[1] MIGLIORINI F, MAFFULLI N, BARONCINI A, et al. Allograft versus autograft osteochondral transplant for chondral defects of the talus: systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Sports Med. 2022;50(12):3447-3455.
[2] MATIĆ S, VUČKOVIĆ Č, LEŠIĆ A, et al. Pedicled vascularized bone grafts compared with xenografts in the treatment of scaphoid nonunion. Int Orthop. 2021;45(4): 1017-1023.
[3] MAUFFREY C, BARLOW BT, SMITH W. Management of segmental bone defects. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2015;23(3):143-153.
[4] ZHANG Y, LIU X, ZENG L, et al. Tissue engineering: polymer fiber scaffolds for bone and cartilage tissue engineering. Adv Funct Mater. 2019;29(36):1970246.
[5] WANG C, HUANG W, ZHOU Y, et al. 3D printing of bone tissue engineering scaffolds. Bioact Mater. 2020;5(1):82-91.
[6] LEPPIK L, GEMPP A, KUÇI Z, et al. A new perspective for bone tissue engineering: human mesenchymal stromal cells well-survive cryopreservation on β-TCP scaffold and show increased ability for osteogenic differentiation. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(3):1425.
[7] HE J, CHEN G, LIU M, et al. Scaffold strategies for modulating immune microenvironment during bone regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;108:110411.
[8] ZHANG J, TONG D, SONG H, et al. Osteoimmunity-regulating biomimetically hierarchical scaffold for augmented bone regeneration. Adv Mater. 2022;34(36): e2202044.
[9] 孔祥宇,王兴,裴志伟,等.生物支架材料及打印技术修复骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(3):479-485.
[10] LU T, YUAN X, ZHANG L, et al. Enhancing osteoinduction and bone regeneration of biphasic calcium phosphate scaffold thought modulating the balance between pro-osteogenesis and anti-osteoclastogenesis by zinc doping. Mater Today Chem. 2023;29:101410.
[11] 赵豆豆,林开利.多细胞构建血管化组织工程骨在骨修复中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(27):4386-4392.
[12] CHEN R, HAO Z, WANG Y, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-immune cell interaction and related modulations for bone tissue engineering. Stem Cells Int. 2022; 2022:7153584.
[13] CHEN Z, XING F, ZHOU Y, et al. Integrated osteoimmunomodulatory strategies based on designing scaffold surface properties in bone regeneration. J Mater Chem B. 2023;11(29):6718-6745.
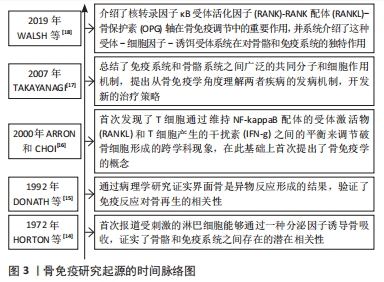
[14] HORTON JE, RAISZ LG, SIMMONS HA, et al. Bone resorbing activity in supernatant fluid from cultured human peripheral blood leukocytes. Science. 1972;177(4051): 793-795.
[15] DONATH K, LAASS M, GüNZL HJ.The histopathology of different foreign-body reactions in oral soft tissue and bone tissue. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1992;420(2):131-137.
[16] ARRON JR, CHOI Y. Bone versus immune system. Nature. 2000;408(6812):535-536.
[17] TAKAYANAGI H. Osteoimmunology: shared mechanisms and crosstalk between the immune and bone systems. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7(4):292-304.
[18] WALSH MC, TAKEGAHARA N, KIM H, et al. Updating osteoimmunology: regulation of bone cells by innate and adaptive immunity. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2018;14(3):146-156.
[19] CHEN Z, KLEIN T, MURRAY RZ, et al. Osteoimmunomodulation for the development of advanced bone biomaterials. Mater Today. 2016;19(6):304-321.
[20] TRINDADE R, ALBREKTSSON T, GALLI S, et al. Bone immune response to materials, Part II: copper and polyetheretherketone (PEEK) compared to titanium at 10 and 28 days in rabbit tibia. J Clin Med. 2019;8(6):814.
[21] CAI B, LIN D, LI Y, et al. N2-polarized neutrophils guide bone mesenchymal stem cell recruitment and initiate bone regeneration: a missing piece of the bone regeneration puzzle. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021;8(19):e2100584.
[22] KOVTUN A, MESSERER DAC, SCHARFFETTER-KOCHANEK K, et al. Neutrophils in tissue trauma of the skin, bone, and lung: two sides of the same coin. J Immunol Res. 2018;2018:8173983.
[23] ONO T, OKAMOTO K, NAKASHIMA T, et al. IL-17-producing γδ T cells enhance bone regeneration. Nat Commun. 2016;7:10928.
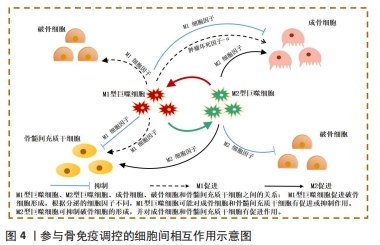
[24] NIU Y, WANG Z, SHI Y, et al. Modulating macrophage activities to promote endogenous bone regeneration: biological mechanisms and engineering approaches. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(1):244-261.
[25] MUñOZ J, AKHAVAN NS, MULLINS AP, et al. Macrophage polarization and osteoporosis: a review. Nutrients. 2020;12(10):2999.
[26] ZHAO M, DAI W, WANG H, et al. Periodontal ligament fibroblasts regulate osteoblasts by exosome secretion induced by inflammatory stimuli. Arch Oral Biol. 2019;105:27-34.
[27] GLASS GE, CHAN JK, FREIDIN A, et al. TNF-alpha promotes fracture repair by augmenting the recruitment and differentiation of muscle-derived stromal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108(4):1585-1590.
[28] OSTA B, BENEDETTI G, MIOSSEC P. Classical and paradoxical effects of TNF-α on bone homeostasis. Front Immunol. 2014;5:48.
[29] ZHA L, HE L, LIANG Y, et al. TNF-α contributes to postmenopausal osteoporosis by synergistically promoting RANKL-induced osteoclast formation. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;102:369-374.
[30] KANESHIRO S, EBINA K, SHI K, et al. IL-6 negatively regulates osteoblast differentiation through the SHP2/MEK2 and SHP2/Akt2 pathways in vitro. J Bone Miner Metab. 2014;32(4):378-392.
[31] WANG F, KONG L, WANG W, et al. Adrenomedullin 2 improves bone regeneration in type 1 diabetic rats by restoring imbalanced macrophage polarization and impaired osteogenesis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):288.
[32] LI T, PENG M, YANG Z, et al. 3D-printed IFN-γ-loading calcium silicate-β-tricalcium phosphate scaffold sequentially activates M1 and M2 polarization of macrophages to promote vascularization of tissue engineering bone. Acta Biomater. 2018;71:96-107.
[33] SPILLER KL, NASSIRI S, WITHEREL CE, et al. Sequential delivery of immunomodulatory cytokines to facilitate the M1-to-M2 transition of macrophages and enhance vascularization of bone scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2015;37:194-207.
[34] SCHLUNDT C, EL KHASSAWNA T, SERRA A, et al. Macrophages in bone fracture healing: their essential role in endochondral ossification. Bone. 2018;106:78-89.
[35] PAJARINEN J, LIN T, GIBON E, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-macrophage crosstalk and bone healing. Biomaterials. 2019;196:80-89.
[36] WANG Y, SMITH W, HAO D, et al. M1 and M2 macrophage polarization and potentially therapeutic naturally occurring compounds. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;70:459-466.
[37] GORDON S.Alternative activation of macrophages. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003;3(1): 23-35.
[38] FERRANTE CJ, LEIBOVICH SJ. Regulation of macrophage polarization and wound healing. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2012;1(1):10-16.
[39] RŐSZER T. Understanding the mysterious M2 macrophage through activation markers and effector mechanisms. Mediators Inflamm. 2015;2015:816460.
[40] KRZYSZCZYK P, SCHLOSS R, PALMER A, et al. The role of macrophages in acute and chronic wound healing and interventions to promote pro-wound healing phenotypes. Front Physiol. 2018;9:419.
[41] SINDRILARU A, SCHARFFETTER-KOCHANEK K. Disclosure of the culprits: macrophages-versatile regulators of wound healing. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2013;2(7):357-368.
[42] LI X, HUANG Q, ELKHOOLY TA, et al. Effects of titanium surface roughness on the mediation of osteogenesis via modulating the immune response of macrophages. Biomed Mater. 2018;13(4):045013.
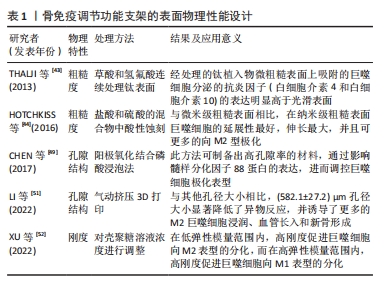
[43] THALJI G, GRETZER C, COOPER LF. Comparative molecular assessment of early osseointegration in implant-adherent cells. Bone. 2013;52(1):444-453.
[44] HOTCHKISS KM, REDDY GB, HYZY SL, et al. Titanium surface characteristics, including topography and wettability, alter macrophage activation. Acta Biomater. 2016;31:425-434.
[45] LUU TU, GOTT SC, WOO BW, et al. Micro- and nanopatterned topographical cues for regulating macrophage cell shape and phenotype. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7(51):28665-28672.
[46] KARAGEORGIOU V, KAPLAN D. Porosity of 3D biomaterial scaffolds and osteogenesis. Biomaterials. 2005;26(27):5474-5491.
[47] HANNINK G, ARTS JJ. Bioresorbability, porosity and mechanical strength of bone substitutes: what is optimal for bone regeneration? Injury. 2011;42 Suppl 2: S22-S25.
[48] LOH QL, CHOONG C.Three-dimensional scaffolds for tissue engineering applications: role of porosity and pore size. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2013;19(6): 485-502.
[49] CHEN Z, NI S, HAN S, et al. Nanoporous microstructures mediate osteogenesis by modulating the osteo-immune response of macrophages. Nanoscale. 2017; 9(2):706-718.
[50] GARG K, PULLEN NA, OSKERITZIAN CA, et al. Macrophage functional polarization (M1/M2) in response to varying fiber and pore dimensions of electrospun scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2013;34(18):4439-4451.
[51] LI W, DAI F, ZHANG S, et al. Pore size of 3D-printed polycaprolactone/polyethylene glycol/hydroxyapatite scaffolds affects bone regeneration by modulating macrophage polarization and the foreign body response. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022;14(18):20693-20707.
[52] XU J, GUAN W, KONG Y, et al. Regulation of macrophage behavior by chitosan scaffolds with different elastic modulus. Coatings. 2022;12(11):1742.
[53] FIRKOWSKA-BODEN I, ZHANG X, JANDT KD. Controlling protein adsorption through nanostructured polymeric surfaces. Adv Healthc Mater. 2018;7(1):1700995.
[54] BATOOL F, ÖZçELIK H, STUTZ C, et al. Modulation of immune-inflammatory responses through surface modifications of biomaterials to promote bone healing and regeneration. J Tissue Eng. 2021;12:20417314211041428.
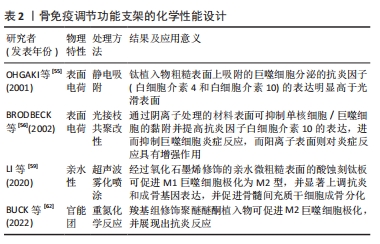
[55] OHGAKI M, KIZUKI T, KATSURA M, et al. Manipulation of selective cell adhesion and growth by surface charges of electrically polarized hydroxyapatite. J Biomed Mater Res. 2001;57(3):366-373.
[56] BRODBECK WG, NAKAYAMA Y, MATSUDA T, et al. Biomaterial surface chemistry dictates adherent monocyte/macrophage cytokine expression in vitro. Cytokine. 2002;18(6):311-319.
[57] ZHANG K, HUANG H, HUNG HC, et al. Strong hydration at the poly(ethylene glycol) brush/albumin solution interface. Langmuir. 2020;36(8):2030-2036.
[58] LI N, XU Z, ZHENG S, et al. Superamphiphilic TiO(2) composite surface for protein antifouling. Adv Mater. 2021;33(25):e2003559.
[59] LI Q, SHEN A, WANG Z.Enhanced osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs and M2-phenotype polarization of macrophages on a titanium surface modified with graphene oxide for potential implant applications. RSC Adv. 2020;10(28):16537-16550
[60] HASAN A, PATTANAYEK SK, PANDEY LM. Effect of functional groups of self-assembled monolayers on protein adsorption and initial cell adhesion. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2018;4(9):3224-3233
[61] ARIMA Y, IWATA H. Effect of wettability and surface functional groups on protein adsorption and cell adhesion using well-defined mixed self-assembled monolayers. Biomaterials. 2007;28(20):3074-3082.
[62] BUCK E, LEE S, GAO Q, et al. The Role of Surface Chemistry in the Osseointegration of PEEK Implants. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2022;8(4):1506-1521.
[63] CHEN Z, CHEN L, LIU R, et al. The osteoimmunomodulatory property of a barrier collagen membrane and its manipulation via coating nanometer-sized bioactive glass to improve guided bone regeneration. Biomater Sci. 2018;6(5):1007-1019.
[64] GONG L, LI J, ZHANG J, et al. An interleukin-4-loaded bi-layer 3D printed scaffold promotes osteochondral regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2020;117:246-260.
[65] LI M, WEI F, YIN X, et al. Synergistic regulation of osteoimmune microenvironment by IL-4 and RGD to accelerate osteogenesis. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;109:110508.
[66] LIU W, LI J, CHENG M, et al. Zinc-modified sulfonated polyetheretherketone surface with immunomodulatory function for guiding cell fate and bone regeneration. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2018;5(10):1800749.
[67] CHEN Y, GUAN M, REN R, et al. Improved immunoregulation of ultra-low-dose silver nanoparticle-loaded TiO(2) nanotubes via M2 macrophage polarization by regulating GLUT1 and autophagy. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:2011-2026.
[68] QI D, SU J, LI S, et al. 3D printed magnesium-doped β-TCP gyroid scaffold with osteogenesis, angiogenesis, immunomodulation properties and bone regeneration capability in vivo. Biomater Adv. 2022;136:212759.
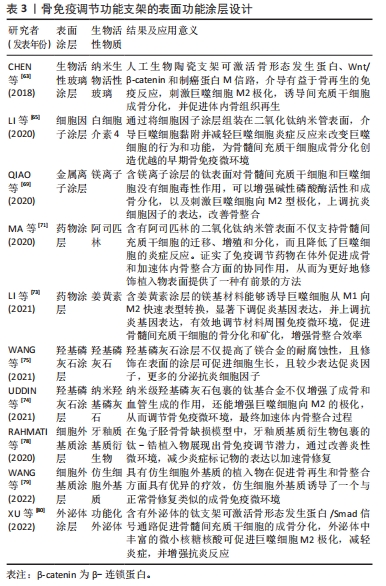
[69] QIAO X, YANG J, SHANG Y, et al. Magnesium-doped nanostructured titanium surface modulates macrophage-mediated inflammatory response for ameliorative osseointegration. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:7185-7198.
[70] HE M, YANG B, HUO F, et al. A novel coating with universal adhesion and inflammation-responsive drug release functions to manipulate the osteoimmunomodulation of implants. J Mater Chem B. 2021;9(26):5272-5283.
[71] MA A, YOU Y, CHEN B, et al. Icariin/aspirin composite coating on TiO2 nanotubes surface induce immunomodulatory effect of macrophage and improve osteoblast activity. Coatings. 2020;10(4):427.
[72] 熊伟,袁灵梅,钱国文,等.“补肾壮骨”中药应用于骨组织工程支架修复节段性骨缺损[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2023,27(21):3438-3444.
[73] LI B, HUANG R, YE J, et al. A self-healing coating containing curcumin for osteoimmunomodulation to ameliorate osseointegration. Chem Eng J. 2021; 403:126323.
[74] UDDIN M, HALL C, SANTOS V, et al. Synergistic effect of deep ball burnishing and HA coating on surface integrity, corrosion and immune response of biodegradable AZ31B Mg alloys. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;118:111459.
[75] WANG X, MEI L, JIANG X, et al. Hydroxyapatite-coated titanium by micro-arc oxidation and steam-hydrothermal treatment promotes osseointegration. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021;9:625877.
[76] XING H, LEE H, LUO L, et al. Extracellular matrix-derived biomaterials in engineering cell function. Biotechnol Adv. 2020;42:107421.
[77] AAMODT JM, GRAINGER DW.Extracellular matrix-based biomaterial scaffolds and the host response. Biomaterials. 2016;86:68-82.
[78] RAHMATI M, FRANK MJ, WALTER SM, et al. Osteoimmunomodulatory effects of enamel matrix derivate and strontium coating layers: a short- and long-term in vivo study. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2020;3(8):5169-5181.
[79] WANG Y, WANG J, GAO R, et al. Biomimetic glycopeptide hydrogel coated PCL/nHA scaffold for enhanced cranial bone regeneration via macrophage M2 polarization-induced osteo-immunomodulation. Biomaterials. 2022;285:121538.
[80] XU H, CHAI Q, XU X, et al. Exosome-functionalized Ti6Al4V scaffolds promoting osseointegration by modulating endogenous osteogenesis and osteoimmunity. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022;14(41):46161-46175. |