|
[1] Gronthos S, Brahim J, Li W, et al. Stem cell properties of human dental pulp stem cells. J Dent Res. 2002;81(8):531- 535.
[2] Laino G, d'Aquino R, Graziano A, et al. A new population of human adult dental pulp stem cells: a useful source of living autologous fibrous bone tissue (LAB). J Bone Miner Res, 2005;20(8):1394-402.
[3] Okamoto Y, Sonoyama W, Ono M, et al. Simvastatin induces the odontogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells in vitro and in vivo. J Endod. 2009;35(3):367-372.
[4] Qin C, Baba O, Butler WT. Post-translational modifications of sibling proteins and their roles in osteogenesis and dentinogenesis. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 2004;15(3):126-136.
[5] Papagerakis P, Berdal A, Mesbah M, et al. Investigation of osteocalcin, osteonectin, and dentin sialophosphoprotein in developing human teeth. Bone. 2002;30(2):377-385.
[6] Suzuki S, Sreenath T, Haruyama N, et al. Dentin sialoprotein and dentin phosphoprotein have distinct roles in dentin mineralization. Matrix Biol. 2009;28(4):221-229.
[7] Qin C, Brunn JC, Jones J, et al. A comparative study of sialic acid-rich proteins in rat bone and dentin. Eur J Oral Sci. 2001; 109(2):133-141.
[8] d'Aquino R, Graziano A, Sampaolesi M, et al. Human postnatal dental pulp cells co-differentiate into osteoblasts and endotheliocytes: a pivotal synergy leading to adult bone tissue formation. Cell Death Differ. 2007;14(6):1162-1171.
[9] Liu H, Li W, Shi S, et al. MEPE is downregulated as dental pulp stem cells differentiate. Arch Oral Biol. 2005;50(11): 923-928.
[10] Wei X, Ling J, Wu L, et al. Expression of mineralization markers in dental pulp cells. J Endod. 2007;33(6):703-708.
[11] Wang H, Kawashima N, Iwata T, et al. Differentiation of odontoblasts is negatively regulated by MEPE via its C-terminal fragment. Biochem Biophys Res Common. 2010;398(3):406-412.
[12] Owen TA, Aronow M, Shalhoub V, et al. Progressive development of the rat osteoblast phenotype in vitro: reciprocal relationships in expression of genes associated with osteoblast proliferation and differentiation during formation of the bone extracellular matrix. J Cell Physiol. 1990;143(3):420-430.
[13] Huang GT, Shagramanova K, Chan SW. Formation of odontoblast-like cells from cultured human dental pulp cells on dentin in vitro. J Endod. 2006;32(11):1066-1073.
[14] Toupadakis CA, Wong A, Genetos DC, et al. Comparison of the osteogenic potential of equine mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow, adipose tissue, umbilical cord blood, and umbilical cord tissue. Am J Vet Res. 2010;71(10):1237-1245.
[15] Bakopoulou A, Leyhausen G, Volk J, et al. Comparative analysis of in vitro osteo/odontogenic differentiation potential of human dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) and stem cells from the apical papilla (SCAP). Arch Oral Biol. 2011;56(7):709-721.
[16] Liu M, Sun Y, Liu Y, et al. Modulation of the differentiation of dental pulp stem cells by different concentrations of beta-glycerophosphate. Molecules. 2012;17(2):1219-1232.
[17] Gronthos S, Mankani M, Brahim J, et al. Postnatal human dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(25):13625-13630.
[18] Proudfoot D, Skepper JN, Shanahan CM, et al. Calcification of human vascular cells in vitro is correlated with high levels of matrix Gla protein and low levels of osteopontin expression. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1998;18(3):379-388.
[19] About I, Bottero MJ, de Denato P, et al. Human dentin production in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 2000;258(1):33-41.
[20] Lee JH, Lee DS, Choung HW, et al. Odontogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells induced by preameloblast-derived factors. Biomaterials. 2011;32(36):9696-9706.
[21] Huang GT, Sonoyama W, Chen J, et al. In vitro characterization of human dental pulp cells: various isolation methods and culturing environments. Cell Tissue Res. 2006; 324(2):225-236.
[22] Batouli S, Miura M, Brahim J, et al. Comparison of stem-cell-mediated osteogenesis and dentinogenesis. J Dent Res. 2003;82(12):976-981.
[23] Liu J, Jin T, Ritchie HH, et al. In vitro differentiation and mineralization of human dental pulp cells induced by dentin extract. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2005;41(7):232-238.
[24] Tye CE, Rattray KR, Warner KJ, et al. Delineation of the hydroxyapatite-nucleating domains of bone sialoprotein. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(10):7949-7955.
[25] Couble ML, Farges JC, Bleicher F, et al. Odontoblast differentiation of human dental pulp cells in explant cultures. Calcif Tissue Int. 2000;66(2):129-138.
[26] Yokose S, Kadokura H, Tajima Y, et al. Establishment and characterization of a culture system for enzymatically released rat dental pulp cells. Calcif Tissue Int. 2000;66(2): 139-144.
[27] Zhang W, Walboomers XF, Wolke JG, et al. Differentiation ability of rat postnatal dental pulp cells in vitro. Tissue Eng. 2005;11(3-4):357-368.
[28] Argiro L, Desbarats M, Glorieux FH, et al. Mepe, the gene encoding a tumor-secreted protein in oncogenic hypophosphatemic osteomalacia, is expressed in bone. Genomics. 2001;74(3):342-351.
[29] Lu C, Huang S, Miclau T, et al. Mepe is expressed during skeletal development and regeneration. Histochem Cell Biol. 2004;121(6):493-499.
Gowen LC, Petersen DN, Mansolf AL, et al. Targeted disruption of the osteoblast/osteocyte factor 45 gene (OF45) results in increased bone formation and bone mass. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(3):1998-2007. |
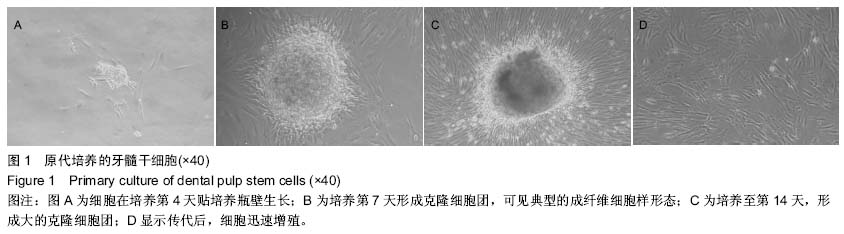
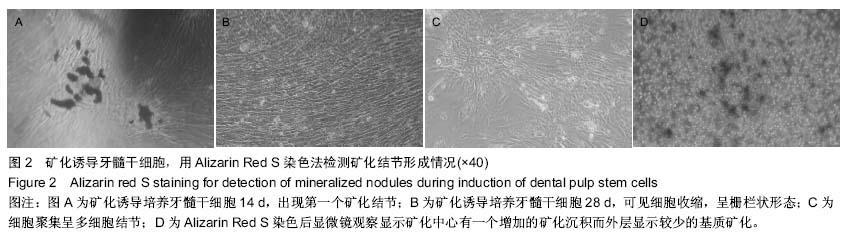

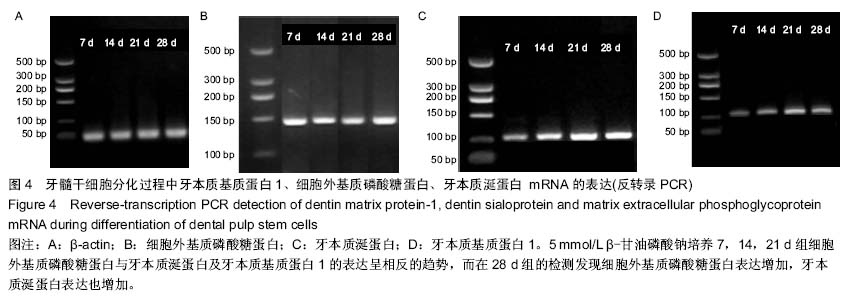
b1.jpg)