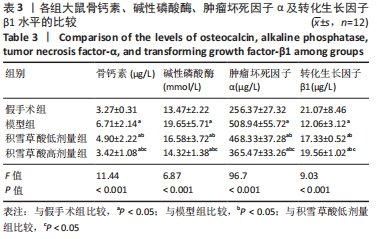
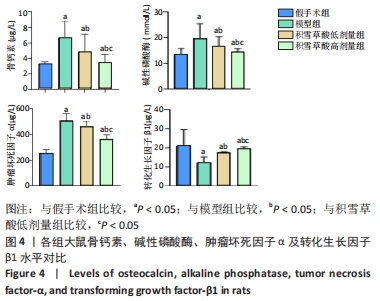
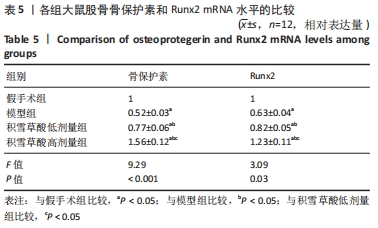
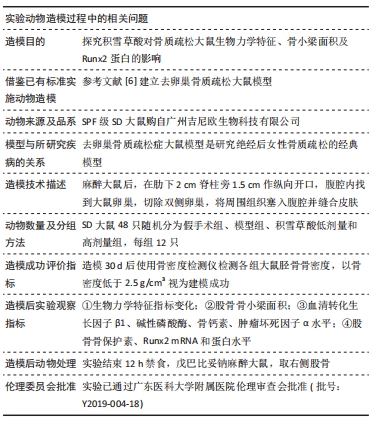
[1] SCHBER C, PAPAGEORGIOU E, HARSTRICK A, et al. Are glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis recommendations sufficient to determine antiosteoporotic treatment for patients with rheumatoid arthritis?.Cancer. 2015;72(7):2242-2247.
[2] WRIGHT NC, LOOKER AC, SAAG KG, et al. The Recent Prevalence of Osteoporosis and Low Bone Mass in the United States Based on Bone Mineral Density at the Femoral Neck or Lumbar Spine. J Bone Miner Res. 2014;29(11):2520-2526.
[3] 梁广胜, 陈伟才, 殷嫦嫦,等. 淫羊藿总黄酮对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化过程BMP-2/RunX2/OSX通路的影响[J]. 中国中西医结合杂志,2016,36(5):614-618.
[4] 张雅雯, 尹丽娜, 梁泽华,等. 积雪草酸大鼠体内药动学考察[J]. 中国现代应用药学,2015,32(3):314-317.
[5] 许可, 郑绿珍, 王清清,等. 信号通路信号抑制剂或蛋白合成抑制剂或羟基积雪草苷在制备治疗骨质疏松药物上的应用[P].CN110215517A. 2019.
[6] 许燕, 肖明, 李涛,等. 积雪草酸促进成骨细胞分化的机制[J]. 华西药学杂志,2019,34(4):5.
[7] 吴少科,陈晓驷,陈海聪,等.积雪草酸抑制去卵巢大鼠骨质疏松的作用[J].实用医学杂志,2019,35(13):2051-2055.
[8] 孟炜晴,张福杰.人类免疫缺陷病毒相关骨质疏松的诊断与治疗的研究进展[J].中华传染病杂志,2021,39(3):182-184.
[9] SANDOMIERSKI M, ZIELIŃSKA M, BUCHWALD T, et al. Controlled release of the drug for osteoporosis from the surface of titanium implants coated with calcium titanate. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2022;110(2):431-437.
[10] 张家国,徐晓峰,李明,等.银杏叶提取物对糖皮质激素诱导的骨质疏松症大鼠骨密度和骨生物力学的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2019,25(4):461-464+471.
[11] 李兴勇, 魏晓辉, 李喜香,等. 亚麻木酚素对实验性骨质疏松大鼠骨生物力学和AKP活性的影响[J]. 西部中医药,2015,28(10):43-45.
[12] 郎小琴, 高越, 周叶,等. 牛膝多糖对老年骨质疏松大鼠模型骨代谢及生物力学特征的影响[J]. 中华全科医学,2019,17(4):547-550,589.
[13] 喻伟光,田振峰,李彦敏,等.羟基积雪草酸通过调控MMPs的表达抑制大鼠炎性骨破坏的作用研究[J].医学动物防制,2021, 37(1):57-60+103.
[14] 郝春波,邓伟,巩蕾,等.积雪草酸对人牙周膜细胞增殖、迁移和成骨分化的影响[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2020,36(4):666-670.
[15] 吴少科, 陈晓驷, 孙欣,等. 积雪草酸对高血脂小鼠骨量丢失的保护作用[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2018,24(3):281-289.
[16] CHIARETTI M, FEGATELLI DA, PAPPALARDO G, et al. Comparison of Centella with Flavonoids for Treatment of Symptoms in Hemorrhoidal Disease and After Surgical Intervention: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Randomized Controlled Trial Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):8009.
[17] 张峻玮,李琰,薛海鹏,等.骨碎补经骨髓间充质干细胞调节OPG/RANKL/RANK通路抑制破骨细胞的实验研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2019,25(5):617-624.
[18] 胡流超, 罗毅文, 程英雄,等. 补肾活血汤通过Runx2/Osterix促进骨质疏松模型大鼠的骨折愈合[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2019,23(11): 1717-1722.
[19] 沈耿杨, 江晓兵, 任辉,等. 龟板联合阿伦磷酸钠对激素性骨质疏松大鼠腰椎Runx2、CTSK表达的影响[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2017, 32(5):2181-2185.
[20] 耿骥, 郭文洁, 刘佳,等. 积雪草酸对结肠癌HCT116细胞增殖及自噬水平的影响[J]. 江苏大学学报(医学版),2015,25(2):133-136.
[21] 王剑, 郑洪新, 刘研, 等.补肾益髓中药复方对去卵巢骨质疏松症大鼠骨组织Runx2 mRNA 及蛋白表达的影响[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志, 2014,20(8):890-895.
[22] DIEGO EMD, NACHER M, RAPADO A, et al. Immunoreactive osteocalcin forms in conditioned media from human osteoblast culture and in sera from healthy adult control subjects and patients with bone pathologies. Eur J Clin Invest. 1998;28(1):48-58.
[23] RITA PM, MARCO R, NICOLA A, et al. Inhibition of miR-21 restores RANKL/OPG ratio in multiple myeloma-derived bone marrow stromal cells and impairs the resorbing activity of mature osteoclasts. Oncotarget. 2015;6(29):27343-27358.
[24] 张倩,杨旭,王媛,等.二仙汤对去势大鼠骨微结构及ALP、OPG、IL-6的影响[J].世界中西医结合杂志,2020,15(11):2053-2057+2061.
[25] 廖腾,孙猛,王众,等.PFNA配合骨化三醇对股骨骨折患者功能康复及血清ALP、OPG水平的影响[J].广东医学,2020,41(7): 713-717.
[26] ALP HH, HUYUT Z, YILDIRIM S, et al. The effect of PDE5 inhibitors on bone and oxidative damage in ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017;242(10):1051-1061.
[27] KANATLI U,ATAOLU B,OZER M, et al. Kyphoplasty for Intractable Pain Due to Glucocorticosteroid-induced Osteoporotic Vertebra Fracture of a 9-Year-Old Patient With Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: 8-Year Follow-up. J Pediatr Orthop. 2015;35(6):e55-59.
[28] 付远锋,李家伟, 陈阳斌,等. 阿仑膦酸钠片联合骨碎补煎剂对老年骨质疏松患者血清MMP-9和TNF-α水平的影响[J]. 现代生物医学进展,2016,16(29):5756-5759.
[29] 李晓曦,陈宇恒,唐秀凤,等. 淫羊藿和女贞子配伍对绝经后骨质疏松症大鼠TGF-β1/Smads信号通路的实验研究[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2019,25(12):1685-1690.
[30] 叶文静, 朱小春, 王晓冰,等. 积雪草苷通过抑制炎症和纤维化减弱平阳霉素诱导的肺间充质纤维化[J]. 中国药理学与毒理学杂志, 2016,30(1):29-37.
|