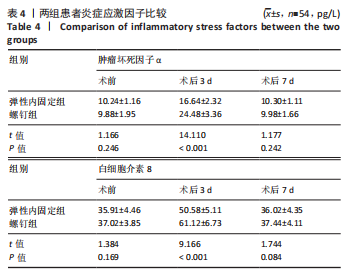
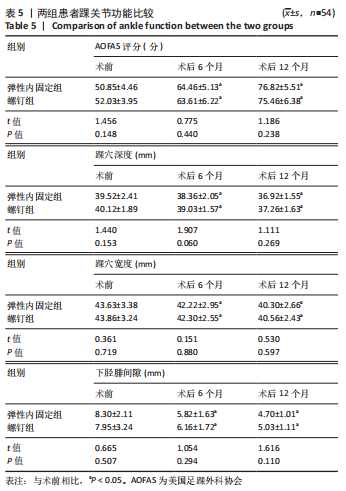
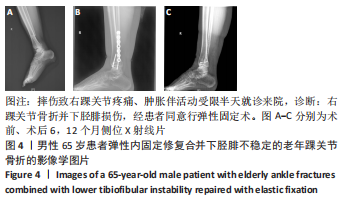
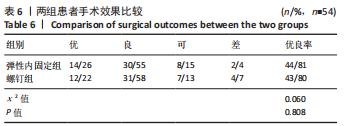
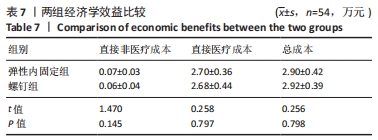
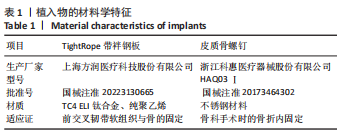
[1] WANG J, STRIDE D, HORNER NS, et al. The role of deltoid ligament repair in ankle fractures with syndesmotic instability:a systematic review. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2021;60(1): 132-139.
[2] ZHAO J, ZHANG Y, XIA Y, et al. Application of an arched,ni-ti shape-memory connector in repairing distal tibiofibular syndesmosis ligament injury. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):476.
[3] XU Y, KANG R, LI M, et al. The clinical efficacy of suture-button fixation and trans-syndesmotic screw fixation in the treatment of ankle fracture combined with distal tibiofibular syndesmosis injury:a retrospective study. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2022;61(1):143-148.
[4] STREET SB, RAWLINS M, MILLER J, et al. Effectiveness of the tightrope® fixation in treating ankle syndesmosis injuries:a critically appraised topic. J Sport Rehabil. 2021; 30(4):676-679.
[5] 刘玉波,张会增,张同润,等.踝关节骨折术后踝穴形态变化与踝关节功能的相关因素分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(3):440-445.
[6] 吴佳俊,沈超,周小小,等.距下关节镜辅助下经跗骨窦入路治疗Sanders Ⅱ型跟骨骨折[J].骨科,2022,13(5):409-413.
[7] PRIVALOV M, SWARTMAN B, BEISEMANN N, et al. Influence of unstable ankle fracture (type weber c),osteosynthesis and syndesmotic transfixation on position of fibula in tibiofibular notch:a cadaveric study. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2022;48(2):1445-1452.
[8] HENNINGS R, FUCHS C, SPIEGL UJ, et al. “Flexible nature of fixation” in syndesmotic stabilization of the inferior tibiofibular joint affects the radiological reduction outcome. Int Orthop. 2022; 46(11):2649-2657.
[9] STREET SB, RAWLINS M, MILLER J, et al. Effectiveness of the tightrope® fixation in treating ankle syndesmosis injuries: a critically appraised topic. J Sport Rehabil. 2021; 30(4):676-679.
[10] 林需枰,刘庆军,丁真奇,等.下胫腓螺钉固定联合下胫腓韧带修复治疗踝关节骨折合并下胫腓联合损伤的疗效[J].中华创伤杂志,2022,38(5):424-429.
[11] 贺毅,郑聪,何敏辉,等.螺钉内固定与保守治疗后踝骨折:踝关节功能和足底压力的差异[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(27):4379-4385.
[12] IVANOV S, STEFANOV A, ZDERIC I, et al. Percutaneous fixation of intraarticular joint-depression calcaneal fractures with different screw configurations - a biomechanical human cadaveric analysis. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2022;48(4):3305-3315.
[13] ZHANG L, XIONG JX, ZHOU X, et al. Biomechanical comparison of screw, tightrope and novel double endobutton in the treatment of tibiofibular syndesmotic injuries. Injury. 2021;52(10): 2813-2819.
[14] KURTOGLU A, KOCHAI A, INANMAZ ME, et al. A comparison of double single suture-button fixation,suture-button fixation, and screw fixation for ankle syndesmosis injury:a retrospective cohort study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021;100(13):e25328.
[15] DOLL J, WAIZENEGGER S, BRUCKNER T, et al. Differences in gait analysis and clinical outcome after TightRope® or screw fixation in acute syndesmosis rupture:study protocol for a prospective randomized pilot study. Trials. 2020;21(1):606.
[16] 张绍春,周彬,王冶,等.TightRope带袢钢板与皮质骨螺钉内固定治疗踝关节骨折合并的下胫腓联合损伤疗效比较[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2021,36(12):1262-1265.
[17] HUNT KJ. In fibular fractures with associated syndesmotic injury,open reduction and internal fixation with the tightrope device reduced malreduction at 3 months compared with screw fixation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2020;102(16):1465.
[18] WAKE J, MARTIN KD. Syndesmosis injury from diagnosis to repair:physical examination, diagnosis,and arthroscopic-assisted reduction. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2020;28(13):517-527.
[19] GRÄFF P, ALANAZI S, ALAZZAWI S, et al. Screw fixation for syndesmotic injury is stronger and provides more contact area of the joint surface than tightrope®:a biomechanical study. Technol Health Care. 2020;28(5):533-539.
[20] ZHU N, ZHONG Q, ZHAN J, et al. A new type of elastic fixation, using an encircling and binding technique, for tibiofibular syndesmosis stabilization: comparison to traditional cortical screw fixation. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):269.
[21] 曹尚鹏,周飞,郑娜,等.弹性内固定治疗踝关节骨折合并下胫腓联合分离的临床疗效[J].医学临床研究,2022,39(3):445-448.
[22] 段添栋,刘伟.TightRope带袢钢板内固定治疗踝关节骨折合并的下胫腓联合损伤[J]. 中医正骨,2022,34(12):36-41,44.
[23] 苏博源,姚彬富,曾广龙,等. TightRope纽扣钢板与横行螺钉固定治疗胫腓联合损伤的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(30):4845-4850.
[24] 许国泰,周姣丽,朱小华,等.带袢钢板弹性固定与螺钉内固定治疗下胫腓联合损伤患者效果观察[J].包头医学院学报,2021,37(4):24-27.
[25] HOFMANN-KIEFER KF, GAUBE F, GROENE P, et al. “High ankle block” for surgery at the ankle joint. Foot Ankle Surg. 2022;28(8):1254-1258.
[26] 薛浩文,褚虹宇,左解鹏,等.基于CT的中国正常成人踝关节三维形态学分析及应用研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2021,39(5):539-545.
[27] CHI YL, GAO X, XU YJ, et al. Open total dislocation of ankle joint without fractures: A case report.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021;100(22):e26247.
[28] GABRIELLI AS, GALE T, HOGAN M, et al. Bilateral symmetry,sex differences,and primary shape factors in ankle and hindfoot bone morphology. Foot Ankle Orthop. 2020;5(1): 2473011420908796.
[29] 彭明,刘荣,肖金辉,等.2种麻醉策略对下肢骨折患者术后镇痛作用,炎性反应及血管内皮功能的影响[J].河北医科大学学报,2021,42(1):71-76.
[30] 张瑜,邓锦锋,赵敏,等.前侧与外侧入路MIPO技术对肱骨干中段骨折患者机体应激反应,骨代谢活性以及肩肘关节功能的影响[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2021,36(11):1200-1202.
[31] VILOTIĆ A, NACKA-ALEKSIĆ M, PIRKOVIĆ A, et al. Il-6 and il-8:an overview of their roles in healthy and pathological pregnancies. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(23):14574.
[32] CHEN T, ZHANG X, ZHU G, et al. Quercetin inhibits tnf-α induced huvecs apoptosis and inflammation via downregulating nf-kb and ap-1 signaling pathway in vitro. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020;99(38):e22241. |