| [1] Zuk PA ,Zhu M ,Mizuno H ,et al. Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue:implications for cell-based therapies. Tissue Eng.2001;7(2):211-228.[2] Gronthos S, Franklin DM, Leddy HA, et al. Surface proteincharacterization of human adipose tissue-derived stromal cells. J Cellular Physiology.2001;189:54-63.[3] Cousin B, Andre M, Arnaud E, et al. Reconstitution of lethally irradiated mice by cells isolated from adipose tissue. Biochemical Biophysical Res Communications. 2003,301: 1016-1022.[4] Wang Y, Chen GH, Shao J, et al.Shandong Daxue Xuebao:Yi Xue Ban.2005;43(7): 578-581.王燕,陈光辉,邵建,等.大鼠脂肪组织源性间充质干细胞的分离及向心肌细胞的诱导分化[J].山东大学学报:医学版,2005,43(7): 578-581.[5] Wickham MQ, Geoffrey RE, Jeffrey MG, et al. Multipotent stromal cells derived from the infrapatellar fat pad of the knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2003;412(7): 196-212.[6] Yang LY ,Liu XM ,Sun B ,et al.Zhonghua Shenjign Yixue Zazhi.2002;1(1):45-48. 杨立业,刘相名,孙兵,等. 脂肪组织源性基质细胞表达神经元表型的实验研究[J].中华神经医学杂志,2002,1(1):45-48. [7] Liang D ,Fan YG ,Wang HB ,et al .Guangzhou Zhongyiyao Daxue Xuebao.2009;26(4):412-418.梁笃,樊粤光,王海彬,等.成人脂肪来源干细胞定向诱导分化为软骨细胞的实验研究[J].广州中医药大学学报,2009,26(4): 412-418.[8] Sen A,Leacurrie YR,Sujkowska D,et al. Adipogenic potential of human adipose derived stromal cells from multiple donors is heterogeneous. J Cell Biochem.2001;81:312-319.[9] Lee JA,Parrett BM,Conejero JA,et al.Biological alchemy-engineering bone and fat from fat-derived stem cells.Ann Plast Surg.2003;50(6):610-710.[10] Halvorsen YD,Franklin D,Bond Al,et al. Extracellular matrix mineralization and osteoblast gene expression by human adipose tissue-derived stromal cells.Tissue Eng.2001;7(6): 729-741.[11] Li BG ,Zeng QT ,Wang HX ,et al.Zhonghua Qiguan Yizhi Zazhi.2006;27(3):142-144. 李宾公,曾秋棠,王红祥,等. 脂肪来源与骨髓来源的基质干细胞的比较[J]. 中华器官移植杂志,2006,27(3):142-144.[12] Zuk PA, Zhu M, Ashjian P,et al. Human adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2002;13(12): 4279-4295.[13] Lee JA,Parrett BM,Conejero JA,et al.Biological alchemy-engineering bone and fat from fat-derived stem cells.Ann Plast Surg.2003;50(6):610-710.[14] Ju XD ,Lou SQ ,Ma QJ ,et al.Gu Yu Guanjie Sunshang Zazhi. 2004;19(6):390-392.鞠晓东,娄思权,马庆军,等.脂肪间充质干细胞的成骨诱导分化[J].骨与关节损伤杂志,2004;19(6):390-392.[15] Caplan AL.Cartilage begets bone versus endochondral myelopoiesis.Clin Orthop Relat Res.1990;121(261):257-267.[16] Shimizu K,Ito A,Honda H.Mag-seeding of rat bone marrow stromal cells into porous hydroxyapatite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering.J Biosci Bioeng.2007;104(3):171-177.[17] Huang JI,Beanes SR,Zhu M,et al. Rat extramedullary adipose tissue as a source of osteo chondrogenic progenitor cells. Plast Reconstr Surg.2002;109(3):1033-1043.[18] Awad HA,Halvorsen YD,Gimble JM,et al.Effects of transforming growth factor beta1 and dexamethasone on the growth and chondrogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stromal cells.Tissue Eng.2003;9(6):1301-1312.[19] Hani A,David L.Autologous mesenchymal stem cells-mediated repair of tendon.Tissue Engineering,1999;5: 267-274.[20] Heng BC,Cao T,Lee EH.Directing stem cell differentiation into the chondrogenic lineage in vitro.Stem Cells.2004;22: 1152-1167.[21] Gao H ,Wang YL ,Yao YN ,et al.Zhongguo Quanke Yixue. 2011; 14(5B):1568-1571.高华,王玉玲,姚亚妮,等.脂肪来源干细胞体外成骨和成脂及成神经的诱导分化研究[J].中国全科医学,2011,14(5B):1568-1571.[22] Bochkov NP,Voronina ES,Kosyakova NV,et al.Chromosome variability of human multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. Bull Exp Biol Med.2007;143(1):122-126. |

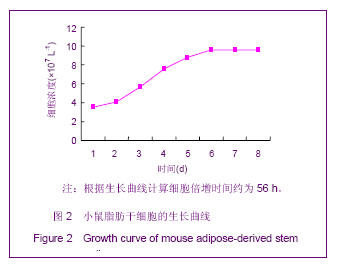
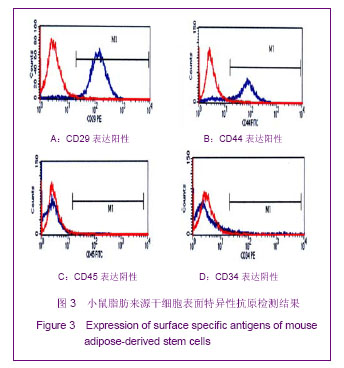
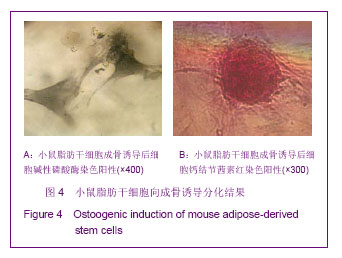
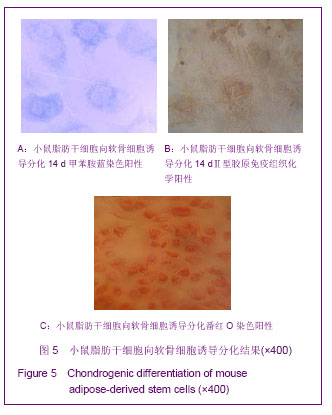
.jpg)