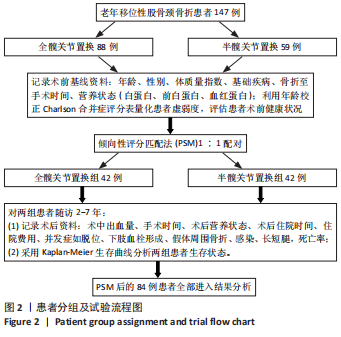
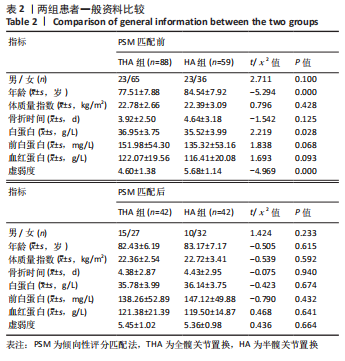
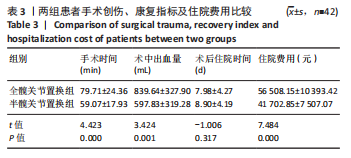
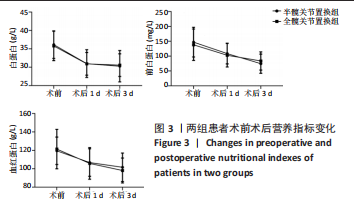
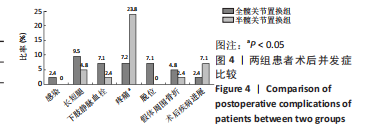
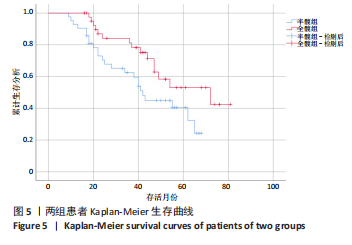
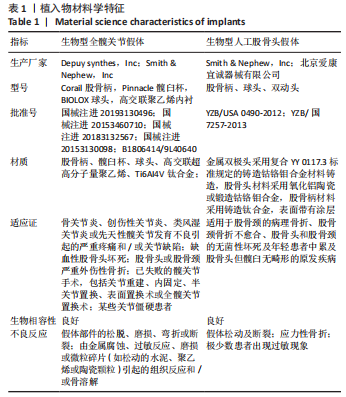
[1] SIMON P, GOUIN F, VEILLARD D, et al. [Femoral neck fractures in patients over 50 years old]. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 2008;94 Suppl(6):S108-S132.
[2] LEONARDSSON O, KARRHOLM J, AKESSON K, et al. Higher risk of reoperation for bipolar and uncemented hemiarthroplasty. Acta Orthop. 2012;83(5):459-466.
[3] 张殿英, 付中国, 杨明, 等. 加压空心钉与全髋关节置换治疗老年股骨颈骨折的疗效分析[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2009,11(5):443-445.
[4] HEETVELD MJ, ROGMARK C, FRIHAGEN F, et al. Internal fixation versus arthroplasty for displaced femoral neck fractures: what is the evidence? J Orthop Trauma. 2009;23(6):395-402.
[5] BAIG SA, BAIG MN. Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: Etiology, Investigations, and Management. Cureus. 2018;10(8):e3171.
[6] LU Y, UPPAL HS. Hip Fractures: Relevant Anatomy, Classification, and Biomechanics of Fracture and Fixation. Geriatr Orthop Surg Rehabil. 2019;10:1467856957.
[7] EKHTIARI S, GORMLEY J, AXELROD DE, et al. Total Hip Arthroplasty Versus Hemiarthroplasty for Displaced Femoral Neck Fracture: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2020; 102(18):1638-1645.
[8] BHANDARI M, EINHORN TA, GUYATT G, et al. Total Hip Arthroplasty or Hemiarthroplasty for Hip Fracture. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(23):2199-2208.
[9] BLOMFELDT R, TORNKVIST H, ERIKSSON K, et al. A randomised controlled trial comparing bipolar hemiarthroplasty with total hip replacement for displaced intracapsular fractures of the femoral neck in elderly patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007;89(2):160-165.
[10] HEDBECK CJ, BLOMFELDT R, LAPIDUS G, et al. Unipolar hemiarthroplasty versus bipolar hemiarthroplasty in the most elderly patients with displaced femoral neck fractures: a randomised, controlled trial. Int Orthop. 2011;35(11):1703-1711.
[11] BAKER RP, SQUIRES B, GARGAN MF, et al. Total hip arthroplasty and hemiarthroplasty in mobile, independent patients with a displaced intracapsular fracture of the femoral neck. A randomized, controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(12):2583-2589.
[12] OGAWA T, YOSHII T, MORIWAKI M, et al. Association between Hemiarthroplasty vs Total Hip Arthroplasty and Major Surgical Complications among Patients with Femoral Neck Fracture. J Clin Med. 2020;9(10):3203.
[13] BORDINI B. CORR Insights((R)): The Frank Stinchfield Award: Total Hip Arthroplasty for Femoral Neck Fracture Is Not a Typical DRG 470: A Propensity-matched Cohort Study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017;475(2):361-363.
[14] 李骏然, 李力更, 翟婧秀, 等. 微创直接前侧入路与后外侧入路全髋关节置换术治疗老年人股骨颈骨折的早期临床疗效对照研究[J]. 中华解剖与临床杂志, 2021,26(2):182-187.
[15] KOPPIE TM, SERIO AM, VICKERS AJ, et al. Age-adjusted Charlson comorbidity score is associated with treatment decisions and clinical outcomes for patients undergoing radical cystectomy for bladder cancer. Cancer. 2008;112(11):2384-2392.
[16] PEETERS CM, VISSER E, VAN DE REE CL, et al. Quality of life after hip fracture in the elderly: A systematic literature review. Injury. 2016;47(7):1369-1382.
[17] GUYEN O. Hemiarthroplasty or total hip arthroplasty in recent femoral neck fractures? Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2019;105(1S):S95-S101.
[18] MILLER BJ, CALLAGHAN JJ, CRAM P, et al. Changing trends in the treatment of femoral neck fractures: a review of the american board of orthopaedic surgery database. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014;96(17):e149.
[19] ZELLE BA, SALAZAR LM, HOWARD SL, et al. Surgical treatment options for femoral neck fractures in the elderly. Int Orthop. 2022;46(5):1111-1122.
[20] MIGLIORINI F, MAFFULLI N, TRIVELLAS M, et al. Total hip arthroplasty compared to bipolar and unipolar hemiarthroplasty for displaced hip fractures in the elderly: a Bayesian network meta-analysis. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2022;48(4):2655-2666.
[21] 吕辉, 黄邓华, 邹龙飞, 等. 全髋关节置换和人工股骨头置换修复移位型股骨颈骨折效果:基于14项随机对照试验的Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021,25(27):4421-4428.
[22] CHARLSON M, SZATROWSKI TP, PETERSON J, et al. Validation of a combined comorbidity index. J Clin Epidemiol. 1994;47(11):1245-1251.
[23] LIN JX, HUANG YQ, XIE JW, et al. Association of the age-adjusted Charlson Comorbidity Index and systemic inflammation with survival in gastric cancer patients after radical gastrectomy. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2019;45(12):2465-2472.
[24] JIANG L, CHOU A, NADKARNI N, et al. Charlson Comorbidity Index Predicts 5-Year Survivorship of Surgically Treated Hip Fracture Patients. Geriatr Orthop Surg Rehabil. 2018;9:1468909654.
[25] SCHMOLDERS J, FRIEDRICH MJ, MICHEL R, et al. Validation of the Charlson comorbidity index in patients undergoing revision total hip arthroplasty. Int Orthop, 2015;39(9):1771-1777.
[26] ASANO T, YAMADA S, FUJII T, et al. The Charlson age comorbidity index predicts prognosis in patients with resected pancreatic cancer. Int J Surg. 2017;39:169-175.
[27] BOVONRATWET P, NELSON SJ, ONDECK NT, et al. Comparison of 30-Day Complications Between Navigated and Conventional Single-level Instrumented Posterior Lumbar Fusion: A Propensity Score Matched Analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2018;43(6):447-453.
[28] BOVONRATWET P, FU MC, TYAGI V, et al. Safety of Outpatient Single-level Cervical Total Disc Replacement: A Propensity-Matched Multi-institutional Study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2019;44(9):E530-E538.
[29] KANE LT, FANG T, GALETTA MS, et al. Propensity Score Matching: A Statistical Method. Clin Spine Surg. 2020;33(3):120-122.
[30] YEUNG CY, TSAI SW, WU PK, et al. Low rates of all-cause revision in displaced subcapital femoral neck fractures treated with hip hemiarthroplasty - a retrospective review of 4516 patients from a single institute. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):700.
[31] WANG Z, BHATTACHARYYA T. Outcomes of Hemiarthroplasty and Total Hip Arthroplasty for Femoral Neck Fracture: A Medicare Cohort Study. J Orthop Trauma. 2017;31(5):260-263.
[32] GONZALEZ DVA, COMBA F, TAVERAS N, et al. The utility and precision of analogue and digital preoperative planning for total hip arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2008;32(3):289-294.
[33] CIDAMBI KR, BARNETT SL, MALLETTE PR, et al. Impact of Femoral Stem Design on Failure After Anterior Approach Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(3): 800-804.
[34] HASSANI H, CHERIX S, EK ET, et al. Comparisons of preoperative three-dimensional planning and surgical reconstruction in primary cementless total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(6):1273-1277.
[35] INOUE D, KABATA T, MAEDA T, et al. Value of computed tomography-based three-dimensional surgical preoperative planning software in total hip arthroplasty with developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Orthop Sci. 2015;20(2):340-346.
[36] COLEMAN SH, BANSAL M, CORNELL CN, et al. Failure of bipolar hemiarthroplasty: a retrospective review of 31 consecutive bipolar prostheses converted to total hip arthroplasty. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2001;30(4):313-319.
[37] FENG B, REN Y, CAO S, et al. Comparison of ceramic-on-ceramic bearing vs ceramic-on-highly cross-linked polyethylene-bearing surfaces in total hip arthroplasty for avascular necrosis of femoral head: a prospective cohort study with a mid-term follow-up. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):388.
[38] MACAULAY W, NELLANS KW, GARVIN KL, et al. Prospective randomized clinical trial comparing hemiarthroplasty to total hip arthroplasty in the treatment of displaced femoral neck fractures: winner of the Dorr Award. J Arthroplasty. 2008;23(6 Suppl 1):2-8.
[39] VAN DEN BEKEROM MP, HILVERDINK EF, SIEREVELT IN, et al. A comparison of hemiarthroplasty with total hip replacement for displaced intracapsular fracture of the femoral neck: a randomised controlled multicentre trial in patients aged 70 years and over. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010;92(10):1422-1428.
[40] BURGERS PT, VAN GEENE AR, VAN DEN BEKEROM MP, et al. Total hip arthroplasty versus hemiarthroplasty for displaced femoral neck fractures in the healthy elderly: a meta-analysis and systematic review of randomized trials. Int Orthop. 2012;36(8):1549-1560.
[41] SMITH D, WILKIE R, CROFT P, et al. Pain and Mortality in Older Adults: The Influence of Pain Phenotype. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2018;70(2):236-243.
[42] TSAI MH, TSAY WI, HER SH, et al. Long-term mortality in older adults with chronic pain: a nationwide population-based study in Taiwan. Eur Geriatr Med. 2019;10(5):777-784.
[43] TORRANCE N, ELLIOTT AM, LEE AJ, et al. Severe chronic pain is associated with increased 10 year mortality. A cohort record linkage study. Eur J Pain. 2010;14(4): 380-386.
[44] PAGANINI-HILL A, KAWAS CH, CORRADA MM. Activities and mortality in the elderly: the Leisure World cohort study. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2011;66(5): 559-567.
[45] SIBILLE KT, STEINGRIMSDOTTIR OA, FILLINGIM RB, et al. Investigating the Burden of Chronic Pain: An Inflammatory and Metabolic Composite. Pain Res Manag. 2016;2016:7657329.
[46] GENERAAL E, VOGELZANGS N, MACFARLANE GJ, et al. Basal inflammation and innate immune response in chronic multisite musculoskeletal pain. Pain. 2014; 155(8):1605-1612.
[47] MARCHAND F, PERRETTI M, MCMAHON SB. Role of the immune system in chronic pain. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2005;6(7):521-532.
[48] GLASER R, KIECOLT-GLASER JK. Stress-induced immune dysfunction: implications for health. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5(3):243-251. |