中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (10): 1494-1500.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.10.018
• 干细胞移植 stem cell transplantation • 上一篇 下一篇
骨髓间充质干细胞移植改善慢性哮喘气道炎症
张 起,郭蕊蕊,胡江平
- 郑州大学附属郑州中心医院呼吸内科,河南省郑州市 450000
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation improves airway inflammation due to chronic asthma
Zhang Qi, Guo Rui-rui, Hu Jiang-ping
- Department of Respiratory Medicine, Zhengzhou Central Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
气道变应性炎症:过去大多数学者将哮喘的气道炎症笼统归为非特异性炎症范畴,近年来根据哮喘病气道炎症的发病机制,更多的作者倾向认为炎症的性质属于变态反应,因而进一步提出了气道变应性炎症的概念,该概念已经得到了越来越多学者的认可。现已证实哮喘病的变应性气道炎症比气道平滑肌痉挛更为重要,变应性气道炎症既是引起气道高反应性从而导致气道平滑肌敏感和痉挛的主要原因,也可直接导致气道通气障碍和气道重塑,因此消除气道过敏性炎症应该是哮喘治疗的主要措施。
骨髓间充质干细胞免疫调节作用:大量研究证实,骨髓间充质干细胞可以通过旁分泌机制以及骨髓间充质干细胞与免疫细胞间的相互作用,介导调节免疫反应平衡,最终促使局部炎症反应下调,减轻组织炎症损伤。骨髓间充质干细胞对炎症免疫反应的调节主要包括对先天免疫和获得性免疫反应的调节。
背景:以往研究提示骨髓间充质干细胞移植能够通过减轻炎症程度来改善病情。
目的:探讨骨髓间充质干细胞对慢性哮喘大鼠的治疗效果。
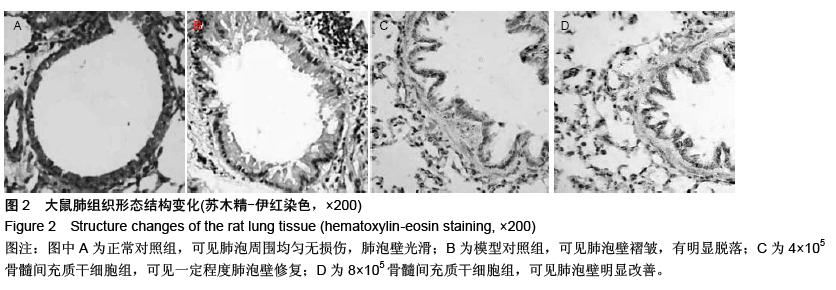
方法:通过卵白蛋白腹腔注射加雾化刺激的方式制备大鼠慢性哮喘模型,待模型稳定后,尾静脉注射4×105及8×105个骨髓间充质干细胞。治疗30 d后,苏木精-伊红染色观察肺组织病理变化,RT-qPCR、ELISA法检测肺组织和外周血中白细胞介素10、肿瘤坏死因子α、γ-干扰素水平。
结果与结论:①卵白蛋白腹腔注射配合雾化刺激的方法可以制备稳定的慢性哮喘模型。②治疗后30 d,肺组织病理显著改善,肺组织及外周血中炎症因子白细胞介素10、肿瘤坏死因子α、γ-干扰素水平显著下降,两治疗组之间的数据差异无显著性意义。③实验结果表明骨髓间充质干细胞具有治疗慢性哮喘的潜力。
.jpg)
.jpg)