中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (23): 3628-3632.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.23.004
• 骨髓干细胞 bone marrow stem cells • 上一篇 下一篇
骨髓间充质干细胞联合还原型谷胱甘肽对肺损伤小鼠的保护
陈 飞1,2,李国庆1,胡丰庆1,梅 举1,王明松1,2
- 1上海交通大学医学院附属新华医院崇明分院心胸外科,上海市 202150;
2上海交通大学医学院附属新华医院心胸外科,上海市 200092
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells with reduced glutathione against mouse lung injury
Chen Fei1, 2, Li Guo-qing1, Hu Feng-qing1, Mei Ju1, Wang Ming-song1, 2
- 1Department of?Cardiothoracic Surgery, Affiliated Xinhua Hospital (Chongming Branch) of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 202150, China;
2Department of?Cardiothoracic Surgery, Affiliated Xinhua Hospital of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200092, China
摘要:
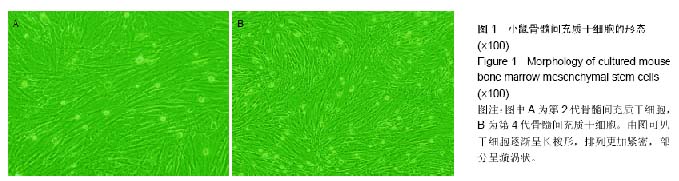
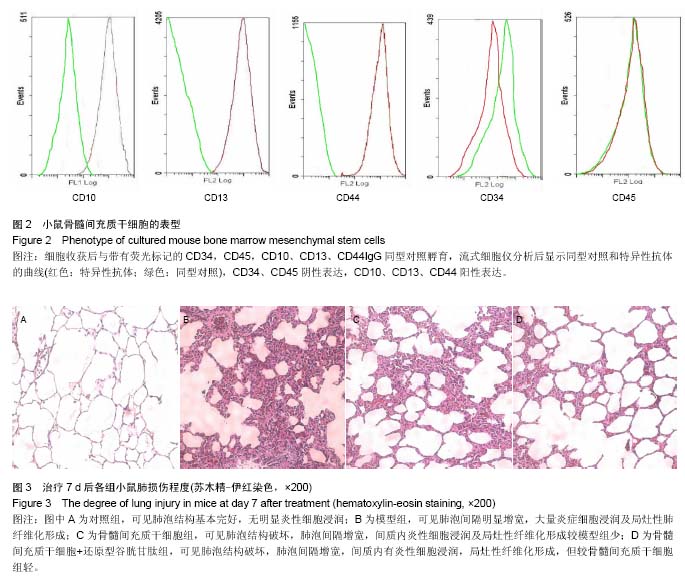
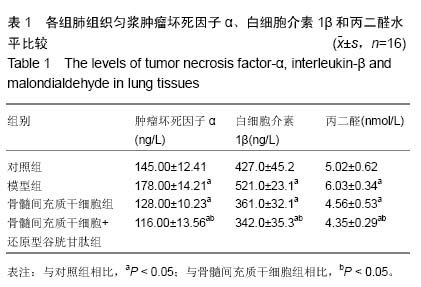
背景:大量实验证明骨髓间充质干细胞治疗肺部疾病或改善肺损伤方面具有良好的效果,其治疗作用主要以减少炎性反应为主。 目的:观察骨髓间充质干细胞移植联合还原型谷胱甘肽对博来霉素诱导的小鼠肺损伤的保护效果。 方法:取1只雄性NOD/SCID小鼠制备骨髓间充质干细胞,并观察其形态、表型。将64只雌性NOD/SCID小鼠按随机数字表法分为对照组、模型组、骨髓间充质干细胞组和骨髓间充质干细胞+还原型谷胱甘肽组,每组16只。对照组气管内注入生理盐水,模型组气管内注入博来霉素,骨髓间充质干细胞组气管内注入博来霉素2 h后尾静脉内注入培养的骨髓间充质干细胞,骨髓间充质干细胞+还原型谷胱甘肽组气管内注入博来霉素2 h后尾静脉注入培养的骨髓间充质干细胞与还原型谷胱甘肽,7 d后处死动物,按照试剂盒说明测定肺组织匀浆肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β、丙二醛水平,同时留取肺组织进行病理检查,确认骨髓间充质干细胞联合还原型谷胱甘肽对肺损伤的保护效果。 结果与结论:雄性小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞呈上皮细胞样,其CD34、CD45阴性表达,CD10、CD13、CD44阳性表达。雌性小鼠中,与对照组相比,模型组肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β及丙二醛水平上升,骨髓间充质干细胞组和骨髓间充质干细胞+还原型谷胱甘肽组肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β及丙二醛水平下降(P < 0.05),骨髓间充质干细胞+还原型谷胱甘肽组较骨髓间充质干细胞组下降更明显(P < 0.05)。病理切片显示,骨髓间充质干细胞+还原型谷胱甘肽组肺损伤较模型组及骨髓间充质干细胞组轻。以上结果表明骨髓间充质干细胞联合还原型谷胱甘肽能更有效保护博来霉素诱导的肺损伤。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号: