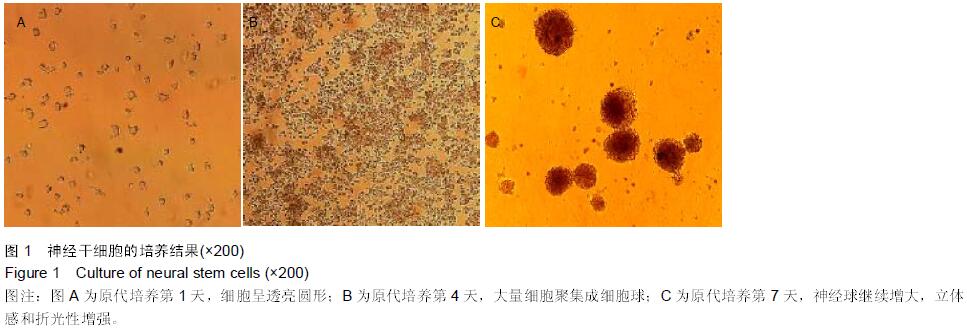
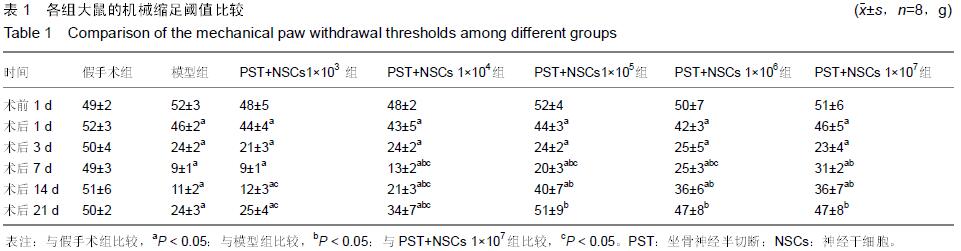
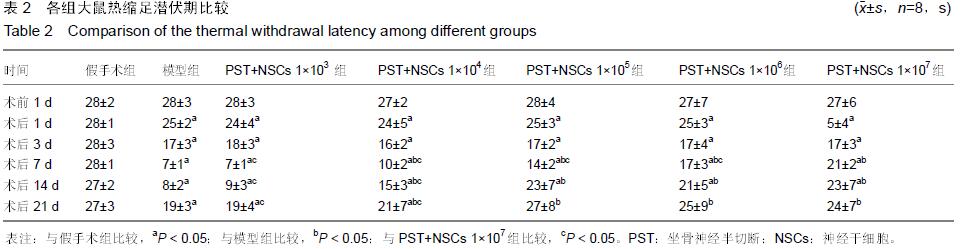
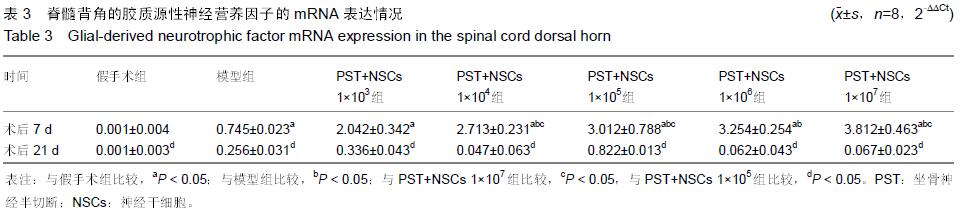
|
[1] Coleman MP, Freeman MR. Wallerian degeneration, wld(s), and Nmnat. Ann Rev Neurosci. 2010;33:245-267.
[2] Zheng L, Cui HF. Enhancement of nerve regeneration along a chitosan conduit combinedwith bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2012;23(9):2291-2302.
[3] Okawa T, Kamiya H, Himeno T, et al. Transplantation of neural crest like cells derived from induced pluripotent stem cells improves diabetic polyneuropathy in mice. Cell Transplantation. 2012.
[4] Xu L, Zhou S, Feng GY, et al.Neural stem cells enhance nerve regeneration after sciatic nerve injury in rats. Mol Neurobiol. 2012;46(2):265-274.
[5] Kato N, Matsumoto M, Kogawa M, et al. Critical role of p38 MAPK for regeneration of the sciatic nerve following crush injury in vivo. J Neuroinflammation. 2013;10:1.
[6] Cao X, Zhao P, Tao Q, et al. The role ofC-terminal binding protein 2 in Schwann cell differentiation after sciatic nerve crush. J Mol Neurosci. 2013;49(3):531-538.
[7] Aigner A. Delivery systems for the direct application of siRNAs to induce RNA interference (RNAi) in vivo. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2006;2006:1-15.
[8] Viana F, Dela peña E, Belmonte C. Specificity of cold thermotransduction is determined by differential ionic channel expression. Nat Neurosci. 2002;5(3):254-260.
[9] Linden AM, Sandu C, Aller MI, et al. TASK-3 knockout mice exhibit exaggerated nocturnal activity, impairments in cognitive functions, and reduced sensitivity to inhalation anesthetics. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007;323(3):924-934.
[10] Pitcher GM, Henry JL. Governing role of primary afferent drive in increased excitation of spinal nociceptive neurons in a model of sciatic neuropathy. Exp Neurol. 2008;214(2): 219-228.
[11] Khan GM, Chen SR, Pan HL. Role of primary afferent nerves in allodynia caused by diabetic neuropathy in rats. Neuroscience. 2002;114(2):291-299.
[12] Han HC, Lee DH, Chung JM. Characteristics of ectopic discharges in a rat neuropathic pain model. Pain. 2000;84: 253-262.
[13] Baron R. Neuropathic pain. The long path from mechanisms to mechanism-based treatment. Anaesthesist. 2000;49(5): 373-386.
[14] Baron R. Peripheral neuropathic pain: from mechanisms to symptoms. Clin J Pain. 2000;16(2 Suppl):S12-S20.
[15] Devor M. Ectopic discharge in Aβ afferents as a source of neuropathic pain. Exp Brain Res. 2009;196(1):115-128.
[16] Sandkuhler J. Undersanding LTP in pain pathways. Mol Pain. 2007;3:9.
[17] Adler JE, Nico I, Vande Vord P, et al.Modulation of neuropathic pain by a glial derived factor.Pain Med. 2009; 10(7):1229-1236.
[18] Han M, Huang RY, Du YM, et al. Early intervention of ERK activation in the spinal cord can block initiation of peripheral nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain in rats. Acta Physiologica Sinica. 2011;63(2):106-114.
[19] Zhang Z, Zhang ZY, Fauser U, et al. Mechanical allodynia and spinal up-regulation of P2X4 receptor in experinental auto immune neuritis rats. Neuroscience. 2008;152(2):495-501.
[20] 刘峰,袁贤瑞.白血病抑制因子在周围神经损伤修复中的应用[J].国际神经病学神经外科杂志,2005,32(5):442-444.
[21] Moalem-Taylor G, Li M, Allbutt HN, et al. A preconditioning nerve lesion inhibits mechanical pain hypersensitivity following subsequent neuropathic injury. Pain. 2011;7(5):1-9.
[22] 万有,刘风雨.急性疼痛早期治疗的必要性[J].中国疼痛医学杂志, 2011,17(1):1-5.
[23] Casula MA, Facer P, Powell AJ, et al. Expression of the sodium channel [beta] 3 subunit in injured human sensory neurons. Neuroreport. 2004;15(10):1629-1632.
[24] Groebner M,David R,Franz WM.Embryonic stem cells. Internist (Berl). 2006;47(5):502–508.
[25] McKay R. Stem cells in the central nervous system. Science. 1997;276 (5309):66-71.
[26] Mothe AJ, Bozkurt G, Catapano J, et al. Intrathecal transplantation of stem cells by lumbar puncture for thoracic spinal cord injury in the rat. Spinal Cord. 2011;49(9):967-973.
[27] Rao MS, Mattson MP. Stem cells and aging:expanding the possibilities. Mech Ageing Dev. 2001;122(7):713-734.
[28] Ghosh M, Tuesta LM, Puentes R, et al. Extensive cell migration, axon regeneration,and improved function with polysialic acid-modified Schwann cells after spinal cord injury. Glia. 2012;60(6):979-992 .
[29] Chen W, Xu ZM, Wang G, et al. Non-motor symptoms of Parkinson, s disease in china: a review of the literature. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2012;18(5):446-452.
[30] 韩志桐,苏宁,吴日乐,等.GFP转基因小鼠神经干细胞移植治疗大鼠帕金森病的实验研究[J].临床神经外科杂志,2012,9(3):139- 142.
[31] 陈涛,田增民,尹丰,等.神经干细胞移植治疗帕金森病的临床研究[J].中国微侵袭神经外科杂志,2012,17(10):452-453.
[32] 包晓群,宋亚彬,李松涛,等.神经干细胞移植治疗帕金森病[J].中国老年学杂志,2013,33(8):3591-3592.
[33] Fattore C, Perucca E. Novel medications for epilepsy. Drugs. 2011;71(16):2151-2178.
[34] Berg AT, Scheffer IE. New concepts in classification of the epilepsies: entering the 21st century. Epilepsia. 2011;52(6): 1058-1062.
[35] Kvalsund MP, Birbeck GL. Epilepsy care challenges in developing countries. Curr Opin Neurol. 2012;25(2):179-186.
[36] Zhao Y, Wu H, Wang X, et al. Clinical epidermiology of posttraumatic epilepsy in a group of Chinese patients. Seizure. 2012;21(5):322-326.
[37] 张化明,杨海,马江红,等.神经干细胞移植并手术治疗重型颅脑损伤的疗效分析[J].中国实用神经疾病杂志,2013,16(13):52-53.
[38] Lu P, Wang Y, Graham L, et al. Long-distance growth and connectivity of neural stem cells after severe spinal cord injury. Cell. 2012;150:1264-1273.
[39] 娄永利.神经干细胞移植治疗脊髓损伤的临床研究[J].中外医疗, 2012,31(2):22. |