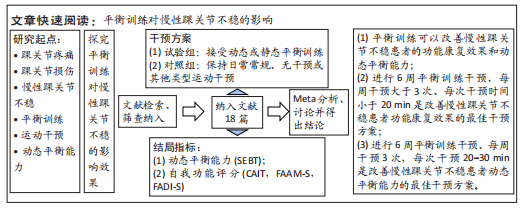
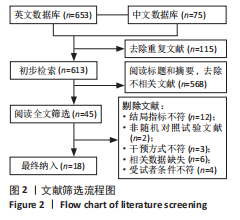
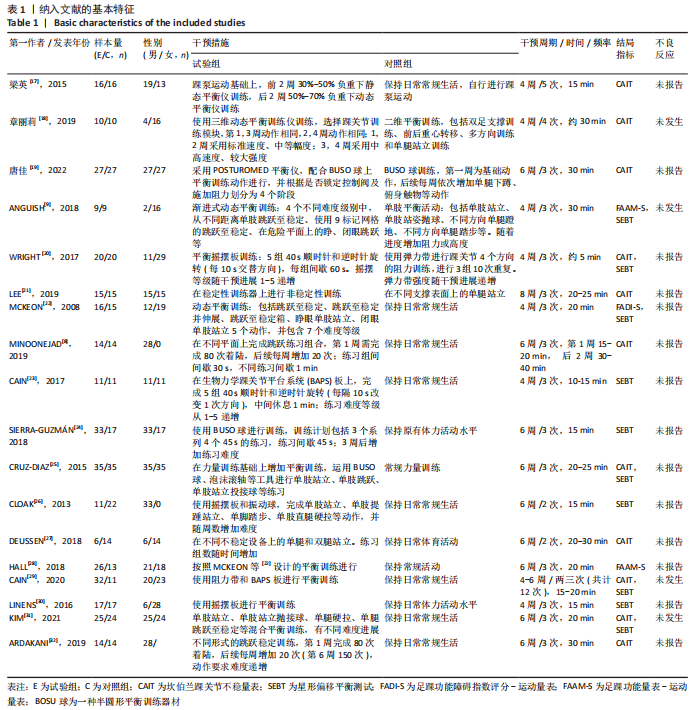
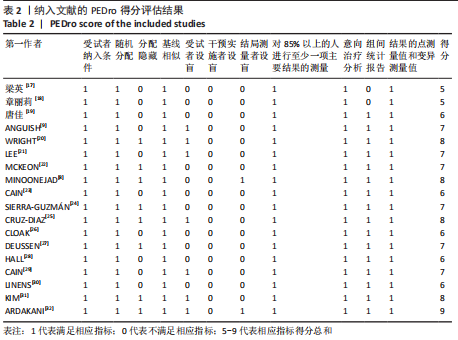
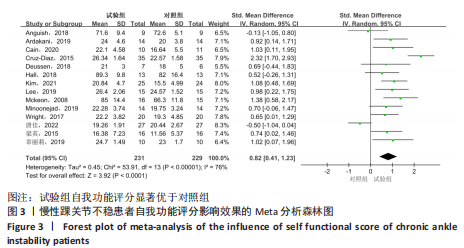
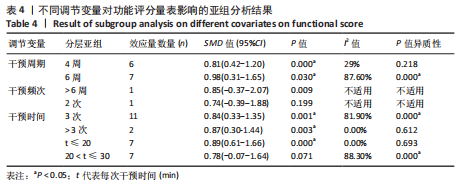
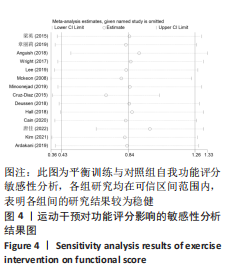
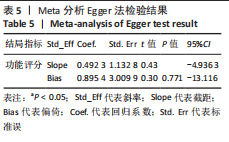
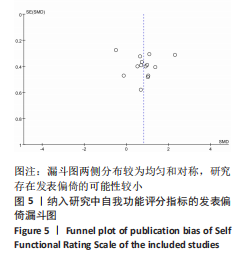
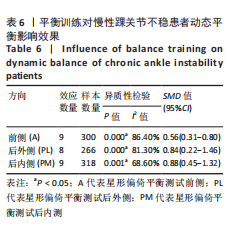
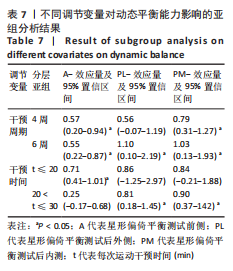
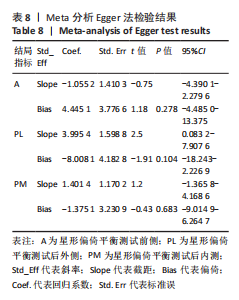
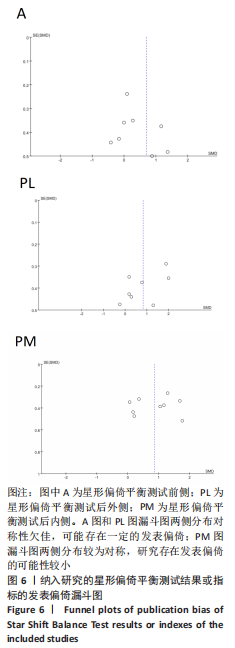
[1] DOHERTY C, DELAHUNT E, CAULFIELD B, et al. The incidence and prevalence of ankle sprain injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective epidemiological studies. Sports Med. 2014;44(1):123-140.
[2] YEUNG MS, CHAN KM, SO CH, et al. An epidemiological survey on ankle sprain. Br J Sports Med. 1994;28(2):112-116.
[3] DELAHUNT E, COUGHLAN GF, CAULFIELD B, et al. Inclusion criteria when investigating insufficiencies in chronic ankle instability. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2010;42(11):2106-2121.
[4] 施晓剑,韩甲,刘宇,等.慢性踝关节不稳的病理机制和评估诊断研究进展[J].中国运动医学杂志,2019,38(9):816-824.
[5] 苏应军,童新延,胡力.以踝关节解剖结构及生物力学特征分析慢性踝关节不稳[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(15):2415-2419.
[6] 章丽莉,杨玉珊,郑洁皎.慢性踝关节不稳姿势稳定性的研究进展[J].中国康复理论与实践,2019,25(8):908-912.
[7] TAUBE W, GRUBER M, GOLLHOFER A. Spinal and supraspinal adaptations associated with balance training and their functional relevance. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2008;193(2):101-116.
[8] MINOONEJAD H, KARIMIZADEH ARDAKANI M, RAJABI R, et al. Hop stabilization training improves neuromuscular control in college basketball players with chronic ankle instability: a randomized controlled trial. J Sport Rehabil. 2019;28(6):576-583.
[9] ANGUISH B, SANDREY MA. Two 4-week balance-training programs for chronic ankle instability. J Athl Train. 2018;53(7):662-671.
[10] MOLLÀ-CASANOVA S, INGLÉS M, SERRA-AÑÓ P. Effects of balance training on functionality, ankle instability, and dynamic balance outcomes in people with chronic ankle instability: systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Rehabil. 2021;35(12):1694-1709.
[11] JIANG C, HUANG DB, LI XM, et al. Effects of balance training on dynamic postural stability in patients with chronic ankle instability: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2022;62(12):1707-1715.
[12] 高淑青,王晓晨,张连成.循证锻炼在大众锻炼实践领域的应用思考[J].体育学刊, 2022,29(3):139-144.
[13] 苏玉莹,尹洪满,石旅畅,等.飞轮离心超负荷训练对预防模拟失重人群废用性肌萎缩效果的meta分析[J].中国康复医学杂志, 2022,37(2):224-230.
[14] DE VRIES JS, KRIPS R, SIEREVELT IN, et al. Interventions for treating chronic ankle instability. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011; (8):CD004124.
[15] MAHER CG, SHERRINGTON C, HERBERT RD, et al. Reliability of the PEDro scale for rating quality of randomized controlled trials. Phys Ther. 2003;83(8):713-721.
[16] 刘鸣.系统评价、Meta-分析设计与实施方法[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2011:158-164.
[17] 梁英,高敏,王萍芝,等.动静态平衡训练治疗慢性踝关节不稳的疗效研究[J].中华老年骨科与康复电子杂志,2015,1(2):23-28.
[18] 章丽莉.三维和二维动态平衡训练对功能性踝关节不稳者姿势控制的影响[D].上海:上海体育学院,2019.
[19] 唐佳.两种平衡训练对功能性踝关节不稳患者稳定性影响的研究[D].天津:天津体育学院,2022.
[20] WRIGHT CJ, LINENS SW, CAIN MS. A randomized controlled trial comparing rehabilitation efficacy in chronic ankle instability. J Sport Rehabil. 2017;26(4):238-249.
[21] LEE E, CHO J, LEE S. Short-foot exercise promotes quantitative somatosensory function in ankle instability: a randomized controlled trial. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25: 618-626.
[22] MCKEON PO, INGERSOLL CD, KERRIGAN DC, et al. Balance training improves function and postural control in those with chronic ankle instability. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2008; 40(10):1810-1819.
[23] CAIN MS, GARCEAU SW, LINENS SW. Effects of a 4-week biomechanical ankle platform system protocol on balance in high school athletes with chronic ankle instability. J Sport Rehabil. 2017;26(1):1-7.
[24] SIERRA-GUZMÁN R, JIMÉNEZ-DIAZ F, RAMÍREZ C, et al. Whole-body-vibration training and balance in recreational athletes with chronic ankle instability. J Athl Train. 2018;53(4): 355-363.
[25] CRUZ-DIAZ D, LOMAS-VEGA R, OSUNA-PÉREZ MC, et al. Effects of 6 weeks of balance training on chronic ankle instability in athletes: a randomized controlled trial. Int J Sports Med. 2015;36(9):754-760.
[26] CLOAK R, NEVILL A, DAY S, et al. Six-week combined vibration and wobble board training on balance and stability in footballers with functional ankle instability. Clin J Sport Med. 2013;23(5):384-391.
[27] DEUSSEN S, ALFUTH M. The influence of sensorimotor training modalities on balance, strength, joint function, and plantar foot sensitivity in recreational athletes with a history of ankle sprain: a randomized controlled pilot study. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2018;13(6):993-1007.
[28] HALL EA, CHOMISTEK AK, KINGMA JJ, et al. Balance- and strength-training protocols to improve chronic ankle instability deficits, part II: assessing patient-reported outcome measures. J Athl Train. 2018;53(6):578-583.
[29] CAIN MS, BAN RJ, CHEN YP, et al. Four-week ankle-rehabilitation programs in adolescent athletes with chronic ankle instability. J Athl Train. 2020;55(8):801-810.
[30] LINENS SW, ROSS SE, ARNOLD BL. Wobble board rehabilitation for improving balance in ankles with chronic instability. Clin J Sport Med. 2016;26(1):76-82.
[31] KIM KM, ESTUDILLO-MARTÍNEZ MD, CASTELLOTE-CABALLERO Y, et al. Short-term effects of balance training with stroboscopic vision for patients with chronic ankle instability: a single-blinded randomized controlled trial. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(10):5364.
[32] ARDAKANI MK, WIKSTROM EA, MINOONEJAD H, et al. Hop-stabilization training and landing biomechanics in athletes with chronic ankle instability: a randomized controlled trial. J athl train. 2019;54(12):1296-1303.
[33] 尹彦,罗冬梅,刘卉,等.功能性踝关节不稳的机制与自评量表的研究进展[J].中国康复理论与实践,2018,24(6):671-677.
[34] LOUDON JK, SANTOS MJ, FRANKS L, et al. The effectiveness of active exercise as an intervention for functional ankle instability: a systematic review. Sports Med. 2008;38(7): 553-563.
[35] 尹金玲,王松,熊禄全,等.整合性神经肌肉训练对运动员运动表现影响的Meta分析[J].武汉体育学院学报,2021,55(10):77-85.
[36] 魏智丰,王子朴,杜承润,等.平衡能力训练在下肢运动损伤预防及康复中的应用研究[J].中国体育科技,2022,58(10):9-13.
[37] ERGEN E, ULKAR B. Proprioception and ankle injuries in soccer. Clin Sports Med. 2008; 27(1):195-217.
[38] DE VASCONCELOS GS, CINI A, SBRUZZI G, et al. Effects of proprioceptive training on the incidence of ankle sprain in athletes: systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Rehabil. 2018;32(12):1581-1590.
[39] NAGANO Y, IDA H, AKAI M, et al. Effects of jump and balance training on knee kinematics and electromyography of female basketball athletes during a single limb drop landing: pre-post intervention study. Sports Med Arthrosc Rehabil Ther Technol. 2011;3(1):14.
[40] SHAMSEDDINI SOFLA F, HADADI M, REZAEI I, et al. The effect of the combination of whole body vibration and shoe with an unstable surface in chronic ankle instability treatment: a randomized clinical trial. BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2021;13(1):28.
[41] YOUSSEF NM, ABDELMOHSEN AM, ASHOUR AA, et al. Effect of different balance training programs on postural control in chronic ankle instability: a randomized controlled trial. Acta Bioeng Biomech. 2018;20(2):159-169.
[42] O’DRISCOLL J, DELAHUNT E. Neuromuscular training to enhance sensorimotor and functional deficits in subjects with chronic ankle instability: a systematic review and best evidence synthesis. Sports Med Arthrosc Rehabil Ther Technol. 2011;3:19.
[43] 刘展.人体动作模式和运动链的理念在运动损伤防护和康复中的应用[J].成都体育学院学报,2016,42(6):1-11. |