• 干细胞移植 stem cell transplantation • 上一篇 下一篇
人脐带间充质干细胞移植肝硬化大鼠肝脏miRNA的差异表达
刘祥忠1,邹志强1,王贵强2,李 栋3,邵志英1
- 1烟台市传染病医院,山东省烟台市 264001;
2北京大学第一医院,北京市 100034;
3山东大学齐鲁医院,山东省济南市 250012
MicroRNA differential expression in liver cirrhosis rats undergoing human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation
Liu Xiang-zhong1, Zou Zhi-qiang1, Wang Gui-qiang2, Li Dong3, Shao Zhi-ying1
- 1Hospital of Infectious Diseases of Yantai, Yantai 264001, Shandong Province, China;
2Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China;
3Qilu Hospital of Shandong University, Jinan 250012, Shandong Province, China
摘要:
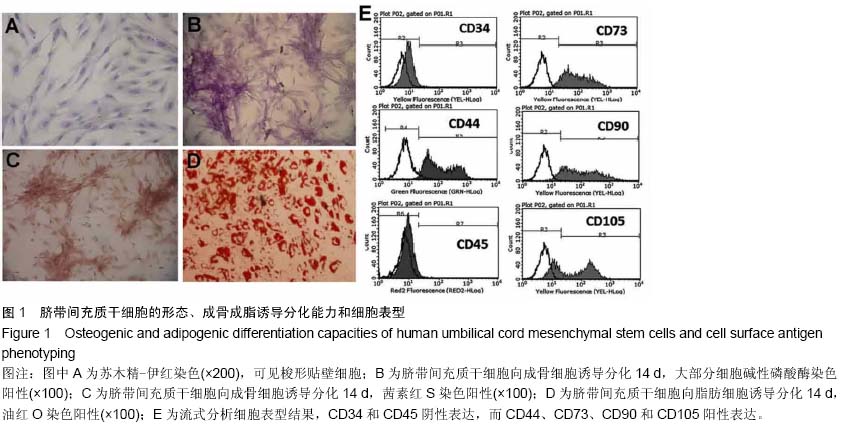
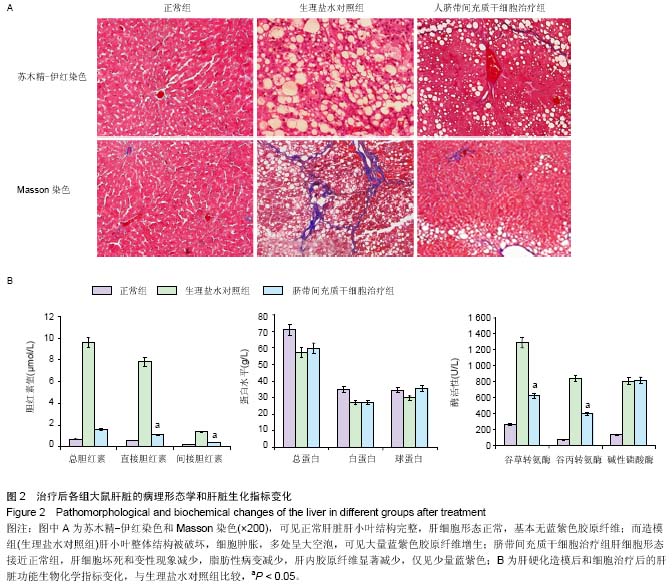
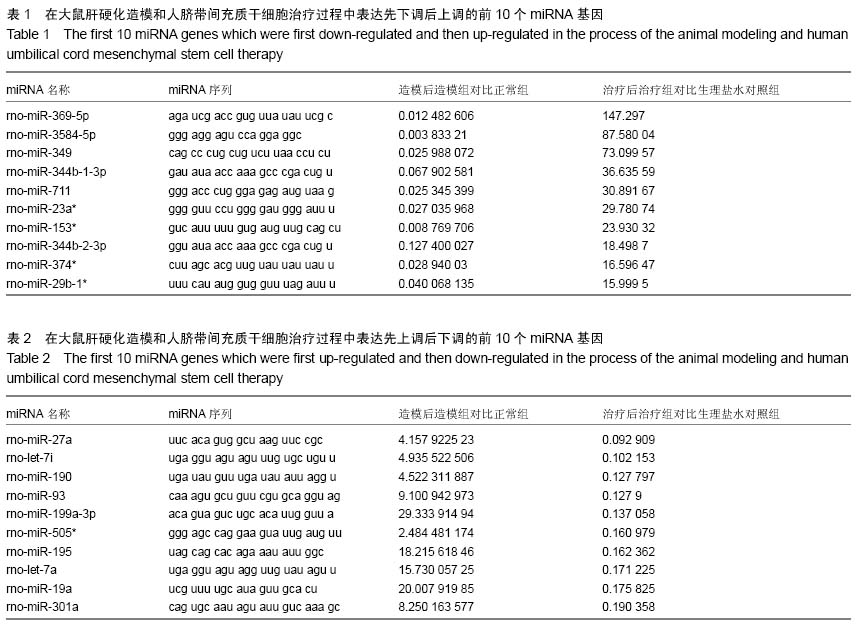
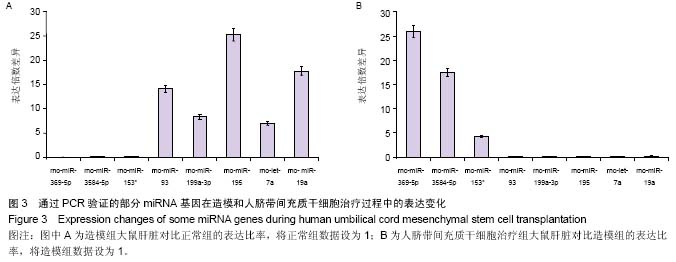
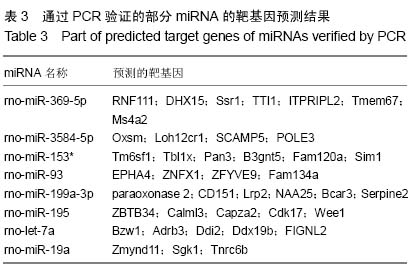
背景:研究表明脐带间充质干细胞可以显著改善肝硬化的程度,进而修复肝损伤,但其治疗肝硬化的分子调控机制,尤其是非编码RNA调控的肝内基因变化,目前并没有得到详细的阐释。 目的:分析人脐带间充质干细胞移植肝硬化大鼠肝细胞中微小RNA基因表达的变化。 方法:采用四氯化碳皮下注射联合乙醇喂服方法建立肝硬化大鼠模型,造模8周后经尾静脉输注人脐带间充质干细胞,每周1次,连续注射4周。最后一次注射治疗1周后收集大鼠肝脏组织进行石蜡切片和提取肝脏RNA进行表达谱基因芯片分析,同时收集血清利用自动生化分析仪测定肝功能指标变化。 结果与结论:人脐带间充质干细胞治疗可以显著降低谷丙转氨酶、谷草转氨酶和转肽酶水平,脂肪病变和肝细胞坏死显著减少。微小RNA表达谱芯片杂交分析和PCR验证结果显示rno-miR-369-5p、rno-miR-3584-5p和rno-miR-153*这3种微小RNA基因在造模过程中先下调表达,并在人脐带间充质干细胞治疗后显著上调;而rno-miR-93、rno-miR-199a-3p、rno-miR-195、rno-let-7a和rno-miR-19a这5种微小RNA基因在造模过程中先上调表达,并在人脐带间充质干细胞治疗后显著下调。以上结果表明人脐带间充质干细胞逆转肝硬化和肝细胞损伤过程中,可能通过上调rno-miR-369-5p、rno-miR-3584-5p和rno-miR-153*等miRNA基因表达,下调rno-miR-93、rno-miR-199a-3p、rno-miR-195、rno-let-7a和rno-miR-19a等相关miRNA基因表达发挥治疗作用。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号: