| [1] Weerheijm KL,Kreulen CM,Soet JJ,et al. Bacterial counts in carious dentine under restorations: 2-year in vivo effects. Caries Res.1999;33 (2): 130-134.[2] Yang L,Hu DH.Xiandai Zhongxiyi Jiehe Zazhi. 2003;16(9): 964.杨柳,胡定和.义齿性口炎的中西医结合治疗[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2003,16(9): 964.[3] Chen JH,Xiao YH,Li F,et al.Beijing Kouqiang Yixue. 2010; 18(4): 181-184.陈吉华,肖玉鸿,李芳,等.季铵盐抗菌单体改性牙本质粘接剂的抗菌性能研究[J].北京口腔医学,2010,18(4):181-184.[4] Zhang JT,Che TJ,He XY.Shanxi Zhongyi. 2009;30(3): 341-343.张金婷,车团结,何祥一.甘草及黄芪浸出液对致龋菌的体外菌抑作用[J].陕西中医,2009,30(3):341-343.[5] Walshaw PR,Mccomb D.SEM evaluation of the resin-dentin interface with proprietary bonding agents in human subjects J Dent Res.1994;73(5): 1079-1087.[6] Goracci G,Mori G,Bazzucchi M. Marginal seal and biocompatibility of a fourth generation bonding agent. Dent Mater.1995;11(6): 343-347.[7] Perdigão J,Lambrechts P,Van Meerbeek B,et al.The interaction of adhesive systems with human dentin. Am J Dent.1996;9(4): 167-173.[8] Imazato S,Ohmori K,Russell RR,et al. Determination of bactericidal activity of antibacterial monomer MDPB by a viability staining method. Dent Mater J. 2008; 27(1):145-148. [9] Imazato S. Antibacterial properties of resin composites and dentin bonding systems. Dental Mater. 2003;19(6): 449-457.[10] Imazato S,Kinomoto Y,Tarumi H,et al. Antibacterial activity and bonding characteristics of an adhesive resin containing antibacterial monomer MDPB. Dent Mater. 2003; 19(4): 313-319.[11] Imazato S,Walls AW,Kuramoto A,et al. Penetration of an antibacterial dentine-bonding system into demineralized human root dentine in vitro. Eur J Oral Sci.2002; 110(2): 168-174.[12] Pedrosa VO,Flório FM,Turssi CP,et al.Influence of pH Cycling on the Microtensile Bond Strength of Self-etching Adhesives Containing MDPB and Fluoride to Dentin and Microhardness of Enamel and Dentin Adjacent to Restorations.J Adhes Dent.2012. doi:10.3290 [Epub ahead of print][13] Izutani N,Imazato S,Nakajo K,et al.Effects of the antibacterial monomer 12-methacryloyloxydodecylpyridinium bromide (MDPB) on bacterial viability and metabolism.Eur J Oral Sci. 2011;119(2):175-181.[14] Izutani N,Imazato S,Noiri Y,et al.Antibacterial effects of MDPB against anaerobes associated with endodontic infections.Int Endod J.2010; 43(8):637-645.[15] Giammanco GM,Cumbo EM,Luciani A,et al.In vitro evaluation of the antibacterial activity of cured dentin/enamel adhesive incorporating the antimicrobial agent MDPB. New Microbiol. 2009;32(4):385-390.[16] Nishida M,Imazato S,Takahashi Y,et al.The influence of the antibacterial monomer 12-methacryloyloxydodecylpyridinium bromide on the proliferation, differentiation and mineralization of odontoblast-like cells.Biomaterials. 2010; 31(7):1518-1532.[17] Thomé T,Mayer MP,Imazato S,et al. In vitro analysis of inhibitory effects of the antibacterial monomer MDPB-containing restorations on the progression of secondary root caries. J Dent.2009; 37(9): 705-711.[18] Li F,Chen J,Chai Z,et al.Effects of a dental adhesive incorporating antibacterial monomer on the growth, adherence and membrane integrity of Streptococcus mutans.J Dent.2009;37(4):289-296.[19] Giammanco GM,Cumbo EM,Luciani A,et al.In vitro evaluation of the antibacterial activity of cured dentin/enamel adhesive incorporating the antimicrobial agent MDPB. New Microbiol. 2009;32(4):385-390.[20] Poureslami HR,Sajadi F,Sharifi M,et al.Marginal Microleakage of Low-shrinkage Composite Silorane in Primary Teeth: An In Vitro Study.J Dent Res Dent Clin Dent Prospects.2012;6(3): 94-97.[21] Baygin O,Korkmaz FM,Arslan I.Effects of different types of adhesive systems on the microleakage of compomer restorations in Class V cavities prepared by Er,Cr:YSGG laser in primary teeth.Dent Mater J.2012; 31(2):206-214.[22] Dalpian DM,Casagrande L,Franzon R,et al.Dentin microhardness of primary teeth undergoing partial carious removal.J Clin Pediatr Dent.2012; 36(4):363-367.[23] da Silva BM,França FM,Flório FM,et al.In situ anticariogenic effect of adhesive systems containing fluoride and MDPB.Am J Dent. 2010;23(2):75-80.[24] Poggio C,Arciola CR,Cepurnykh S,et al.In vitro antibacterial activity of different self-etch adhesives.Int J Artif Organs.2012 Oct 16:0. doi: 10.5301 [25] Korkmaz Y,Ozalp M,Attar N.Comparison of the antibacterial activity of different self-etching primers and adhesives.J Contemp Dent Pract.2008;9(7):57-64.[26] Weiger R,de Lucena J,Decker HE,et al.Vitality status of microorganisms in infected human root dentine. Int Endod J.2002; 35: 166-171. [27] Imazato S,Kuramoto A,Takahashi Y,et al.In vitro antibacterial effects of the dentinprimer of Clearfil Protect Bond. Dent Mater.2006; 22(6): 527-532.[28] Yoshikawa K,Clark DT,Brailsford SR,et al.The effect of antibacterialmonomer MDPB on the growth of organismsassociated with root caries. Dent Mater J. 2007;26(3): 388-392.[29] Xiao YH,Chen JH,Shen LJ,et al.Shiyong Kouqiang Yixue Zazhi. 2008;24(2): 67-70.肖玉鸿,陈吉华,沈丽娟,等. 三种可聚合季铵盐型单体对口腔病原菌的抗菌活性[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2008,24(2): 67-70.[30] Kuramoto A,Imazato S,Walls AW,et al.Inhibition of root caries progression by an antibacterial adhesive. Dent Res.2005;84: 89-93. |
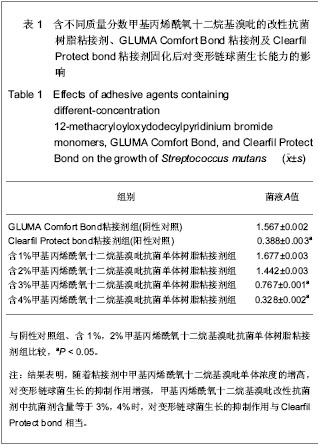
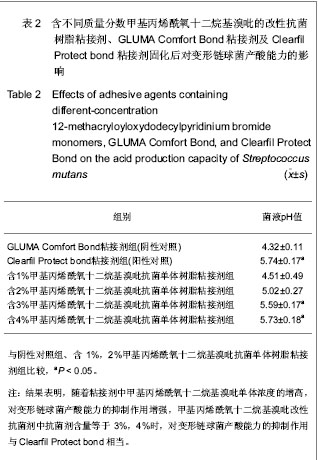
.jpg) 甲基丙烯酰氧十二烷基溴吡是20世纪90年代日本可乐丽公司(Kuraray Co. Ltd.)发明的专利产品,此产品购买难度大,成本高。Clearfil Protect bond是目前惟一一种上市的、含甲基丙烯酰氧十二烷基溴吡的抗菌自酸蚀粘接系统,甲基丙烯酰氧十二烷基溴吡抗菌单体的含量为5%,大量实验已经证实其对口腔常见致龋菌的抑制作用[13-16]。常用作树脂基粘接材料基质的单体双酚A双甲基丙烯酸缩水甘油酯、稀释单体的甲基丙烯酸羟乙酯等均无抗菌活性。所以,实验将含甲基丙烯酰氧十二烷基溴吡单体的Clearfil Protect bond添加入商品树脂基粘接剂GLUMA Comfort Bond中后形成实验性抗菌粘接剂,检测固化后粘接剂对主要致龋菌变形链球菌生长能力和产酸能力的抑制作用,目的是能研制一种国内能普遍应用的抗菌树脂粘接剂。
甲基丙烯酰氧十二烷基溴吡是20世纪90年代日本可乐丽公司(Kuraray Co. Ltd.)发明的专利产品,此产品购买难度大,成本高。Clearfil Protect bond是目前惟一一种上市的、含甲基丙烯酰氧十二烷基溴吡的抗菌自酸蚀粘接系统,甲基丙烯酰氧十二烷基溴吡抗菌单体的含量为5%,大量实验已经证实其对口腔常见致龋菌的抑制作用[13-16]。常用作树脂基粘接材料基质的单体双酚A双甲基丙烯酸缩水甘油酯、稀释单体的甲基丙烯酸羟乙酯等均无抗菌活性。所以,实验将含甲基丙烯酰氧十二烷基溴吡单体的Clearfil Protect bond添加入商品树脂基粘接剂GLUMA Comfort Bond中后形成实验性抗菌粘接剂,检测固化后粘接剂对主要致龋菌变形链球菌生长能力和产酸能力的抑制作用,目的是能研制一种国内能普遍应用的抗菌树脂粘接剂。.jpg)
.jpg)