J. 2014;35(16):1078-1087. [63] Mehta A, Sequiera GL, Ramachandra CJ, et al. Re-trafficking of hERG reverses long QT syndrome 2 phenotype in human iPS-derived cardiomyocytes. Cardiovasc Res. 2014;102(3):497-506. [64] Fatima A, Kaifeng S, Dittmann S, et al. The disease-specific phenotype in cardiomyocytes derived from induced pluripotent stem cells of two long QT syndrome type 3 patients. PLoS One. 2013;8(12): e83005. [65] Hick A, Wattenhofer-Donzé M, Chintawar S, et al. Neurons and cardiomyocytes derived from induced pluripotent stem cells as a model for mitochondrial defects in Friedreich's ataxia. Dis Model Mech. 2013 May;6(3):608-621. [66] Caspi O, Huber I, Gepstein A, et al. Modeling of arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy with human induced pluripotent stem cells. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2013;6(6):557-568. [67] Drawnel FM, Boccardo S, Prummer M, et al. Disease modeling and phenotypic drug screening for diabetic cardiomyopathy using human induced pluripotent stem cells. Cell Rep. 2014;9(3):810-821. [68] Lin B, Li Y, Han L, et al. Modeling and study of the mechanism of dilated cardiomyopathy using induced pluripotent stem cells derived from individuals with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Dis Model Mech. 2015; 8(5):457-466. [69] Sharma A, Marceau C, Hamaguchi I, et al. Human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes as an in vitro model for coxsackievirus B3-induced myocarditis and antiviral drug screening platform. Circ Res. 2014;115(6):556-566. [70] Doherty KR, Talbert DR, Trusk PB, et al. Structural and functional screening in human induced-pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes accurately identifies cardiotoxicity of multiple drug types. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2015;285(1):51-60. [71] Hayakawa T, Kunihiro T, Ando T, et al. Image-based evaluation of contraction-relaxation kinetics of human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes: Correlation and complementarity with extracellular electrophysiology. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014;77:178-191. [72] Nakamura Y, Matsuo J, Miyamoto N, et al. Assessment of testing methods for drug-induced repolarization delay and arrhythmias in an iPS cell-derived cardiomyocyte sheet: multi-site validation study. J Pharmacol Sci. 2014;124(4):494-501. [73] Lu J, Wei H, Wu J, et al. Evaluation of the cardiotoxicity of mitragynine and its analogues using human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. PLoS One. 2014;9(12):e115648. [74] Han L, Li Y, Tchao J, et al. Study familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy using patient-specific induced pluripotent stem cells.Cardiovasc Res. 2014;104(2): 258-269. [75] Nozaki Y, Honda Y, Tsujimoto S, et al. Availability of human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes in assessment of drug potential for QT prolongation. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2014;278(1): 72-77. [76] Rao C, Prodromakis T, Kolker L, et al. The effect of microgrooved culture substrates on calcium cycling of cardiac myocytes derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells. Biomaterials. 2013;34(10): 2399-2411. [77] Rodriguez ML, Graham BT, Pabon LM, et al. Measuring the contractile forces of human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes with arrays of microposts. J Biomech Eng. 2014;136(5):051005. [78] Josowitz R, Lu J, Falce C, et al. Identification and purification of human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived atrial-like cardiomyocytes based on sarcolipin expression. PLoS One. 2014;9(7):e101316. |
| [1] | 蒲 锐, 陈子扬, 袁凌燕. 不同细胞来源外泌体保护心脏的特点与效应[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | 林清凡, 解一新, 陈婉清, 叶振忠, 陈幼芳. 人胎盘源间充质干细胞条件培养液可上调缺氧状态下BeWo细胞活力和紧密连接因子的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | 张秀梅, 翟运开, 赵 杰, 赵 萌. 类器官模型国内外数据库近10年文献研究热点分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [4] | 王梦婷, 古艳萍, 任文博, 覃 倩, 白冰怡, 廖远朋. 运动干预功能障碍人群血流限制训练的文献热点可视化分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(8): 1264-1269. |
| [5] | 顾 霞, 赵 敏, 王平义, 李一梅, 李文华. 低氧诱导因子1α与低氧相关疾病信号通路的关系[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(8): 1284-1289. |
| [6] | 袁 美, 张新新, 郭祎莎, 毕 霞. 循环microRNA在血管性认知障碍诊断中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(8): 1299-1304. |
| [7] | 刘 聪, 刘 肃. miR-17-5p调控低氧诱导因子1α介导脂肪细胞分化及血管生成的分子机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1069-1074. |
| [8] | 王正东, 黄 娜, 陈婧娴, 郑作兵, 胡鑫宇, 李 梅, 苏 晓, 苏学森, 颜 南. 丁酸钠抑制氟中毒可诱导小胶质细胞活化及炎症因子表达增多[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [9] | 汪显耀, 关亚琳, 刘忠山. 提高间充质干细胞治疗难愈性创面的策略[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [10] | 万 然, 史 旭, 刘京松, 王岩松. 间充质干细胞分泌组治疗脊髓损伤的研究进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1088-1095. |
| [11] | 廖成成, 安家兴, 谭张雪, 王 倩, 刘建国. 口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞的治疗靶点及应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1096-1103. |
| [12] | 赵 敏, 冯柳祥, 陈 垚, 顾 霞, 王平义, 李一梅, 李文华. 低氧环境下外泌体可作为疾病的标志物[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1104-1108. |
| [13] | 谢文佳, 夏天娇, 周卿云, 刘羽佳, 顾小萍. 小胶质细胞介导神经元损伤在神经退行性疾病中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1109-1115. |
| [14] | 李珊珊, 郭笑霄, 尤 冉, 杨秀芬, 赵 露, 陈 曦, 王艳玲. 感光细胞替代治疗视网膜变性疾病[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1116-1121. |
| [15] | 焦 慧, 张一宁, 宋雨晴, 林 宇, 王秀丽. 乳腺癌类器官研究进展及临床应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128. |
1.2.7 检索偏离的描述、原因及对结果的影响 以主题词检索,难免下载与主题无关的文章,但是广泛的阅读有助于对文章内容的总结归纳,更有利于思路产生。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
.jpg)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
文章对诱导性多能干细胞在心血管疾病方面做了较为详尽的综述。自诱导性多能干细胞发现以来,利用其再分化来治疗疾病的研究越来越多,在心血管疾病、神经性疾病、视网膜病变、肝细胞再生等方面都有很多研究,文章总结了诱导性多能干细胞在心肌向分化方面的研究。体外培养的诱导性多能干细胞源心肌细胞不仅用于体内移植,也可在体外建立疾病模型来进行致病机制的研究和药物的筛选。在心血管疾病的研究中,诱导性多能干细胞定向分化为心肌细胞和血管内皮细胞是至关重要的一步。由诱导性多能干细胞分化得到的心肌细胞和血管内皮细胞的表型与分化方法有密切关系。目前,已有很多关于促进诱导性多能干细胞分化为心血管细胞的化学因子和分化系统的研究。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||