| [1] Dipti S, Pradeep T, Gyan PS, et al. A newer simultaneous space creation, eruption, and adjacent root control spring for the management of impacted tooth. Contemp Clin Dent.2014; 5(4): 555–557.[2] Heikinheimo K, Kurppa KJ, Laiho A, et al. Early dental epithelial transcription factors distinguish ameloblastoma from keratocystic odontogenic tumor. J Dent Res. 2015; 94(1): 101-111.[3] Oosterkamp BC, Ockeloen CW, Carels CE, et al. Tooth eruption disturbances and syndromes.Ned Tijdschr Tandheelkd. 2014;121(4):233-238.[4] Romeo U, Galluccio G, Palaia G, et al. Cleidocranial dysplasia: maxillary alterations on the transverse plane.Presence of crown-radicular anomalies and multidisciplinary approach of a clinical case. Oral Health Dent Manag. 2014; 13(2):529-535.[5] Funato N, Nakamura M, Richardson JA, et al. Loss of Tbx1 induces bone phenotypes similar to cleidocranial dysplasia. Hum Mol Genet. 2015; 24(2):424-435.[6] Qin XY, Jia PZ, Zhao HX, et al. Novel Mutation of Cleidocranial Dysplasia-related Frameshift Runt-related Transcription Factor 2 in a Sporadic Chinese Case. Chin Med J (Engl). 2017; 20; 130(2):165-170.[7] Lee KE, Seymen F, Ko J, et al. RUNX2 mutations in cleidocranial dysplasia. Genet Mol Res.2013;12(4): 4567-4574.[8] 李阳飞,秦晗,徐宏志.颅骨锁骨发育不良患者特异性碱性磷酸酶和抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶的水平:1例报告[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(41):7742-7744.[9] Dutra EH, Chen IP, Reichenberger EJ. Dental abnormalities in a mouse model for craniometaphyseal dysplasia. J Dent Res. 2013; 92 (2):173-179.[10] Dinçsoy Bir F, Dinçkan N, Güven Y, et al. Cleidocranial dysplasia: Clinical, endocrinologic and molecular findings in 15 patients from 11 families. Eur J Med Genet.2017;60(3): 163-168.[11] Jaruga A, Hordyjewska E, Kandzierski G, et al. Cleidocranial dysplasia and RUNX2-clinical phenotype-genotype correlation. Clin Genet. 2016; 90(5):393-402.[12] Ahmad I. Altered passive eruption (APE) ?and active secondary eruption (ASE): differential diagnosis and management. Int J Esthet Dent. 2017; 12(3):352-376.[13] Elhaddaoui R, Bahije L, Zaoui F, et al. Timing of alveolar bone graft and sequences of canine eruption in cases of cleft lip and palate: a systematic review. Orthod Fr. 2017; 88(2):193-198.[14] Kwon EY, Lee JY, Choi J. Effect of slow forced eruption on the vertical levels of the interproximal bone and papilla and the width of the alveolar ridge. Korean J Orthod.2016; 46(6): 379-385.[15] Shiyan H. Nanquan R. Shuhao X. et al. Research progress on the cellular and molecular mechanisms of tooth eruption. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi.2016; 34 (3):317-321.[16] Shaun R, Broderick, Michelle L, et al. An Optimized Protocol to Increase Virus-Induced Gene Silencing Efficiency and Minimize Viral Symptoms in Petunia. Plant Mol Biol Report. 2014; 32(1): 219–233.[17] Han YF, Dou K, Ma ZY, et al. SUVR2 is involved in transcriptional gene silencing by associating with SNF2-related chromatin- remodeling proteins in Arabidopsis. Cell Res. 2014; 24(12): 1445-1465.[18] Marc S, Weinberg, Kevin V, et al. Transcriptional gene silencing in humans. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016; 44(14): 6505-6517.[19] Bensaude O.HEXIM1 has different functions within different RNA-protein complexes. Mol Cell.2017; 67(3):357-359.[20] Boeijen LL, Hoogeveen RC, Boonstra A, et al. Hepatitis B virus infection and the immune response: The big questions. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2017; 31(3):265-272.[21] Hongmarn P, Geunu B, Sun CK, et al. Exploring sRNA-mediated gene silencing mechanisms using artificial small RNAs derived from a natural RNA scaffold in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013; 41(6): 3787-3804.[22] Foda BM, Singh U. Dimethylated H3K27 Is a Repressive Epigenetic Histone Mark in the Protist Entamoeba histolytica and Is Significantly Enriched in Genes Silenced via the RNAi Pathway. J Biol Chem. 2015; 290(34): 21114-21130.[23] Susmitha S, Gretchen E, Hanbang Z, et al. Development of RNA Interference Trigger-Mediated Gene Silencing in Entamoeba invadens. Infect Immun. 2016; 84(4): 964-975.[24] Dhamo B, Fennis W, Créton M, et al. The association between WNT10A variants and dental development in patients with isolated oligodontia.Eur J Hum Genet .2016; 25(1):59-65.[25] Mortellaro C, Greco Lucchina A, Prota E. Differing therapeutic approaches to cleidocranial dysplasia (CCD). Minerva Stomatol. 2012; 61(4):155-163. [26] Sun X, Wang X, Zhang C, et al. RUNX2 mutation impairs bone remodelling of dental follicle cells and periodontal ligament cells in patients with cleidocranial dysplasia. Mutagenesis.2016; 31(6):677-685.[27] Bharti K, Goswami M. Cleidocranial dysplasia: A report of two cases with brief review. Intractable Rare Dis Res. 2016; 5(2): 117-120.[28] Franceschi R, Maines E, Fedrizzi M, et al. Familial cleidocranial dysplasia misdiagnosed as rickets over three generations. Pediatr Int. 2015; 57(5):1003-1006. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
颅骨锁骨发育不全(cleidocranial dysplasia,CCD):是一种广泛累及包括锁骨、颅骨在内的整个骨骼系统的常染色体显性遗传性疾病(MM119600),出生发病率约为1∶100 000;研究表明RUNX2基因杂合突变、基因插入、缺失等是造成颅骨锁骨发育不全的重要原因。
Runx2基因:Runx相关因子(runt-related gene,Runxx)是一类转录因子蛋白的统称,主要有Runxl、Runx2和Runx3,其中 Runx2基因位于人类常染色体的6p21,长约220 kb,包括8个外显子,具有和其它家族成员相似的Runt结构域,是骨发育过程中调节骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化和成熟最关键的转录因子。
文题释义:
颅骨锁骨发育不全(cleidocranial dysplasia,CCD):是一种广泛累及包括锁骨、颅骨在内的整个骨骼系统的常染色体显性遗传性疾病(MM119600),出生发病率约为1∶100 000;研究表明RUNX2基因杂合突变、基因插入、缺失等是造成颅骨锁骨发育不全的重要原因。
Runx2基因:Runx相关因子(runt-related gene,Runxx)是一类转录因子蛋白的统称,主要有Runxl、Runx2和Runx3,其中 Runx2基因位于人类常染色体的6p21,长约220 kb,包括8个外显子,具有和其它家族成员相似的Runt结构域,是骨发育过程中调节骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化和成熟最关键的转录因子。.jpg) 文题释义:
颅骨锁骨发育不全(cleidocranial dysplasia,CCD):是一种广泛累及包括锁骨、颅骨在内的整个骨骼系统的常染色体显性遗传性疾病(MM119600),出生发病率约为1∶100 000;研究表明RUNX2基因杂合突变、基因插入、缺失等是造成颅骨锁骨发育不全的重要原因。
Runx2基因:Runx相关因子(runt-related gene,Runxx)是一类转录因子蛋白的统称,主要有Runxl、Runx2和Runx3,其中 Runx2基因位于人类常染色体的6p21,长约220 kb,包括8个外显子,具有和其它家族成员相似的Runt结构域,是骨发育过程中调节骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化和成熟最关键的转录因子。
文题释义:
颅骨锁骨发育不全(cleidocranial dysplasia,CCD):是一种广泛累及包括锁骨、颅骨在内的整个骨骼系统的常染色体显性遗传性疾病(MM119600),出生发病率约为1∶100 000;研究表明RUNX2基因杂合突变、基因插入、缺失等是造成颅骨锁骨发育不全的重要原因。
Runx2基因:Runx相关因子(runt-related gene,Runxx)是一类转录因子蛋白的统称,主要有Runxl、Runx2和Runx3,其中 Runx2基因位于人类常染色体的6p21,长约220 kb,包括8个外显子,具有和其它家族成员相似的Runt结构域,是骨发育过程中调节骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化和成熟最关键的转录因子。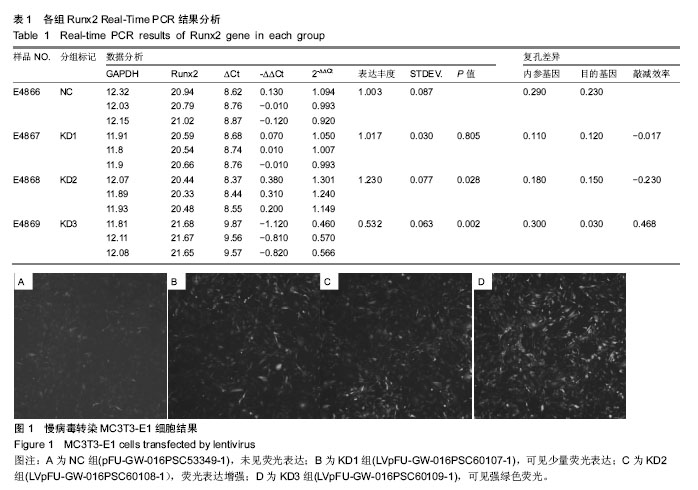
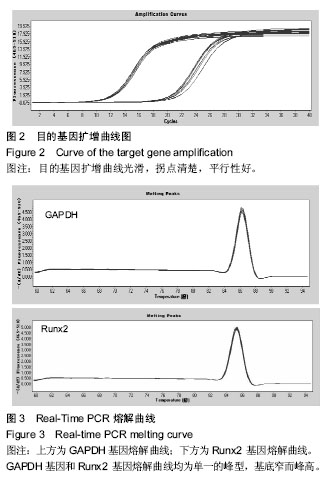
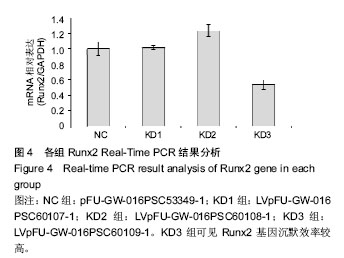
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
颅骨锁骨发育不全(cleidocranial dysplasia,CCD):是一种广泛累及包括锁骨、颅骨在内的整个骨骼系统的常染色体显性遗传性疾病(MM119600),出生发病率约为1∶100 000;研究表明RUNX2基因杂合突变、基因插入、缺失等是造成颅骨锁骨发育不全的重要原因。
Runx2基因:Runx相关因子(runt-related gene,Runxx)是一类转录因子蛋白的统称,主要有Runxl、Runx2和Runx3,其中 Runx2基因位于人类常染色体的6p21,长约220 kb,包括8个外显子,具有和其它家族成员相似的Runt结构域,是骨发育过程中调节骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化和成熟最关键的转录因子。
文题释义:
颅骨锁骨发育不全(cleidocranial dysplasia,CCD):是一种广泛累及包括锁骨、颅骨在内的整个骨骼系统的常染色体显性遗传性疾病(MM119600),出生发病率约为1∶100 000;研究表明RUNX2基因杂合突变、基因插入、缺失等是造成颅骨锁骨发育不全的重要原因。
Runx2基因:Runx相关因子(runt-related gene,Runxx)是一类转录因子蛋白的统称,主要有Runxl、Runx2和Runx3,其中 Runx2基因位于人类常染色体的6p21,长约220 kb,包括8个外显子,具有和其它家族成员相似的Runt结构域,是骨发育过程中调节骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化和成熟最关键的转录因子。