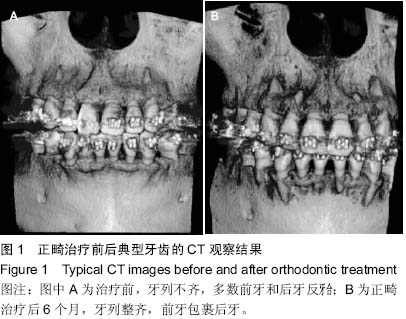
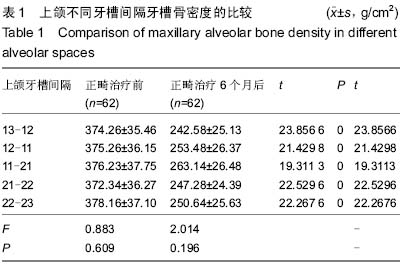
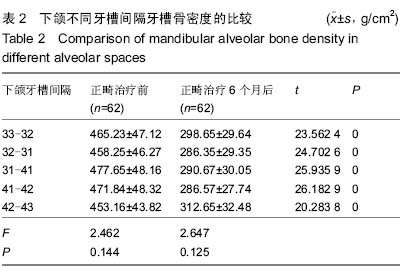
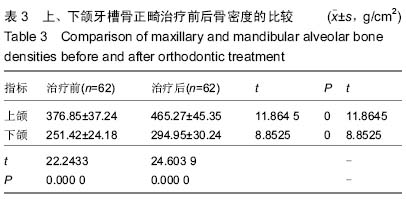
| [1] 陈燕芳.40例牙周病应用正畸治疗的疗效分析[J].当代医学,2011, 17(11):114-115.
[2] 高慧,王旭霞,张君.正畸在牙周病治疗中的应用及其效果的评价[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2011,21(12):725-728.
[3] 宗敏,方冬冬,高慧,等.正畸-牙周联合治疗中重度牙周炎早期牙周状况及龈沟液骨钙素水平变化的研究[J].山东大学学报,2012, 50(1):113-116.
[4] Zafiropoulos GG,di Prisco MO,Deli G,et al.Maintenance after a complex orthoperio treatment in a case of generalized aggressive periodontitis:7-year result.Int Acad Periodontol. 2010;12(4):112-122.
[5] Gkantidis N,Christou P,Topouzelis N.The orthodontic- periodonticinterrelationship in integrated treatment challenges: a systematic review.J Oral Rehabil.2010; 37(5):377-390.
[6] Yan Gu,James A,McNamara Jr,et al.Comparison of craniofacial characteristics of typical Chinese and Caucasian young adults.Eur J Orthod.2011;33(2):205-211.
[7] Thilander B,Pena L,Infante C,et al.Prevalence of malocclusion and orthodontic treatment need in children and adolescents in Bogota, Colombia .An epidemiological study related to different stages of dental development.Eur J Orthod. 2011;23(2):153-167.
[8] 段银钟.口腔TH畸临床拔牙矫治指南[M].北京:人民军医出版社, 2011:3.
[9] 陈云,王旭霞,高慧,等.牙周病正畸与普通正畸患者错牙合类型的比较[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2014,24(8):473-475.
[10] 陈扬熙.口腔正畸学:基础、技术与临床[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2012,661.
[11] 王建宁,张玉杰,肖水清.正畸对龈沟液中细菌微生态及碱性磷酸酶活性影响的研究[J].口腔医学,2011,31(9):531-535.
[12] Dinoi MT,Lacarbonara M,Dimartino S,et al.Periodontal probing of an impacted tooth recovered through a surgical-orthodontic approach: a case report.J Med Case Rep.2014;8:25.
[13] 黄烈平,黄宁,邓晓姝,等.唇腭裂患者牙槽突裂植骨术前使用半固定式四眼圈簧扩大上牙弓的正畸治疗[J].华西口腔医学杂志, 2012, 30(4):393-395.
[14] 李松泽,支方静,巫家晓,等.单侧完全性唇腭裂植骨术与正畸联合治疗12例分析[J].广西医科大学学报,2012,29(1):115-116.
[15] Kurth JR,Kokich VG.Open gingival embrasures after orthodontic treatment in adults: prevalence and etiology.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop.2001;120(2):116-123.
[16] Ghijselings E,Coucke W,Verdonck A,et al.Long-term changes in microbiology and clinical periodontal variables after completion of fixed orthodontic appliances.Orthod Craniofac Res.2014;17(1):49-59.
[17] Ireland AJ,Soro V,Sprague SV.The effects of different orthodontic; appliances upon microbial communities Orthod Craniofa Res.2014;17(2):115-123.
[18] Eid HA,Assiri HA,Kandyala R,et al.Gingival enlargement in different ale groups during fixed orthodontic treatment.Int Oral Health.2014;6(1):1-4.
[19] Joo JY,Kwon EY,Lee JY.Intentional passive eruption combined with scaling and root planing of teeth with moderate chronic periodontitis and traumatic occlusion.J Periodontal Implant Sci.2014;44(1):20-24.
[20] Holberg C,Winterhalder P,Holberg N,et al.Orthodontic; bracket debonding:risk of enamel fracture.Clin Oral Invest. 2014;18(1):327-334.
[21] Evren AD,Nevzatoglu S,Arun T,et al.Periodontal status of ec;topic;canines after orthodontic;treatment.Angle Orthod. 2014;84(1):18-23.
[22] Konstantinova D,Arnautska H.Orthodontic-prosthetic; approach in the treatment of complex clinical case.J IMAB. 2014;20(1):469-472.
[23] Hazan-Molina H,Levin L,Einy S,et al.Aggressive periodontitis diagnosed during or before orthodontic treatment.Acta Odontol Scand.2013;71(5):1023-1031.
[24] 张莉,王博,房兵.骨性Ⅲ类错牙合下前牙区牙槽骨形态的锥形束CT分析[J].中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2012,10(1):38-41.
[25] 王留宏,张冬林,娄新田,等.口腔正畸矫治牙槽突植骨术后唇腭裂临床疗效观察[J].河北医学,2015,21(1):144-146.
[26] Good PM,Mulliken JB,Padwa BL.Frequency of Le Fort I osteotomy after repaired cleft lip and palate or cleft palate.Cleft Palate Craniofac J.2007;44(4):396-401.
[27] 郭奕,陈晶晶,彭诚,等.活动翼矫治器治疗内倾型深覆患者的效果评价[J].天津医药, 2014,42(10):1032-1036.
[28] 王钟华,常新.骨性安氏Ⅲ类伴偏颌畸形术前术后正畸治疗1例[J].大连医科大学学报, 2014,36(2):198-201.
[29] Ellore VP,Ramagoni NK,Taranatha M,et al.Pre: Surgical orthopedic pre-maxillary alignment in bilateral cleft lip and palate patient.Contemp Clin Dent.2012;3(3):359-362.
[30] 王谋,张定铭,冯刚,等.锥形束CT测量单侧后牙正锁牙合髁突的体积和表面积[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(13):2358-2361.
[31] 舒林径,薛俊杰,王璟,等.减阻牵张成骨远移尖牙的三维有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(11):1749-1754.
[32] Turkyilmaz I,Tozum TF,Tumer C. Bone density assessments of oral implant sites using computerized tomography. J Oral Rehabil.2007;34(17):267-272.
[33] Park HS, Lee YJ, Jeong SH. Density of the alveolar and basal bones of the maxilla and the mandible. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop.2008;133(21):30-37. |