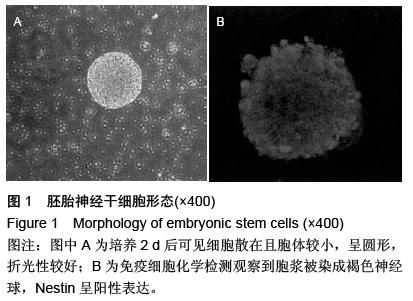
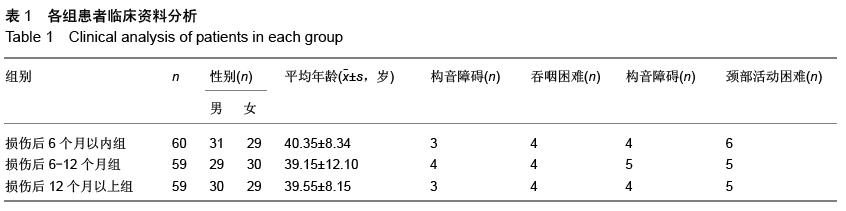
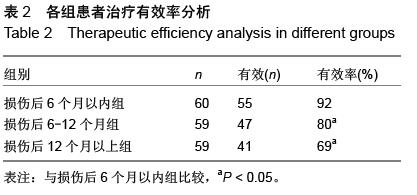
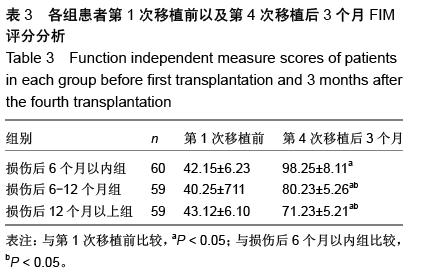
| [1] 寿纪新,马林,付旭东,等.不同时间移植神经干细胞治疗颅脑损伤的对比研究[J].中国实用神经疾病杂志,2010, 13(9):71-73.[2] 王东,张建军,马景鑑,等.神经干细胞NgR基因沉默立体定向移植治疗大鼠脑损伤[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(14):2539-2544.[3] 李红星,赵宗茂,金耀东,等.神经节苷脂联合神经干细胞移植对颅脑损伤大鼠海马的作用[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012, 16(10):1846-1850.[4] 王春亮,刘瑞莲.干细胞移植与运动性颅脑损伤的修复[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(40):7560-7563.[5] 王崇谦,丁鹏,牟临杰,等.颅脑损伤后内源性神经干细胞增殖与迁移中的基质细胞衍生因子1[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(6):998-1002.[6] 刘辉,杨树源,张建宁,等.神经干细胞移植对颅脑损伤大鼠脑皮层的神经保护作用[J].中国神经精神疾病杂志,2010, 36(6):335-338.[7] Wan JF, Zhang SJ, Wang L, et al. Implications for preserving neural stem cells in whole brain radiotherapy and prophylactic cranial irradiation: a review of 2270 metastases in 488 patients. J Radiat Res. 2013;54(2):285-291.[8] 黎国雄,王传湄,龚利平,等.神经干细胞立体定向脑内移植治疗大鼠重型颅脑损伤[J].中国临床神经外科杂志,2009, 14(5):288-290.[9] 刘辉,杨树源,张建宁,等.神经干细胞移植对颅脑外伤神经组织的替代和修复作用[J].中华神经外科杂志,2002, 18(5): 282-285.[10] 李晓红,陈翀,赵霞,等.亚低温对大鼠颅脑创伤后内源性神经干细胞增殖和分化的影响及其机制[J].中华创伤杂志,2014,30(6):500-503.[11] Mondragon-Teran P, Baboo JZ, Mason C, et al. The full spectrum of physiological oxygen tensions and step-changes in oxygen tension affects the neural differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells. Biotechnol Prog. 2011;27(6):1700-1708.[12] 郑小敏,范薇,汪昕,等.神经干细胞移植技术在脑卒中和颅脑损伤治疗中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2007,11(15):2964-2967.[13] 薛蓬,陈镇洲,刘钊,等.骨髓源性神经干细胞诱导分化及移植治疗颅脑损伤[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007, 11(7):1271-1273,1404.[14] Menendez L, Yatskievych TA, Antin PB, et al. Wnt signaling and a Smad pathway blockade direct the differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells to multipotent neural crest cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108(48):19240-19245.[15] 杨小锋,虞军,刘伟国,等.脑源性神经营养因子和神经干细胞联合移植治疗大鼠重度颅脑损伤的研究[J].浙江医学,2005,27(1):1-3,14.[16] 刘建新,王晓峰,张荣军,等.经枕大池移植神经干细胞治疗重型颅脑损伤大鼠的实验研究[J].临床神经外科杂志, 2012, 9(3):133-135.[17] 崔勇,陈静,卢亦成,等.神经干细胞移植治疗创伤性颅脑损伤的研究进展[J].中国综合临床,2011,27(2):220-222.[18] 罗江兵,赵鹏洲,欧英雄,等.神经干细胞在脑损伤模型中的迁移、成活和神经生长因子表达[J].中国微侵袭神经外科杂志,2012,17(5):232-234.[19] 隋立森.大鼠颅脑损伤后神经干细胞原位诱导、增殖分化及Notch信号通路调控机制的实验研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2008.[20] 任维维,周志武.神经干细胞移植治疗颅脑损伤的研究进展[J].中外医学研究,2012,10(1):163-164.[21] Ekici M, Hohl M, Schuit F, et al. Transcription of genes encoding synaptic vesicle proteins in human neural stem cells: chromatin accessibility, histone methylation pattern, and the essential role of rest. J Biol Chem. 2008;283(14):9257-9268.[22] Ostrakhovitch EA, Byers JC, O'Neil KD, et al. Directed differentiation of embryonic P19 cells and neural stem cells into neural lineage on conducting PEDOT-PEG and ITO glass substrates.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2012; 528(1):21-31.[23] 李红星,苑国富,金耀东,等.神经干细胞移植联用神经节苷脂对脑损伤大鼠神经学功能恢复的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(40):7505-7510.[24] 刘辉.神经干细胞生物学特性、神经干细胞移植治疗颅脑损伤后神经功能缺失及免疫基因治疗大鼠胶质瘤的研究[D]. 天津:天津医科大学,2002.[25] Bowman AN, van Amerongen R, Palmer TD, et al. Lineage tracing with Axin2 reveals distinct developmental and adult populations of Wnt/β-catenin- responsive neural stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(18):7324-7329.[26] 黎国雄,王传湄,龚利平,等.神经干细胞立体定向脑内移植治疗大鼠重型颅脑损伤[J].中国临床神经外科杂志,2009, 14(5):288-290.[27] 康建华,杨建平,贺小望,等.干细胞移植技术治疗重度颅脑损伤临床研究[J].江西医药,2012,47(12):1076-1078.[28] 杨小峰,刘伟国,虞军,等.BDNF和神经干细胞移植联合治疗大鼠重度颅脑损伤的研究[C].首届中国中青年神经外科医师论坛论文汇编,2004:641-644.[29] Scanga VI,Goraltchouk A,Nussaiba N,et al. Biomaterials for neural-tissue engineering- Chitosan supports the survival, migration, and differentiation of adult-derived neural stem and progenitor cells.J Canadian Chemistry. 2010, 88(3): 277-287.[30] 张化明,杨海,马江红,等.神经干细胞移植并手术治疗重型颅脑损伤的疗效分析[J].中国实用神经疾病杂志,2013, 16(13):52-53. [31] 张力,张辉,孙黎,等.神经干细胞在创伤性脑损伤灶周边的成活和迁移[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010, 14(36):6715-6719.[32] 刘辉,杨树源,张建宁,等.神经干细胞移植对颅脑外伤神经组织的替代和修复作用[J].中华神经外科杂志,2002, 18(5): 282-285.[33] 郑小敏,范薇,汪昕,等.神经干细胞移植技术在脑卒中和颅脑损伤治疗中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2007,11(15):2964-2967.[34] 王崇谦,丁鹏,牟临杰,等.颅脑损伤后内源性神经干细胞增殖与迁移中的基质细胞衍生因子1[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(6):998-1002.[35] 黎国雄,王传湄,龚利平,等.神经干细胞立体定向脑内移植治疗大鼠重型颅脑损伤[J].中国临床神经外科杂志, 2009, 14(5):288-290.[36] 王东,张建军,马景鑑,等.神经干细胞NgR基因沉默立体定向移植治疗大鼠脑损伤[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14(14):2539-2544.[37] 陈昱,付先明,牛朝诗,等.神经干细胞移植治疗缺血性脑卒中后遗症的实验研究[J].山东医药,2007,47(15): 3-5.[38] Eriksson C, Björklund A, Wictorin K. Neuronal differentiation following transplantation of expanded mouse neurosphere cultures derived from different embryonic forebrain regions. Exp Neurol. 2003; 184(2):615-635.[39] 刘辉,杨树源,张建宁,等.神经干细胞移植对颅脑损伤大鼠脑皮层的神经保护作用[J].中国神经精神疾病杂志, 2010,36(6):335-338.[40] 李红星,赵宗茂,金耀东,等.神经节苷脂联合神经干细胞移植对颅脑损伤大鼠海马的作用[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(10):1846-1850. |
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)