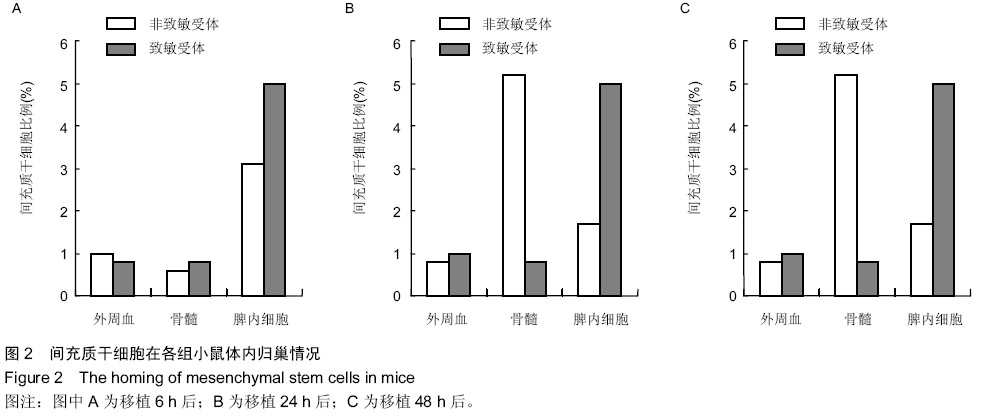
| [1] Shin GY, Shim JK, Lee JH, et al. Changes in the biological characteristics of glioma cancer stem cells after serial in vivo subtransplantation. Childs Nerv Syst. 2013;29(1):55-64.
[2] 许吕宏,洪冬玲,吴燕峰,等.间充质干细胞在致敏受者造血干细胞移植中的作用[J].中山大学学报(医学科学版),2013,34(2): 225-229.
[3] Eberle JJ, Greenwood DR. Life at the top of the greenhouse Eocene world--A review of the Eocene flora and vertebrate fauna from Canada's High Arctic. Geol Soc Am Bull. 2013; 90(12):901-902.
[4] Edinger EN, Copper P, Risk MJ, et al. Oceanography and reefs of recent and Paleozoic tropical epeiric seas. Facies. 2014;47(1):127-149.
[5] 刘银梅,张鹏.骨髓间充质干细胞对移植免疫的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(49):9264-9267.
[6] Dickenson NE, Choudhari SP, Adam PR, et al. Oligomeric states of the Shigella translocator protein IpaB provide structural insights into formation of the type III secretion translocon. Protein Sci. 2013;22(5):614-627.
[7] Voiniciuc C, Dean GH, Griffiths JS, et al. Flying saucer1 is a transmembrane RING E3 ubiquitin ligase that regulates the degree of pectin methylesterification in Arabidopsis seed mucilage. Plant Cell. 2013;25(3):944-959.
[8] 王景昌,白海,魏敦宏,等.自体骨髓间充质干细胞联合自体外周血造血干细胞移植治疗恶性血液病[J].实用医学杂志,2012,28(13): 2240-2241.
[9] Zhang QZ, Su WR, Shi SH, et al. Human gingiva-derived mesenchymal stem cells elicit polarization of m2 macrophages and enhance cutaneous wound healing. Stem Cells. 2010;28(10):1856-1868.
[10] Teixeira FG, Carvalho MM, Sousa N, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells secretome: a new paradigm for central nervous system regeneration? Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013;70(20):3871- 3882.
[11] 田莹,邓宇斌,黄奕俊,等.骨髓间充质干细胞在CD4+CD25+调节性T细胞减轻大鼠移植物抗宿主反应中的作用[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2006,14(6):1210-1214.
[12] Patel SA, Meyer JR, Greco SJ, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells protect breast cancer cells through regulatory T cells: role of mesenchymal stem cell-derived TGF-beta. J Immunol. 2010; 184(10):5885-5894.
[13] Inanç B, Elçin YM. Stem cells in tooth tissue regeneration-- challenges and limitations. Stem Cell Rev. 2011;7(3):683-692.
[14] 黄杨,尹文,张秀敏,等.骨髓间充质干细胞植入对急性百草枯染毒大鼠肺损伤的影响[J].中华劳动卫生职业病杂志,2012,30(9): 645-649.
[15] Al-Ejeh F, Smart CE, Morrison BJ, et al. Breast cancer stem cells: treatment resistance and therapeutic opportunities. Carcinogenesis. 2011;32(5):650-658.
[16] Liberski AR, Al-Noubi MN, Rahman ZH, et al. Adaptation of a commonly used, chemically defined medium for human embryonic stem cells to stable isotope labeling with amino acids in cell culture. J Proteome Res. 2013;12(7):3233-3245.
[17] 蒋秀美.4例异体骨髓间充质干细胞和外周血造血干细胞联合移植治疗白血病的护理[J].南京医科大学学报(自然科学版),2005, 25(2):141-143.
[18] Fan X, Matsui W, Khaki L, et al. Notch pathway inhibition depletes stem-like cells and blocks engraftment in embryonal brain tumors. Cancer Res. 2006;66(15):7445-7452.
[19] 常玉立,孙天胜,张晓东,等.自体骨髓间充质干细胞经皮注射修复骨缺损的实验研究[J].中华医学杂志,2008,88(23):1643-1647.
[20] 马东超,杨志健,王伟,等.骨髓间充质干细胞联合肝细胞生长因子对心肌梗死治疗作用的实验研究[J].中华心血管病杂志,2006, 34(2):119-122.
[21] Butler KL, Goverman J, Ma H, et al. Stem cells and burns: review and therapeutic implications. J Burn Care Res. 2010; 31(6):874-881.
[22] Zubov E, Puzhnyak R, Pashchenko VP, et al. Magnetocaloric effect in (La0.6Ca0.4)0.9Mn1.1O3. Phys Solid State. 2013; 51(10):2090-2094.
[23] Vacanti V, Kong E, Suzuki G, et al. Phenotypic changes of adult porcine mesenchymal stem cells induced by prolonged passaging in culture. J Cell Physiol. 2005;205(2):194-201.
[24] 吴冠宇,李建勇,郑敏,等.自体骨髓间充质干细胞联合外周血造血干细胞移植治疗恶性血液病[J].中华全科医学,2008,6(8): 816-817.
[25] Dontu G, Wicha MS. Survival of mammary stem cells in suspension culture: implications for stem cell biology and neoplasia. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2005;10(1):75-86.
[26] Tsai PC, Fu TW, Chen YM, et al. The therapeutic potential of human umbilical mesenchymal stem cells from Wharton's jelly in the treatment of rat liver fibrosis. Liver Transpl. 2009; 15(5):484-495.
[27] Al-Hajj M. Cancer stem cells and oncology therapeutics. Curr Opin Oncol. 2007;19(1):61-64.
[28] 胡锴勋,赵士富,孙琪云,等.间充质干细胞对H-2半相合骨髓移植小鼠免疫功能的影响[J].中华血液学杂志,2007,28(8):505-509.
[29] Woo SM, Kim J, Han HW, et al. Notch signaling is required for maintaining stem-cell features of neuroprogenitor cells derived from human embryonic stem cells. BMC Neurosci. 2009;10:97.
[30] 侯志峰,龚卫琴,张珊红,等.骨髓间充质干细胞静脉移植对心肌梗死大鼠心功能的影响[J].中华老年心脑血管病杂志,2006,8(4): 265-267.
[31] Galipeau J. The mesenchymal stromal cells dilemma--does a negative phase III trial of random donor mesenchymal stromal cells in steroid-resistant graft-versus-host disease represent a death knell or a bump in the road? Cytotherapy. 2013;15(1):2-8.
[32] Griffin MD, Ryan AE, Alagesan S, et al. Anti-donor immune responses elicited by allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells: what have we learned so far? Immunol Cell Biol. 2013;91(1): 40-51.
[33] Ankrum JA, Ong JF, Karp JM. Mesenchymal stem cells: immune evasive, not immune privileged. Nat Biotechnol. 2014;32(3):252-260.
[34] 李文强,魏捷,万曦,等.兔骨髓间充质干细胞自体移植对扩张型心肌病左心室功能的影响[J].中华小儿外科杂志,2005,26(12): 649-652.
[35] Reinders ME, Roemeling-van Rhijn M, Khairoun M, et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells from patients with end-stage renal disease are suitable for autologous therapy. Cytotherapy. 2013;15(6):663-672.
[36] Shiozawa Y, Nie B, Pienta KJ, et al. Cancer stem cells and their role in metastasis. Pharmacol Ther. 2013;138(2): 285-293.
[37] 梁雪,孔佩艳.骨髓间充质干细胞的生物学特性及临床应用前景[J].西部医学,2007,19(5):949-952.
[38] Tatsumi K, Ohashi K, Matsubara Y, et al. Tissue factor triggers procoagulation in transplanted mesenchymal stem cells leading to thromboembolism. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;431(2):203-209.
[39] Vidal SJ, Rodriguez-Bravo V, Galsky M, et al. Targeting cancer stem cells to suppress acquired chemotherapy resistance. Oncogene. 2014;33(36):4451-4463.
[40] Shin JW, Buxboim A, Spinler KR, et al. Contractile forces sustain and polarize hematopoiesis from stem and progenitor cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2014;14(1):81-93.
[41] 胡军,江明.骨髓间充质干细胞在造血干细胞移植中的作用[J].医学综述,2007,13(7):548-550.
[42] McIntosh KR, Frazier T, Rowan BG, et al. Evolution and future prospects of adipose-derived immunomodulatory cell therapeutics. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2013;9(2):175-184.
[43] Lee HK, Finniss S, Cazacu S, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells deliver synthetic microRNA mimics to glioma cells and glioma stem cells and inhibit their cell migration and self-renewal. Oncotarget. 2013;4(2):346-361.
[44] Lee SU, Maeda M, Ishikawa Y, et al. LRF-mediated Dll4 repression in erythroblasts is necessary for hematopoietic stem cell maintenance. Blood. 2013;121(6):918-929.
[45] Weiss DJ. Stem cells, cell therapies, and bioengineering in lung biology and diseases. Comprehensive review of the recent literature 2010-2012. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2013;10(5): S45-97.
[46] De Lisio M, Parise G. Exercise and hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells: protection, quantity, and function. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2013;41(2):116-122.
[47] 张文志,孔荣,方诗元,等.兔自体骨髓间充质干细胞体内复合移植的成骨研究[J].临床骨科杂志,2002,5(2):81-85.
[48] Ng RL, Scott NM, Strickland DH, et al. Altered immunity and dendritic cell activity in the periphery of mice after long-term engraftment with bone marrow from ultraviolet-irradiated mice. J Immunol. 2013;190(11):5471-5484.
[49] Takashima S, Tempel D, Duckers HJ. Current outlook of cardiac stem cell therapy towards a clinical application. Heart. 2013;99(23):1772-1784.
[50] Arneth A, Veenendaal E M, Best C, et al. Water use strategies and ecosystem-atmosphere exchange of CO2 in two highly seasonal environments. Biogeosciences. 2014;3(4):421-437.
|