中国组织工程研究 ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (14): 2544-2551.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.14.011
• 干细胞移植 stem cell transplantation • 上一篇 下一篇
血管成形与脐带干细胞移植治疗糖尿病足:3个月血管造影评价
秦汉林1,贺克武1,高 斌1,季亚莉2,黄永翠2,王胜琴2,胡国平2,周学勇2
- 1合肥市第一人民医院介入科,安徽省合肥市 236001
2安徽省血液中心,安徽省合肥市 236001
-
收稿日期:2012-10-25修回日期:2012-11-29出版日期:2013-04-02发布日期:2013-04-02 -
通讯作者:高斌,主任医师,主要从事外周血管病介入治疗。合肥市第一人民医院介入科,安徽省合肥市 236001 -
作者简介:秦汉林★,男,1983年生,安徽省利辛县人,汉族,2011年徐州医学院毕业,硕士,主治医师,主要从事外周血管病介入治疗方面的研究。 -
基金资助:安徽省科技厅年度计划项目(09020303043)。
Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation combined with angioplasty for diabetic foot: 3 months angiographic evaluation
Qin Han-lin1, He Ke-wu1, Gao Bin1, Ji Ya-li2, Huang Yong-cui2, Wang Sheng-qin2, Hu Guo-ping2, Zhou Xue-yong2
- 1 Department of Interventional Radiology, First People’s Hospital of Hefei City, Hefei 230061, Anhui Province, China
2 Blood Center of Anhui Province, Hefei 236001, Anhui Province, China
-
Received:2012-10-25Revised:2012-11-29Online:2013-04-02Published:2013-04-02 -
Contact:Gao Bin, Chief physician, Department of Interventional Radiology, First People’s Hospital of Hefei City, Hefei 230061, Anhui Province, China gaobinrm@hotmail.com -
About author:Qin Han-lin★, Master, Attending physician, Department of Interventional Radiology, First People’s Hospital of Hefei City, Hefei 230061, Anhui Province, China qinhanlin18@sina.com -
Supported by:Annual Planning Project of Anhui Science and Technology Department, No. 09020303043
摘要:
背景:目前对糖尿病继发肢体动脉闭塞尚无有效的药物治疗,最终多导致截肢,预后很差。 目的:以血管成形联合人脐带间充质干细胞移植治疗糖尿病足,3个月后行血管造影评价效果。 方法:确诊症状严重伴有下肢动脉不同程度病变的Fontain Ⅳ期糖尿病足40例52条患肢,对照组12例患者18条患肢给予单纯介入治疗,实验组28例34条患肢给予介入联合人脐带间充质干细胞经导管灌注及溃疡周围注射治疗,随访3个月。 结果与结论:治疗后患肢冷感、疼痛、麻木等临床症状持续改善,患肢皮温、踝肱指数值及跛行距离均增加。治疗3个月后复查造影,新生血管增多,溃疡逐渐愈合或缩小,输注前后未出现严重并发症和不良反应。说明采用血管成形联合人脐带间充质干细胞移植治疗糖尿病足,方法可行、安全,近期疗效满意。
中图分类号:
引用本文
秦汉林,贺克武,高 斌,季亚莉,黄永翠,王胜琴,胡国平,周学勇. 血管成形与脐带干细胞移植治疗糖尿病足:3个月血管造影评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2013, 17(14): 2544-2551.
Qin Han-lin, He Ke-wu, Gao Bin, Ji Ya-li, Huang Yong-cui, Wang Sheng-qin, Hu Guo-ping, Zhou Xue-yong. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation combined with angioplasty for diabetic foot: 3 months angiographic evaluation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(14): 2544-2551.
Changes in the number of participants (Table 1)
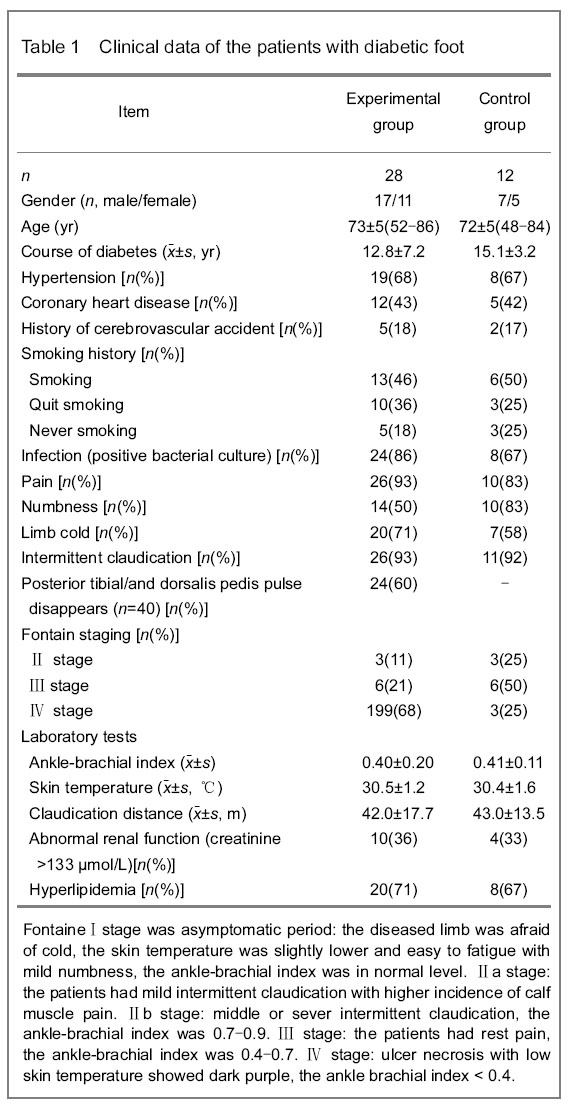
All the patients with diabetic foot were included in the final analysis without any loss, including 28 patients (34 limbs) in the experimental group, and 12 patients (18 limbs) in the control group.
Among the 40 patients (52 limbs), 84 diseased vessels below the knee joint were observed, including 28 patients (34 limbs) in the experimental group and 12 patients (18 limbs) in the control group. Stenosis was observed in 67 vessels and occlusion in 17 vessels. The success rate of percutaneous transluminal angioplasty was 82%(69/84), the success rate for the treatment of stenosis was 88%(59/67), and the success rate for the treatment of occlusion was 59%(10/17). The foot blood supply was improved and the collateral vessels were increased on the review contrast image at 2 months after treatment when compared with those before treatment.
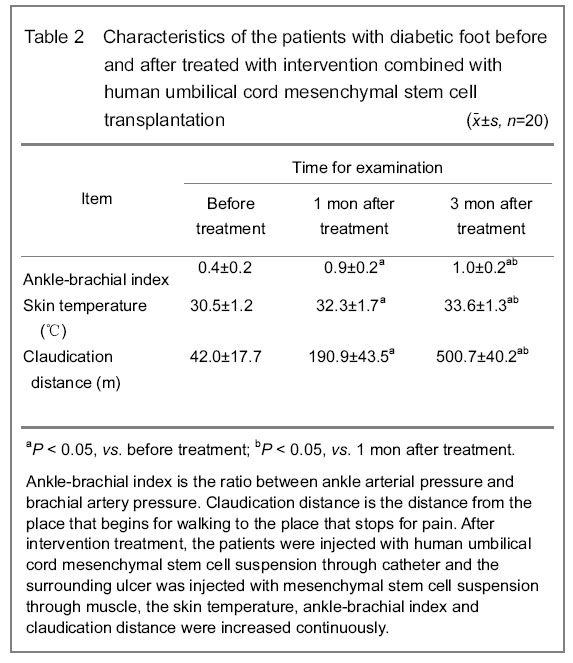
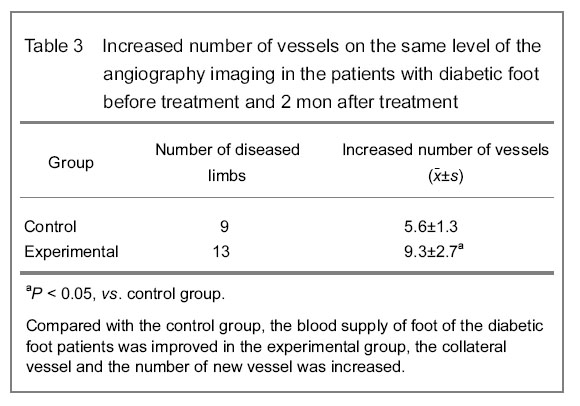
After intervention treatment, 28 patients (34 limbs) injected with human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell suspension through catheter, and the surrounding ulcer was injected with mesenchymal stem cell suspension through muscle, the skin temperature was increased and the coldness of diseased limb was improved. The ankle-brachial index, skin temperature and the claudication distance were improved continuously (P < 0.05). Angiography at 3 months after treatment showed the vessel count in the same level was increased when compared with that before treatment (P < 0.05). Among the 16 cases in the Fontaine Ⅳ stage, the ulcers of 12 cases were healed in 3 months; two cases had smaller ulcer area and one case (one limb) failed due to the popliteal artery long occlusion, and the two cases had dry gangrene of left foot with severe infections and treated with knee amputation; the other one case had amputation at 6 weeks after transplantation because of severe foot gangrene accompanied with infection, and the amputation at 6 weeks after treatment could decrease the amputation surface and keep the heel. The review angiography at 2 months after treatment showed the foot blood supply was improved, the number of collateral vessel was increased and number of new vessel in the experimental group wad larger than that in the control group (P < 0.05) (Table 3).
Angiography in one patient during the intervention treatment showed contrast extravasation, and it was considered to be caused by the perforation of blood vessels with guidewire. The operation was terminated to open other blood vessels according to the speed and the amount contrast agent exudation. Angiography again after 1 hour, the bleeding was stopped. Three cases (five limbs) had pain, and the symptoms disappeared after symptomatic treatment for 4-12 hours. No hematoma, pseudoaneurysm, arterial dissection or complications of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular accident were observed at puncture site.
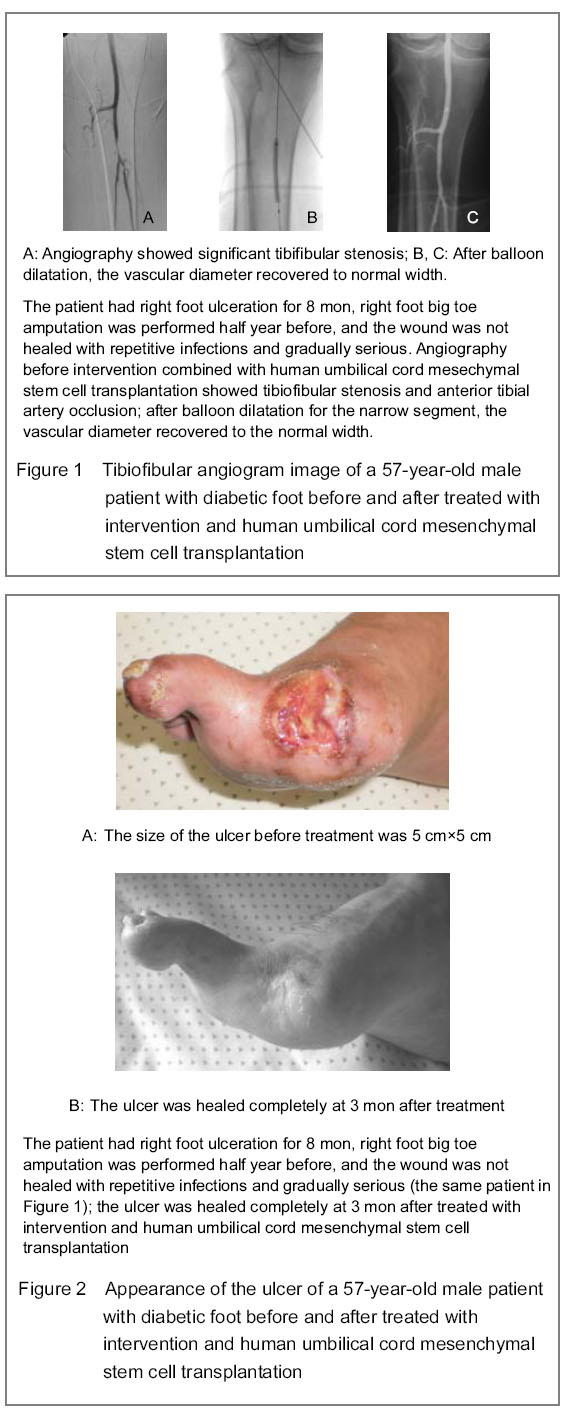
A 57-year-old male patient, dry mouth, polydipsia, emaciation for 9 years, and had a history of chronic myelitis for 5 years, and lie on bed for years basically; right foot ulceration for 8 months, right foot big toe amputation was performed half year before, and the wound was not healed, repetitive infections and gradually serious. Angiography before intervention combined with human umbilical cord mesechymal stem cells transplantation showed tibiofibular stenosis and anterior tibial artery occlusion; after balloon dilatation for the narrow segment, the vascular diameter recovered to the normal width (Figures 1, 2).
| [1] Apelqvist J, Bakker K, van Houtum WH, et al. Practical guidelines on the management and prevention of the diabetic foot: based upon the International Consensus on the Diabetic Foot (2007) Prepared by the International Working Group on the Diabetic Foot. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2008;24 Suppl 1:S181-187.[2] Fang C, Li MH, Cheng YS, et al. Clinical effect and necessity of interventional treatment in diabetic foot before and after amputation. Jieru Fangshe Xue Zazhi. 2006; 15(7): 390-392.[3] Liu CW, Shao J, Liu B, et al. A clinical study of infrapopliteal balloon angioplasty for patients with critical lower limb ischemia. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2010;48(4):253-256.[4] Qian RL. New criteria of diagosis and typing of diabetes mellitus. Linchuang Neike Zazhi. 2000;17(3):5-6.[5] Wang SM, Li XX. Peripheral Vascular Interventional Treatment. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House. 2010:336.[6] Gao YS, Li JQ, Yang YG. Application of percutaneous transluminal angioplasty(PTA) in treatment of Infragenual artery occlusive diseases for diabetes patients. Zhongguo Jieru Yingxiang yu Zhiliao Xue. 2008;5(5):389-391. [7] Sumpio BE, Lee T, Blume PA. Vascular evaluation and arterial reconstruction of the diabetic foot. Clin Podiatr Med Surg. 2003;20(4):689-708.[8] Tepper OM, Galiano RD, Capla JM, et al. Human endothelial progenitor cells from type II diabetics exhibit impaired proliferation, adhesion, and incorporation into vascular structures. Circulation. 2002;106(22):2781-2786.[9] Fan MS, Yang XF, Wu YX, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells transplantation improves lower limb ischemia of diabetic rabbits. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011;15(1):33-36.[10] Adam DJ, Beard JD, Cleveland T, et al. Bypass versus angioplasty in severe ischaemia of the leg (BASIL): multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2005; 366(9501):1925-1934.[11] Li SQ, Jiang GM, Zhao JW, et al. Inferior knee arterial endoluminal angioplasty in treating severe lower limb ischemia though the DEEP balloon catheter. Jieru Fangshe Xue Zazhi. 2008;17(12):858-861.[12] Schillinger M, Sabeti S, Loewe C, et al. Balloon angioplasty versus implantation of nitinol stents in the superficial femoral artery. N Engl J Med. 2006;354(18): 1879-1888.[13] Ziegelhoeffer T, Fernandez B, Kostin S, et al. Bone marrow-derived cells do not incorporate into the adult growing vasculature. Circ Res. 2004;94(2):230-238. [14] Scheinert D, Ulrich M, Scheinert S, et al. Comparison of sirolimus-eluting vs. bare-metal stents for the treatment of infrapopliteal obstructions. EuroIntervention. 2006;2(2): 169-174.[15] Carbayo JA, Divisón JA, Escribano J, et al. Using ankle-brachial index to detect peripheral arterial disease: prevalence and associated risk factors in a random population sample. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2007; 17(1):41-49. [16] Aquino R, Johnnides C, Makaroun M, et al. Natural history of claudication: long-term serial follow-up study of 1244 claudicants. J Vasc Surg. 2001;34(6):962-970.[17] Yang JG, Wang JQ, Li J. Guidelines of Peripheral Arterial Disease Treatment. Shanghai: Tongji University Press. 2006:42.[18] Pearson TA. New tools for coronary risk assessment: what are their advantages and limitations? Circulation. 2002; 105(7):886-892.[19] Zhong H, Xu ZD, Liu C, et al. The optimal injection rate and reconstruction matrix study of CT arteriography for lower limb artery by 64-slice CT. Zhongguo Yixue Yingxiang Jishu. 2005;21(10):1569-1571.[20] Faglia E, Dalla Paola L, Clerici G, et al. Peripheral angioplasty as the first-choice revascularization procedure in diabetic patients with critical limb ischemia: prospective study of 993 consecutive patients hospitalized and followed between 1999 and 2003. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2005; 29(6):620-627. [21] Gu YQ, Zhang J, Yu HX, et al. Infrapopliteal artery endoluminal angioplasty for the treatment of severe limb ischemia. Zhonghua Putong Waike Zazhi. 2007;22(2): 123-125. |
| [1] | 蒲 锐, 陈子扬, 袁凌燕. 不同细胞来源外泌体保护心脏的特点与效应[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | 周继辉, 李新志, 周 游, 黄 卫, 陈文瑶. 髌骨骨折修复内植物选择的多重问题[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [3] | 张秀梅, 翟运开, 赵 杰, 赵 萌. 类器官模型国内外数据库近10年文献研究热点分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [4] | 王正东, 黄 娜, 陈婧娴, 郑作兵, 胡鑫宇, 李 梅, 苏 晓, 苏学森, 颜 南. 丁酸钠抑制氟中毒可诱导小胶质细胞活化及炎症因子表达增多[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [5] | 汪显耀, 关亚琳, 刘忠山. 提高间充质干细胞治疗难愈性创面的策略[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [6] | 万 然, 史 旭, 刘京松, 王岩松. 间充质干细胞分泌组治疗脊髓损伤的研究进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1088-1095. |
| [7] | 廖成成, 安家兴, 谭张雪, 王 倩, 刘建国. 口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞的治疗靶点及应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1096-1103. |
| [8] | 谢文佳, 夏天娇, 周卿云, 刘羽佳, 顾小萍. 小胶质细胞介导神经元损伤在神经退行性疾病中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1109-1115. |
| [9] | 李珊珊, 郭笑霄, 尤 冉, 杨秀芬, 赵 露, 陈 曦, 王艳玲. 感光细胞替代治疗视网膜变性疾病[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1116-1121. |
| [10] | 焦 慧, 张一宁, 宋雨晴, 林 宇, 王秀丽. 乳腺癌类器官研究进展及临床应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128. |
| [11] | 王诗琦, 张金生. 中医药调控缺血缺氧微环境对骨髓间充质干细胞增殖、分化及衰老的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [12] | 曾燕华, 郝延磊. 许旺细胞体外培养及纯化的系统性综述[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [13] | 孔德胜, 何晶晶, 冯宝峰, 郭瑞云, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, 吕 飞, 张舒涵, 张晓琳, 马 隽, 崔慧先. 间充质干细胞修复大动物模型脊髓损伤疗效评价的Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [14] | 侯婧瑛, 于萌蕾, 郭天柱, 龙会宝, 吴 浩. 缺氧预处理激活HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA通路促进骨髓间充质干细胞生存和血管再生[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [15] | 史洋洋, 秦英飞, 吴福玲, 何 潇, 张雪静. 胎盘间充质干细胞预处理预防小鼠毛细支气管炎[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
Comparative clinical observation in the same period.
The experiment was completed in the Department of Interventional Radiology and Department of Endocrinology, First People’s Hospital of Hefei City and the Blood Center of Anhui Province from March 2010 to October 2011.
The patients with diabetes accompanied with lower extremity artery stenosis or occlusion who were treated in the Department of Interventional Radiology and Department of Endocrinology, First People’s Hospital of Hefei City from April 2009 to December 2010 were collected. Diagnostic criteria: Coincidence with the standard of type 2 diabetes proposed by the World Health Organization in 1999[4]. Inclusion criteria: The patients that met the diagnostic criteria; met the diagnostic criteria of diabetic foot; met the Ⅱ-Ⅳ phase of Fontain staging[5]; patients with lower extremity artery stenosis or occlusion confirmed through color Doppler ultrasound or angiography; the patients and their families have been informed and consented with the process and the purpose of the experiment. Exclusion criteria: Patients with acute complications of diabetic ketoacidosis or hyperosmolar coma; patients combined with renal dysfunction; patients combined with hypercortisolism, thyroid dysfunction and other endocrine system disorders; patients accompanied with tumors and tumor-like lesions. Finally, 40 patients (52 limbs) with diabetic foot were selecting, including 24 males and 16 females. The age was 48-86 years old, averaged in (73±5) years. The course was 1-30 years and the median course was 16.5 years. Twelve cases were treated with simple percutaneous angioplasty, and 28 cases were treated with percutaneous angioplasty combined with human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell infusion. All the patients received lower limbs vascular Doppler ultrasound, limb ankle-brachial index, detailed clinical history review and physical examination.
Experimental group and control group
The patients were divided into experimental group and control group according to their willingness, and treated with intervention combined with human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell infusion and simple intervention therapy, respectively.
The relative examination, such as the lower limbs vascular Doppler ultrasound, electrocardiogram, echocardiography, blood routine, coagulation function, blood biochemistry and electrolyte examinations were improved. After admission, the patients received intravenous infusion of Shenxiong glucose injection (Guizou Yi Bai) to improve the microcirculation, then the patients received oral administration of 75 mg/d clopidogrel (Plavix, Sanofi-Aventis, Hangzhou) at 3 days (at least 1 day) before operation, and changed for oral administration of 150 mg clopidogrel at 1 hour before operation. The indicators of blood glucose, blood lipids, blood pressure and heart function were improved to the normal levels or close to normal levels. Changed the dressing and received anti-inflammatory treatment when ulcer infection appeared.
The human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell suspension was prepared by the Blood Center of Anhui Province, including collection, preservation and pre-processing of umbilical cord, cell culture,amplification, cryopreservation and recovery. Each mesenchymal stem cell suspension contained 4.8×107-8.6×107 cells, and the cells were preserved at 4 ℃after recovery. The treatment was completed in 2 hours.
The femoral artery on the affected side was treated with routine antegrade puncture after local anesthesia, and
for the patients had failure puncture due to long segment femoral artery occlusion, the contralateral femoral artery retrograde puncture was preferred. Introduced under the guidance of guidewire to support the polysheath to the iliac, femoral artery of the affected side, then 3 000-4 000 U heparin was intravenously injected for whole body heparinization, and 1 000-2 000 U heparin were added additional according to the length of operation time. 4F Cr catheter was implanted for contrast examination, then 0.889 mm soft or hard super-smooth guidewire (Terumo Corporation of Japan) was implanted through the lesion segment. For the blood vessels had long segment occlusion (> 3 cm), usually the head of the guidewire should be bent into a “U”-shape or went through the bilateral femoral arteries in the same time. When the guidewire and catheter went through blood vessels of the lesion segment and confirmed in the true lumen, the guidewire was changed into the hard super-smooth guidewire, and then treated with simple balloon dilatation or stent implantation after expansion according to the different parts of the lesions. After covered the lesions by the balloons (deep high-pressure balloon, Invatec) with different diameters (1.5-4.0 mm) and lengths (10-12 cm), the lesions were gradually pressurized expanded with pressure pump, the lesions were pressurized with 4.04×105-10.10×105 for 3-5 minutes usually, re-expanded once every 5 minutes. Self-expanding vascular stent was implanted when the vascular stenosis greater than 30%, severe mural thrombus or coronary dissection appeared after iliac, femoral and popliteal arteries dilatation. Generally, the stent would not to be implanted on the anterior tibial, posterior tibial and peroneal artery. For the adjacent multiple short segment stenosis, the long balloon was preferred for forming by one step. The order of multi-stage expansion should be changed from distal to proximal and treated from light to serious, from main branch to branch according to degree of vascular lesions; the long lesions could be divided into multi-segments and expanded from distal to proximal, and then overlapped with the segment expanded previously for 1 cm. The purpose of percutaneous transluminal angioplasty/or stet therapy was try to reconstruct the three vascular vessels below the knee joint, and the vessel angiography should be displayed below the ankle, outflow tract was the prerequisite. Angiography again after treatment to confirmed patency of vessels, and to observe whether there was contrast agent extravasation. The number of vessels on the same contrast level was reviewed before treatment and at different time points within 2 months after treatment.
Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell infusion
The catheter tip was retained in the knee level after intervention treatment, and thighed with a rubber band in 1/3 of the junction part to ligate the limb and to slow down the return rate of the stem cells, then released at 3-5 minutes after stem cell infusion. The stem cell suspension was slowly injected into the catheter with a syringe and asked whether the patients had discomfort when injecting. After injection, the catheter was washed through injecting the heparin water into the catheter with the 1/2 volume of stem cells. Then the knee joint was disinfected with povidone-iodine for three times, and the ulcer wound was washed with hydrogen peroxide for three times and covered with sterile drapes. The human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell suspension was injected into the diseased limb from multi-point, 0.5-1.0 mL in each point, interval injected in 3 cm×3 cm×3 cm; the part with rich muscles was stratified injected and focused injection in the surrounding ulcers. According to the different numbers of stem cells, the patients were injected with stem cells ranged from 4.8×107-8.6×107.
After intervention treatment, the angiography revealed vascular residual stenosis in the lesion segment was less than 30% of the reference vessel diameter; for the lesion vessles below the knee joint, when the vascular local stenosis of at least one of the anterior tibial or posterior tibial artery was less than 30%, and there was blood flow that directly reached to the ankle-foot, at this time, the surgery could be considered success[5].
Conventional hemostasis was performed on the puncture point for 20-30 minutes, then pressure dressed with elastic bandage. After back to the ward, the patients were subcutaneously injected with low molecular weight heparin 5 000 U per time, injected every 12 hours and lasted for 3 days. The patients received oral administration of clopidogrel 75 mg/d for 6 months, and after that, the patients began to take aspirin or (and) warfarin sodium for life. The platelet count and prothrombin time were regularly monitored. The patients had local ulcers that were regularly debrided and dressed.
The local cool-feeling, intermittent claudication distance, rest pain and ulcer healing were observed, the limb skin temperature and ankle-brachial index were measured. All the patients were followed-up at 1-3 months after infusion.
The skin temperature, ankle-brachial index and intermittent claudication distance, as well as the number of vessels in the same contrast level.
The measurement data were presented with mean±SD, and the statistical software SPSS 13.0 was used for analyzing and processing, the difference between two time points was compared with paired t-test. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Most of the patients with diabetic foot are elderly, whom have less stem cells, and poor proliferative potential, adhesion and angiogenesis capacity[8]. The animal experiments confirmed that the human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells could participate in the generation of new blood capillaries in the patients with diabetic lower extremity vascular disease[9], and the number of limb collateral vessels and new blood vessels was increased. Balloon dilatation and stent implantation during intervention as a means of revascularization for the treatment of diabetic peripheral vascular disease is a new technology developed in recent years[10]. For the elderly patients with more complications, high surgical risk or surgical contraindications, intervention treatment can promote foot revascularization and collateral circulation formation with significant short-term effect, and the intervention treatment has the advantages of less trauma, strong repeatability and few complications[3, 11]. Prospective study abroad found that the effect of self-expanding stent implantation for the treatment of femoropopliteal artery stenosis or occlusive disease was better than that of percutaneous angioplasty[12]. The patients included in the experiment mostly suffered below-knee vascular disease, stenosis degree of only one case of femoral artery lesions is still greater than 30% after balloon dilation, and treated with stent implantation. According to the range of the lesions, balloon with suitable length was used to perform the balloon angioplasty for stenosis or occlusion lesions, and for the treatment of unique multi-segment and long distance stenosis or occlusion of diabetic lower extremity vascular disease, long balloon was preferred for angioplasty[13]. However, percutaneous angioplasty is difficult to operate for below-knee microvascular disease, and has high restenosis rate for the opened vessels. It is reported that the percentage of restenosis at 6 months after percutaneous angioplasty (stenosis > 50%) is nearly 30%[14]. As restenosis is a gradual process, the limb blood supply can be improved rapidly after angioplasty, and with the formation of restenosis, the limbs collateral circulation is also come to establish compensatory after combined with human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation, which save time for the healing of the foot ulcer. Angioplasty combined with stem cell infusion has great promotion and magnifying effect on limb angiogenesis and collateral circulation formation[10].
Claudication distance is the distance from the place that begins for walking to the place that stops for pain, and it is a main clinical manifestation of lower limb ischemia with certain subjectivity[15]. Skin temperature of the lower limbs can reflect lower extremity arterial stenosis to some extent. In the general population, ankle-brachial index has a great diagnostic value for peripheral artery disease[16-17]. As a non-invasive examination method, the ankle-brachial index is widely used to evaluate the degree of lower limb ischemia. However, because of the ankle-brachial index can reflect the blood perfusion of lower extremity arterial, and not sensitive to reflect improvement of collateral circulation that cannot reflect the improvement of the peripheral circulation[18]. The combination of three indicators can better evaluate the effect of intervention and human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation from the subjective and objective aspects. The increasing of the collateral vessels of the diseased limb from the review angiography is the gold standard to evaluate the improvement of lower limb blood supply[19]. But a significant proportion of patients cannot accept the invasive therapy.
The 28 patients (34 limbs) included in this experiment received angioplasty and human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell infusion. The femoropopliteal lesions with stenosis degree more than 30% after balloon dilatation were treated with stent implantation, and the vascular lesions below the knee joint were only treated with balloon dilatation. The patients received transcatheter infusion and intramuscular injection of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells around the ulcer, and most of the patients had foot pain relief, increased skin temperature, improved skin color and increased ulcer exudate at 1 week after infusion. At this time, the new blood vessels have not yet formed, so it may due to the improvement of local blood circulation after percutaneous angioplasty; the infused stem cells can secrete a variety of cytokines and interleukin which lead to partial aseptic inflammatory reaction, vascular dilatation, skin temperature increasing. At 3 months after treatment, the review angiography showed that the number of blood vessels in the same level was increased when compared with that before hospitalization; the ankle-brachial index, skin temperature and claudication distance were increased when compare with those before hospitalization and 1 month after treatment. The changes above may relate with follows: the blood vessels without retwnosis after the local blood circulation improved with percutaneous angioplasty; the chemotaxis, proliferation and differentiation of infused stem cells into the vascular endothelial cells, and the ultimate formation of new blood vessels on the distal end of the blocked artery which can increase the blood supply for the ischemia tissue. The effect of the later reason was considered as the main effect, because with the time prolonging, major arterial might suffered restenosis in varying degrees, and the differentiation of stem cells can promote the angiogenesis, thus provide blood to the ischemia part by newborn collateral circulation. With the improvement of the blood supply around the ulcer, the newborn granulation tissue could be seen in the surface of the ulcer and filled the ulcer gradually, which made the ulcer healed in 3 months. For the patients, the cost and the risk of amputation is not less than the intervention combined with stem cell infusion, and the intervention combined with stem cell infusion method can provide the opportunities of ischemia improvement, symptoms relief, and preservation of diseased limbs[20-21]. So, for the patients have no choice except amputation, intervention combined with stem cell infusion is the best method. Strict control of blood glucose and the application of microcirculation improvement and anti-platelet aggregation drugs combined with wound dressing, as well as other comprehensive treatments are contribute to recovery of ischemic tissue blood supply and tissue repairing. Ideally control of blood glucose will help to promote tissue repair of the diabetes patients, provide good external environment for the chemotaxis and proliferation and differentiation of stem cells, and thus improve the treatment effect.
1 人脐带间充质干细胞输注是近几年兴起的一种治疗缺血性糖尿病足的新方法,但经皮血管成形联合人脐带间充质干细胞治疗糖尿病足尚未见文献报道。 2 把干细胞输注与经皮血管成形联合起来,二者取长补短,既能开通大的狭窄或闭塞血管又能促进患肢小血管再生,从根本上改善微循环,进一步提高糖尿病足溃疡的愈合率。 基金项目: 安徽省科技厅年度计划项目(09020303043)。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||