| [1] Hicks JM, Singla A, Shen FH, et al. Complications of pedicle screw fixation in scoliosis surgery: a systematic review. Spine. 2010;35(11):E465-470.
[2] Lonstein JE, Denis F, Perra JH,et al. Complications associated with pedicle screws. J Bone J Surg Am. 1999;81(11):1519-528.
[3] Gautschi OP, Schatlo B, Schaller K, et al. Clinically relevant complications related to pedicle screw placement in thoracolumbar surgery and their management: a literature review of 35,630 pedicle screws. Neurosurg Focus. 2011; 31(4):E8.
[4] Wegener B, Birkenmaier C, Fottner A, et al. Delayed perforation of the aorta by a thoracic pedicle screw. Eur Spine J. 2008;17(Suppl 2):S351-354.
[5] Watanabe K, Matsumoto M, Tsuji T, et al. Ball tip technique for thoracic pedicle screw placement in patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Neurosurg Spine. 2010;13(2): 246-252.
[6] 陈克冰,刘少喻,李浩淼,等.球形探针技术在椎弓根螺钉置钉术中的应用[J].中华骨科杂志,2011,31(12):1314-1318.
[7] Lee GY, Massicotte EM, Rampersaud YR. Clinical accu-racy of cervicothoracic pedicle screw placement: a comparison of the“open”lamino-foraminotomy and computer-assisted techniques. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2007;20(1): 25-32.
[8] Lonner BS, Auerbach JD, Estreicher MB, et al. Thoracic pedicle screw instrumentation: the learning curve and evolution in technique in the treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine. 2009;34(20): 2158-2164.
[9] Kim YJ, Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, et al. Free-hand pedicle screw placement in the thoracic spine: is it safe? Spine. 2004; 29(3): 333-342.
[10] Allam Y, Silbermann J, Riese F, et al. Computer tomography assessment of pedicle screw placement in thoracic spine: comparison between free hand and a generic 3D-based navigation techniques. Eur Spine J. 2013;22(3):648-653.
[11] Waschke A, Walter J, Duenisch P, et al. CT-navigation versus fluoroscopy-guided placement of pedicle screws at the thoracolumbar spine: single center experience of 4,500 screws. Eur Spine J. 2013;22(3): 654-660.
[12] Suk SI, Kim WJ, Lee SM,et al. Thoracic pedicle screw fixation in spinal deformities:are they really safe? Spine. 2001;26(18): 2049-2057.
[13] Gang C, Haibo L, Fancai L, et al. Learning curve of thoracic pedicle screw placement using the free-hand technique in scoliosis: how many screws needed for an apprentice? Eur Spine J.2012; 21(6):1151-1156.
[14] Samdani AF, Ranade A, Saldanha V, et al. Learning curve for placement of thoracic pedicle screws in the deformed spine. Neurosurgery. 2010;66(2):290-294.
[15] Bergeson RK, Schwend RM, DeLucia T, et al. How accurately do novice surgeons place thoracic pedicle screws with the free hand technique? Spine.2008;33(15): E501-507.
[16] Chaynes P, Sol JC, Vaysse P, et al. Vertebral pedicle anatomy in relation to pedicle screw fixation: a cadaver study. Surg Radiol Anat. 2001;23(2):85-90.
[17] McCormack BM, Benzel EC, Adams MS, et al. Anatomy of the thoracic pedicle. Neurosurgery. 1995;37(2): 303-308.
[18] Liljenqvist UR, Allkemper T, Hackenberg L, et al. Analysis of vertebral morphology in idiopathic scoliosis with use of magnetic resonance imaging and multiplanar reconstruction. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84-A(3): 359-368.
[19] O’Brien MF, Lenke LG, Mardjetko S, et al. Pedicle morphology in thoracic adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: is pedicle fixation an anatomically viable technique? Spine. 2000;25(18): 2285- 2293.
[20] 刑文华,贾连顺,霍红军,等.胸椎椎弓根-肋骨复合体螺钉置入内固定的应用解剖学特征[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011, 5(43):8063-8067.
[21] Parent S, Labelle H, Skalli W, et al. Morphometric analysis of anatomic scoliotic specimens. Spine. 2002;27(21): 2305-2311.
[22] Chung KJ, Suh SW, Desai S, et al. Ideal entry point for the thoracic pedicle screw during the free hand technique. Int Orthop. 2008;32(5):657-662.
[23] Cui G, Watanabe K, Hosogane N, et al. Morphologic evaluation of the thoracic vertebrae for safe free-hand pedicle screw placement in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a CT-based anatomical study. Surg Radiol Anat. 2012; 34(3): 209-216.
[24] Modi H, Suh SW, Song HR, et al. Accuracy of thoracic pedicle screw placement in scoliosis using the ideal pedicle entry point during the freehand technique. Int Orthop. 2009; 33(2): 469-475.
[25] Modi HN, Suh SW, Fernandez H, et al. Accuracy and safety of pedicle screw placement in neuromuscular scoliosis with free-hand technique. Eur Spine J. 2008;17(12):1686-1696.
[26] Modi HN, Suh SW, Hong JY, et al. Accuracy of thoracic pedicle screw using ideal pedicle entry point in severe scoliosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468(7):1830-1837.
[27] Magerl FP. Stabilization of the lower thoracic and lumbar spine with external skeletal fixation. Clin Orthop.1984;189: 125-141.
[28] Vaccaro AR, Rizzolo SJ, Allardyce TJ, et al. Placement of pedicle screws in the thoracic spine. Part I: Morphometric analysis of the thoracic vertebrae. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995; 77(8):1193-1199.
[29] Cinotti G, Gumina S, Ripani M, et al. Pedicle Instrumentation in the Thoracic Spine: A Morphometric and Cadaveric Study for Placement of Screw. Spine. 1999;24(2):114-119.
[30] 崔冠宇,刘波,渡边航太,等.青少年特发性脊柱侧弯胸椎椎弓根螺钉置入角度研究[J].山东医药,2011,51(8):6-9. |
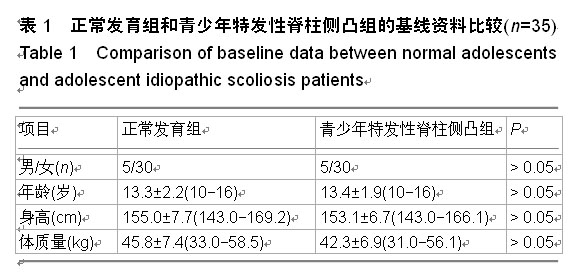
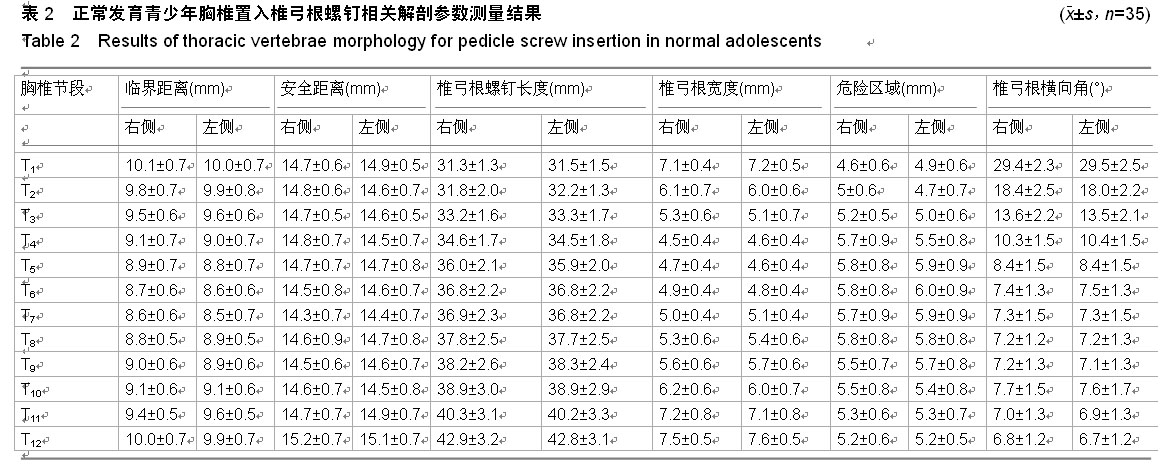
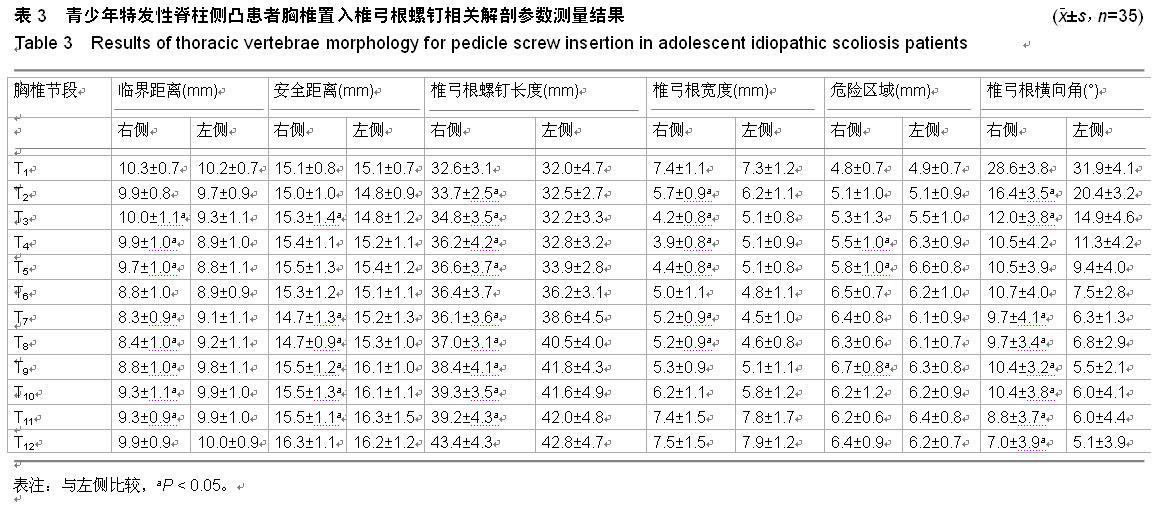
.jpg)
.jpg)