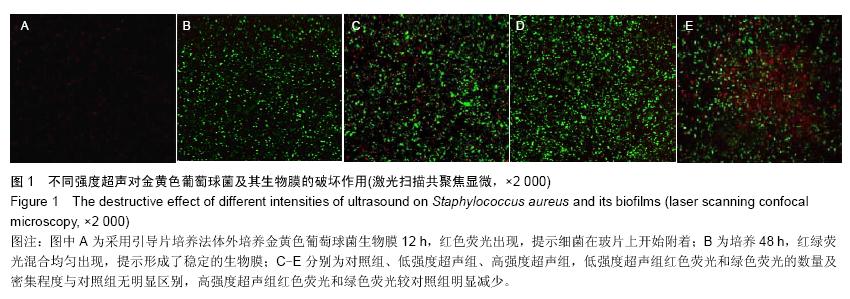
| [1] Sutherland IW.The biofilm matrix-an immobilized but dynamic microbial environment.Trends Microbiol. 2001; 9 (5):222-227.
[2] 黄晓群.细菌生物膜及其相关感染性疾病的研究进展[J].右江医学,2007,35(1):95-96.
[3] Chicurel M.Bacterial biofilms and infections-slimebusters. Nature. 2000;408:284-286.
[4] Costerton JW,Stewart PS,Greenberg EP.Bacterial biofilms: a Common Cause of persistent infections. Science. 1999; 284 (5418):1318-1322.
[5] Alem MA,Douglas LJ.Effects of aspirin and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on biofilms and planktonic cells of Candida albicans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004; 48 (1):41-47.
[6] Sedlacek MJ,Walker C.Antibiotic resistance in an invitro subgingival biofilm model.Oral Microbiol Immunol. 2007; 22(5):333-339.
[7] Bachmann SP,VandeWalle K,Ramage G,et al.In vitro activity of caspofungin against Candida albicans biofilms.Antimicrob Agents Chemother.2002;46(11):3594-3596.
[8] Pitt WG,McBride MO,Lunceford JK,et al.Ultrasonic enhancement of antibiotic action on gram-negative bacteria.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1994; 38 (11): 2577-2582.
[9] Bartley J,Young D.Ultrasound as a treatment for chronic rhinosinusitis.Medical Hypotheses.2009;73(1):15-17.
[10] Miller DL.Overview of experimental studies of biological effects of medical ultrasound caused by gas body activation and inertrial cavitation. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2007; 93(1-3): 314-330.
[11] de Silva GD,Kantzanou M,Justice A,et al.The ica operon and biofilm production in coagulase-negative staphylococci associated with carriage and disease in a neonatal intensive care unit.Clin Microbiol.2002;40(2):382-388.
[12] 白宁.细菌生物被摸体外模型的建立及重组溶葡球菌酶对葡萄球菌生物被膜的体外清除作用[D].北京:中国协和医科大学, 2008.
[13] 荣志东.慢性难愈创面细菌生物膜体外模型的建立及分析[D].呼和浩特:内蒙古大学,2002.
[14] 李京宝,韩峰,于文功.细菌生物膜研究技术[J].微生物学报, 2007, 47(3):558-561.
[15] Burton E,Yakandawala N,Lovetri K,et al.A microplate spectrofluorometric assay for bacterial biofilms.J Ind Microbiol Biatechnol.2006;7:1-4.
[16] O’Toole GA,Kolter R.Innitiation of biofilm formation in Pseudomonas fluorescens WCS365 proceeds via multiple, convergent signalling pathway: A genetic analysis. Mol Microbiol.1998;28(3):449-461.
[17] Head NE,Yu H.Cross-sectional analysis of clinical and environmental isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: biofilm formation, virulence, and genome diversity.Infect Immun. 2004;72(1):133-144.
[18] Wu JA,Kusuma C,Mond JJ,et al.Lysostaphin disrupts Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilms on artificial surfaces.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003;47(11):3407-3414.
[19] Eighmy TT,Maratea D,Bishop PL.Electron microscopic examination of wastewater biofilm formation and structural components.Appl Environ Microbiol.1983;45(6):1921-1931.
[20] Liu Y,Yang H,Sakanishi A.Ultrasound : mechanical gene transfer into plant cells by sonoporation.Biotechnol Adv. 2006;24(1):1-16.
[21] Hernot S,Klibanov AL.Microbubbles in ultrasound-triggered drug and gene delivery.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2008 ; 60 (10): 1153-1166.
[22] Van Wamel A,Bouakaz A,Versluis M,et al.Micromanipulation of endothelial cells: ultrasound-microbubble-cell interaction. Ultrasound Med Biol.2004;30(9):1255-1258.
[23] Dubinsky TJ,Cuevas C,Dighe M,et al.High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound: Current Potential and Oncologic Applications.Am J Roentgenol.2008;190(1):191-199.
[24] Wu F,Chen WZ,Bai J,et al.Tumor vessel destruction resulting from high-intensity focused ultrasound in patients with solid malignancies.Ultrasound Med Biol.2002; 28(4):535–542.
[25] Hynynen K,Colucci V,Chung A,et al.Noninvasive arterial occlusion using MRI-guided focused ultrasound.Ultrasound Med Biol.1996;22(8):1071-1077.
[26] Bigelow TA,Northagen T,Hill TM,et al.The destruction of Escherichia coli biofilms using high-intensity focused ultrasound.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2009;35(6):1026-1031.
[27] 朱秀菊,王嫣,余加林,等.高强度聚焦超声对体外铜绿假单胞菌生物膜的杀菌作用及其空间结构的影响[J].中国超声医学杂志, 2011,27(2):97-101.
[28] Gracia E,Femández A,Conchello P,et al.Adherence of Staphylococcus aureus slime-producing strain variants to biomaterials used in orthopaedic.Int Orthop.1997;21(1):46-51.
[29] Ryder C,Byrd M,Wozniak DJ.Role of polysaccharides in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm development.Curr Opin Microbiol.2007;10(6):644-648.
[30] Haggag W.The Role of Biofilm Exopolysaccharides on Biocontrol of Plant Diseases. Biopolymers.2010;9:271-284.
[31] Everbach EC,Francis CW.Cavitational mechanisms in ultrasound-accelerated thrombolysis at 1 MHz.Ultrasound Med Biol.2000;26(7):1153-1160.
[32] O’Toole GA,Kolter R.Flagellar and twitching motility are necessary for Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm development. Mol Microbiol.1998;30(2):295-304.
[33] Lawrence JR,Neu TR.Confocal laser scanning microscopy for analysis of microbial biofilms.Methods Enzymol. 1999; 310: 131-144.
[34] Rawlings DE.Characteristics and adaptability of iron- and sulfur-oxidizing microorganisms used for the recovery of metals from mineral s and their con cent rates. Microb Cell Fact.2005;4(1):13.
[35] Jefferson KK,Goldmann DA,Pier GB.Use of confocal microscopy to analyze the rate of vancomycin penetration through staphylococcus aureus biofilms.Antimicrob Agents Chemother.2005;49(6):2467-2473.
[36] Lasa I.Towards the identification of the common features of bacterial biofilm development.Int Microbiol.2006;9(1):21-28. |
.jpg)