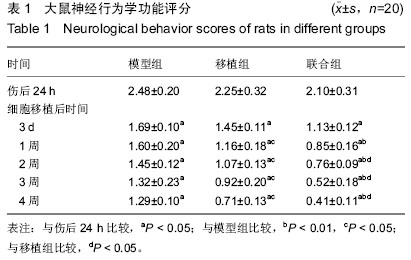
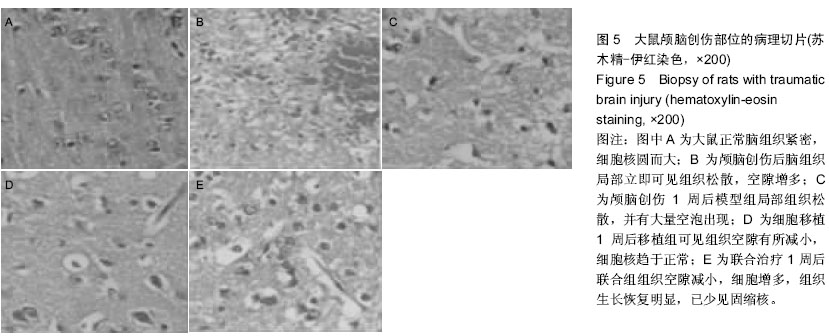
| [1] Xu J, Liao W, Gu D, et al. Neural ganglioside GD2 identifies a subpopulation of mesenchymal stem cells in umbilical cord. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2009;23(4-6):415-424.
[2] 武俏丽,李庆国,刘暌.干细胞移植治疗脊髓损伤研究进展[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(12):2343-2346.
[3] Drayna PC, Abramo TJ, Estrada C. Near-infrared spectroscopy in the critical setting. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2011;27(5):432-439.
[4] She JQ, Wang M, Zhu DM, et al. Monosialoanglioside (GM1) prevents lead-induced neurotoxicity on long-term potentiation, SOD activity, MDA levels, and intracellular calcium levels of hippocampus in rats. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2009;379(5):517-524.
[5] 蒋红梅,龚燕梅.神经节苷脂对急性脑出血患者神经元特异性烯醇化酶的影响[J].医学综述,2011,17(14):2227-2228.
[6] Lim ST, Esfahani K, Avdoshina V, et al. Exogenous gangliosides increase the release of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Neuropharmacology. 2011;60(7-8): 1160-1167.
[7] Cummings DM, Belluscio L. Continuous neural plasticity in the olfactory intrabulbar circuitry. J Neurosci. 2010;30(27): 9172-9180.
[8] Liu YJ, Wang Q, Li B. Neuronal responses to looming objects in the superior colliculus of the cat. Brain Behav Evol. 2011; 77(3):193-205.
[9] Galvin KA, Jones DG. Adult human neural stem cells for cell-replacement therapies in the central nervous system. Med J Aust. 2002;177(6):316-318.
[10] Huang F, Dong X, Zhang L, et al. The neuroprotective effects of NGF combined with GM1 on injured spinal cord neurons in vitro. Brain Res Bull. 2009;79(1):85-88.
[11] Hydén LC. The importance of providing scaffolding to support patient narratives when brain damage impairs storytelling ability. Top Stroke Rehabil. 2011;18(1):52-54.
[12] Agrawal A, Garg LN. Split calvarial bone graft for the reconstruction of skull defects. J Surg Tech Case Rep. 2011; 3(1):13-16.
[13] 穆晓红,赵子义,徐林,等.密度梯度离心法体外培养骨髓间充质干细胞的分化能力[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011, 15(27): 4955-4958.
[14] Wang J, Zhang R, Shen Y, et al. Recent advances in cell sheet technology for periodontal regeneration. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014;9(3):162-173.
[15] Lu Y, Hui G, Liu F, et al. Survival and regeneration of deep-freeze preserved autologous cranial bones after cranioplasty. Br J Neurosurg. 2012;26(2):216-221.
[16] Linden MA, McClure J. The causal attributions of nursing students toward adolescent survivors of brain injury. Nurs Res. 2012;61(1):58-65.
[17] Seyed Jafari SS, Ali Aghaei A, Asadi-Shekaari M, et al. Investigating the effects of adult neural stem cell transplantation by lumbar puncture in transient cerebral ischemia. Neurosci Lett. 2011;495(1):1-5.
[18] Hassanein AH, Arany PR, Couto RA, et al. Cranial particulate bone graft ossifies calvarial defects by osteogenesis. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2012;129(5):796e-802e.
[19] Thompson HJ, Weir S, Rivara FP, et al. Utilization and costs of health care after geriatric traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma. 2012;29(10):1864-1871.
[20] Su J, Haner CV, Imbery TE, et al. Reelin is required for class-specific retinogeniculate targeting. J Neurosci. 2011; 31(2):575-586.
[21] 刘爱民.临床各种体液标本中神经节苷脂变化意义的研究进展[J].中国现代医药杂志,2007,9(2):152-154.
[22] Haider M, Cappello J, Ghandehari H, et al. In vitro chondrogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells in recombinant silk-elastinlike hydrogels. Pharm Res. 2008;25(3):692-699.
[23] 张供,谷兴华,宋毅,等.单唾液酸神经节苷脂对大鼠缺血再灌注脑损伤的保护作用[J].山东大学学报:医学版,2006,44(3):252-255.
[24] Polak SJ, Levengood SK, Wheeler MB, et al. Analysis of the roles of microporosity and BMP-2 on multiple measures of bone regeneration and healing in calcium phosphate scaffolds. Acta Biomater. 2011;7(4):1760-1771.
[25] 张赛.颅脑创伤后神经行为障碍的认识和药物治疗[J].中华神经外科杂志,2007,23(7):481-482.
[26] Becker C. Nursing care of the brain injury patient on a locked neurobehavioral unit. Rehabil Nurs. 2012;37(4):171-175.
[27] 张荣洁.脑损伤高危儿早期干预与护理[J].护理实践与研究,2012, 9(1):56-57.
[28] Li J, Li Y, Ma S, et al. Enhancement of bone formation by BMP-7 transduced MSCs on biomimetic nano-hydroxyapatite/ polyamide composite scaffolds in repair of mandibular defects. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010;95(4):973-981.
[29] Liu Y, Ming L, Luo H, et al. Integration of a calcined bovine bone and BMSC-sheet 3D scaffold and the promotion of bone regeneration in large defects. Biomaterials. 2013;34(38): 9998-10006.
[30] 钟池,钟春玖,罗玉敏,等.骨髓基质细胞静脉移植治疗大鼠短暂性局灶性脑缺血[J].中华神经医学杂志,2004,3(2):89-92.
[31] Kim S, Honmou O, Kato K, et al. Neural differentiation potential of peripheral blood- and bone-marrow-derived precursor cells. Brain Res. 2006;1123(1):27-33. |