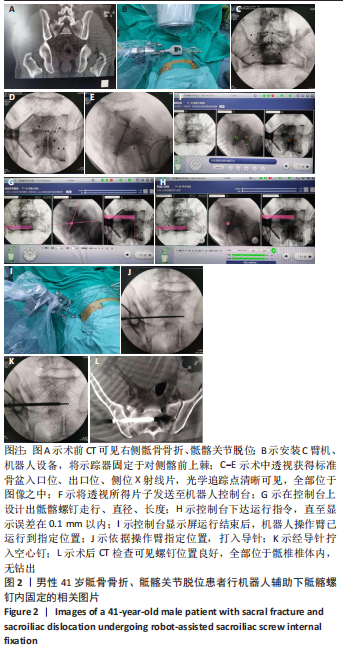
[1] LIUZZA F, SILLUZIO N, FLORIO M, et al. Comparison between posterior sacral plate stabilization versus minimally invasive transiliac-transsacral lag-screw fixation in fractures of sacrum: a single-centre experience. Int Orthop. 2019;43(1):177-185.
[2] SHETTY AP, BOSCO A, PERUMAL R, et al. Midterm radiologic and functional outcomes of minimally-invasive fixation of unstable pelvic fractures using anterior internal fixator(INFIX) and percutaneou iliosacral screws. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2017;8(3):241-248.
[3] MOSHIRFAR A, RAND FF, SPONSELLER PD, et al. Pelvic fixation in spine surgery. Historical overview, indications, biomechanical relevance, and current techniques. J Bone Joint Surg (Am). 2005;87 Suppl 2:89-106.
[4] HOSNY H, MOHAMED MA. One sacroiliac screw for posterior ring fixation in unstable pelvic fractures. Acta Orthop Belg. 2021;87(3):411-418.
[5] 蒋侃凌, 田维, 贾健. TiRobot手术机器人辅助经皮骶髂螺钉固定治疗骨盆后环不稳定损伤[J] .天津医科大学学报,2017,23(3):247-251.
[6] 杨成志,黄站珠,唐经励,等.骨科手术机器人与“O”型臂X线导航辅助骨盆骨折经皮内固定术的比较[J].中华骨科杂志,2021,41(19):1387-1394.
[7] SMITH HE, YUAN PS, SASSO R, et al. An evaluation of image-guidedtechnologies in the placement of percutaneous iliosacral screws. Spine. 2006;31(2):234-238.
[8] 邓宁,吴伟坚,梁国穗,等.机器人和计算机辅助骨科手术[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2005,7(7):620-624.
[9] MOLLIQAJ G, SCHATLO B, ALAID A, et al. Accuracy of robot-guided versus freehand fluoroscopy-assisted pedicle screw insertion in thoracolumbar spinal surgery. Neurosurg Focus. 2017;42(5): E14.
[10] 刘钢,杨强,郝永宏,等.第 2骶椎骶髂螺钉固定骶骨骨盆的优势及意义[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(21):3395-3400.
[11] 孟士超,吴斗,赵恩哲,等.骶髂螺钉治疗骨盆后环骨折及辅助置钉技术的研究进展[J]. 中华老年骨科与康复电子杂志,2021,7(3):187-192.
[12] 张玉坤,李磊,任军.骶髂关节不同固定方式对骶部影响的生物力学研究[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2021,14(2):92-96.
[13] LETOURNEL E. Pelvic fractures. Injury. 1978;10(2):145-148.
[14] 吴新宝,杨明辉,朱仕文,等.不稳定骨盆骨折的手术治疗[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2009,11(7): 619-624.
[15] ROUTT ML, KREGOR PJ, SIMONIAN PT, et al. Early results of percutaneous iliosacral screws placed with the patient in the supine position. J Orthop Trauma. 1995;9(3):207-214.
[16] 贾帅军,吕尚军,贺利军,等.三维导航技术辅助经皮骶髂螺钉治疗骨盆后环骨折[J].创伤外科杂志,2014,16(6):506-510.
[17] 谭山,高仕长,张安维.经皮骶髂关节螺钉固定变异骶骨的影像学初步研究[J].重庆医科大学学报,2018,43(10):1388-1393.
[18] MATITYAHU A, KAHLER D, KRETTEK C, et al. Three-dimensional navigation is more accurate than two-dimensional navigation or conventional fluoroscopy for percutaneous sacroiliac screw fixation in the dysmorphic sacrum: a randomized multicenter study. J Orthop Trauma. 2014;28(12):707-710.
[19] HINSCHE AF, GIANNOUDIS PV, SMITH RM. Fluoroscopy-based multiplanar image guidance for insertion of sacroiliac screws. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002;(395):135-144.
[20] WANG YC, ZHOU ZZ, WANG B, et al. Occipitocervical fusion via cervical pedicle fixation assisted with O-arm navigation. Orthop Surg.2020;12(4): 1100-1107.
[21] 赵春鹏,王军强,苏永刚,等.机器人辅助经皮螺钉内固定治疗骨盆和髋臼骨折[J].北京大学学报(医学版),2017,49(2):274-280.
[22] ZWINGMANN J, KONRAD G, MEHLHORN AT, et al. Percutaneous iliosacral screw insertion: malpositioning and revision rate of screws with regards to application technique (navigated vs. Conventional). J Trauma. 2010;69(6): 1501-1506.
[23] SIDDIQUI MI, WALLACE DJ, SALAZAR LM, et al. Robot assisted pedicle screw placement:learning curve experience. World Neurosurg. 2019;130: E417-E422.
[24] ZWINGMANN J, HAUSCHILD O, BODE G, et al. Malposition and revision rates of different imaging modalities for percutaneous iliosacral screw fixation following pelvic fractures: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013;133(9):1257-1265.
[25] ZWINGMANN J, KONRAD G, KOTTER E, et al. Computer-navigated iliosacral screw insertion reduces malposition rate and radiation exposure. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467(7):1833-1838.
[26] BERGER-GROCH J, LUEERS M, RUERGER JM, et al. Accuracy of navigated and conventional iliosacral screw placement in B- and C-type pelvic ring fractures. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2020;46(1):107-113.
[27] HE M, HAN W, ZHAO CP, et al. Evaluation of a Bi-Planar Robot Navigation System for Insertion of Cannulated Screws in Femoral Neck Fractures. Orthop Surg. 2019;11(3):373-379.
[28] ECKER TM, JOST J, CULLMANN JL, et al. Percutaneous screw fixation of the iliosacral joint: A case-based preoperative planning approach reduces operating time and radiation exposure. Injury. 2017;48(8):1825-1830
[29] KIM JW, OH CW, OH JK, et al. Percutaneous iliosacral screwing in pelvic ring injury using three-dimensional fluoroscopy. J Orthop Sci. 2013;18(1):87-92.
[30] PASSIAS BJ, GRENIER G, BUCHAN J, et al. Use of 3D Navigation Versus Traditional Fluoroscopy for Posterior Pelvic Ring Fixation. Orthopedics. 2021; 44(4):229-234.
[31] THAKKAR SC, THAKKAR RS, SIRISREETREERUX N, et al. 2D versus 3D fluoroscopy-based navigation in posterior pelvic fixation: review of the literature on current technology. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2017;12(1): 69-76.
[32] VERBEEK J, HERMANS E, VAN VUGT A, et al. Correct positioning of percutaneous iliosacral screws with computer-navigated versus fluoroscopically guided surgery in traumatic pelvic ring fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2016;30(6):331-335. |