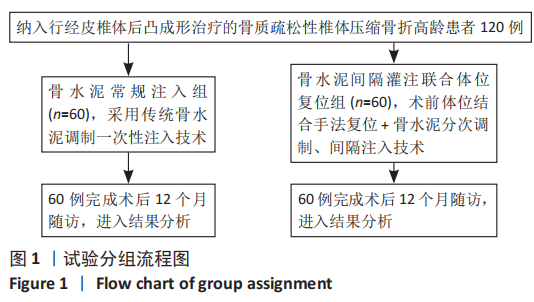
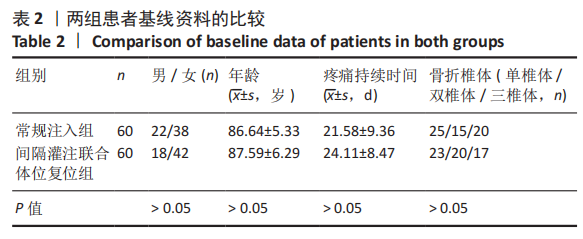
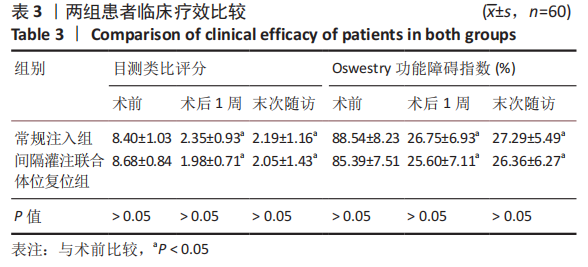
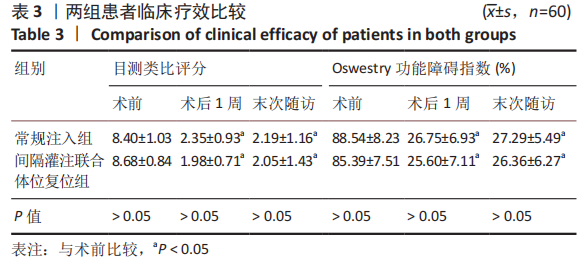
[1] MCCARTHY J, DAVIS A. Diagnosis and Management of Vertebral Compression Fractures. Am Fam Physician. 2016;94(1):44-50.
[2] LONG Y, YI W, YANG D. Advances in Vertebral Augmentation Systems for Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures. Pain Res Manag. 2020;2020:3947368.
[3] MEDIN E, GOUDE F, MELBERG HO, et al. European Regional Differences in All-Cause Mortality and Length of Stay for Patients with Hip Fracture. Health Economics. 2015;24 Suppl 2:53-64.
[4] LING X, CUMMINGS SR, MINGWEI Q, et al. Vertebral fractures in Beijing, China: the Beijing Osteoporosis Project. J Bone Miner Res. 2000;15(10):2019-2025.
[5] YOO JE, SHIN DW, HAN K, et al. Association of Female Reproductive Factors With Incidence of Fracture Among Postmenopausal Women in Korea. JAMA network open. 2021;4(1):e2030405.
[6] LEE YL, YIP KM. The osteoporotic spine. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996; (323):91-97.
[7] GOLDSTEIN CL, CHUTKAN NB, CHOMA TJ, et al. Management of the Elderly With Vertebral Compression Fractures. Neurosurgery. 2015; 77 Suppl 4:S33-45.
[8] NORIEGA D, MARCIA S, THEUMANN N, et al. A prospective, international, randomized, noninferiority study comparing an implantable titanium vertebral augmentation device versus balloon kyphoplasty in the reduction of vertebral compression fractures (SAKOS study). Spine J. 2019;19(11):1782-1795.
[9] CLARK W, BIRD P, GONSKI P, et al. Safety and efficacy of vertebroplasty for acute painful osteoporotic fractures (VAPOUR): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2016; 388(10052):1408-1416.
[10] 杨惠林,李茂,王根林,等.勿忽视骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折经皮椎体强化术后病椎再骨折[J].中华创伤杂志,2015,31(11): 961-962.
[11] VENMANS A, KLAZEN CA, VAN ROOIJ WJ, et al. Postprocedural CT for perivertebral cement leakage in percutaneous vertebroplasty is not necessary--results from VERTOS II. Neuroradiology. 2011;53(1):19-22.
[12] HULME PA, KREBS J, FERGUSON SJ, et al. Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty: a systematic review of 69 clinical studies. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(17):1983-2001.
[13] HUANG S, ZHU X, XIAO D, et al. Therapeutic effect of percutaneous kyphoplasty combined with anti-osteoporosis drug on postmenopausal women with osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture and analysis of postoperative bone cement leakage risk factors: a retrospective cohort study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):452.
[14] KIM HJ, ZUCKERMAN SL, CERPA M, et al. Incidence and Risk Factors for Complications and Mortality After Vertebroplasty or Kyphoplasty in the Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture-Analysis of 1,932 Cases From the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement. Global Spine J. 2020: 2192568220976355.
[15] 江晓兵,莫凌,梁德,等.骨水泥在椎体骨折线内弥散情况对椎体成形术治疗效果的影响[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2014,11(2): 144-149.
[16] 贾建军,李大川,徐炜,等.骨科手术中骨水泥填充物的研究进展[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2020,35(1):109-111.
[17] 马远征,王以朋,刘强,等.中国老年骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2018)[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2018,24(12):1541-1567.
[18] SOZZI C, TRENTADUE M, NICOLI L, et al. Utility of vertebral biopsy before vertebroplasty in patients with diagnosis of vertebral compression fracture. Radiol Med. 2021. doi: 10.1007/s11547-021-01353-9.
[19] 车艳军,李宏倬,牛建民,等.骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折合并腰椎退变性疾病的治疗策略及疗效观察[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2013, 19(7):675-680.
[20] 刘滔,张志明,史金辉,等.骨水泥温度梯度灌注技术在经皮椎体后凸成形术中的应用[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2015,25(12):1073-1078.
[21] 杨惠林,牛国旗,王根林,等.椎体后凸成形术治疗周壁破损的骨质疏松性椎体骨折[J].中华骨科杂志,2006,26(3):165-169.
[22] ZHUANG M, CAI B, WANG F. Effectiveness and safety of percutaneous kyphoplasty combined with zoledronic acid in treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a meta-analysis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2021. doi: 10.1007/s00402-021-03858-4.
[23] YI H, CHEN T, GAN J, et al. Effects of percutaneous kyphoplasty combined with zoledronic acid injection on osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture and bone metabolism indices. J Neurosurg Sci. 2020. doi: 10.23736/S0390-5616.20.05117-6.
[24] ZHANG J, ZHANG T, XU X, et al. Zoledronic acid combined with percutaneous kyphoplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic compression fracture in a single T12 or L1 vertebral body in postmenopausal women. Osteoporos Int. 2019;30(7):1475-1480.
[25] Pan C, Liu X, Li T, et al. Kinetic of bone turnover markers after osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures in postmenopausal female. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018;13(1):314.
[26] 陈卫.国际视野下的中国人口老龄化[J].北京大学学报(哲学社会科学版),2016,53(6):82-92.
[27] HU KZ, CHEN SC, XU L. Comparison of percutaneous balloon dilation kyphoplasty and percutaneous vertebroplasty in treatment for thoracolumbar vertebral compression fractures. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(1 Suppl):96-102.
[28] MARCIA S, MUTO M, HIRSCH JA, et al. What is the role of vertebral augmentation for osteoporotic fractures? A review of the recent literature. Neuroradiology. 2018;60(8):777-783.
[29] FIRANESCU CE, DE VRIES J, LODDER P, et al. Vertebroplasty versus sham procedure for painful acute osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (VERTOS IV): randomised sham controlled clinical trial. BMJ. 2018;361:k1551.
[30] PATEL U, SKINGLE S, CAMPBELL GA, et al. Clinical profile of acute vertebral compression fractures in osteoporosis. Br J Rheumatol. 1991; 30(6):418-421.
[31] CHENG X, LONG HQ, XU JH, et al. Comparison of unilateral versus bilateral percutaneous kyphoplasty for the treatment of patients with osteoporosis vertebral compression fracture (OVCF): a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Spine J. 2016;25(11):3439-3449.
[32] 徐宝山,胡永成.经皮椎体后凸成形术的临床应用进展[J].中华骨科杂志,2003,23(5):271-274.
[33] LIN TY, LIU YC, WANG YC, et al. Cement Augmentation for Single-Level Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture: Comparison of Vertebroplasty With High-Viscosity Cement and Kyphoplasty. World Neurosurg. 2020;141:e266-e270.
[34] ZENG TH, WANG YM, YANG XJ, et al. The clinical comparative study on high and low viscosity bone cement application in vertebroplasty. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(10):18855-18860.
[35] 刘志强,周云龙,雷飞,等.不同时相骨水泥推注对经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折疗效的影响[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2020,34(4):435-441.
[36] PHILLIPS FM. Minimally invasive treatments of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(15 Suppl): S45-S53.
[37] MCCONNELL CT JR, WIPPOLD FJ 2ND, RAY CE JR, et al. ACR appropriateness criteria management of vertebral compression fractures. J Am Coll Radiol. 2014;11(8):757-763.
[38] CHIRAS J, DEPRIESTER C, WEILL A, et al. Percutaneous vertebral surgery. Technics and indications. J Neuroradiol.1997;24(1):45-59.
[39] WICHMANN S, KIRSCHBAUM C, BOHME C, et al. Cortisol stress response in post-traumatic stress disorder, panic disorder, and major depressive disorder patients. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2017;83: 135-141.
[40] QI H, QI J, GAO J, et al. The Impact of Bone Mineral Density on Bone Metabolism and the Fracture Healing Process in Elderly Chinese Patients With Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures. J Clin Densitom. 2021;24(1):135-145.
[41] ENDO T, OHBA T, OBA H, et al. Prevalence and Key Radiographic Spinal Malalignment Parameters Associated with the Risk of Pulmonary Function Impairment in Patients Treated Surgically to Correct Adult Spinal Deformity. Spine Surg Relat Res. 2020;4(4):347-353.
[42] KREGE JH, KENDLER D, KROHN K, et al. Relationship Between Vertebral Fracture Burden, Height Loss, and Pulmonary Function in Postmenopausal Women With Osteoporosis. J Clin Densitom. 2015; 18(4):506-511.
[43] HOYT D, URITS I, ORHURHU V, et al. Current Concepts in the Management of Vertebral Compression Fractures. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2020;24(5):16.
[44] 庞巨涛,张新虎,孙建华,等.经皮球囊扩张椎体后凸成形后椎体再骨折的危险:回顾性多因素分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2019, 23(8):1182-1187.
[45] DONG R, CHEN L, GU Y, et al. Improvement in respiratory function after vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty. Int Orthop. 2009;33(6):1689-1694.
[46] SHENG S, ZHENZHONG S, WEIMIN J, et al. Improvement in Pulmonary Function of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Patients With Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures (OVCFs) After Kyphoplasty Under Local Anesthesia. Int Surg. 2015;100(3):503-509.
[47] NIKOOBAKHT M, GERSZTEN PC, SHOJAEI SF, et al. Percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty in the treatment of vertebral compression fractures: a single-center analysis of pain and quality of life outcomes. Br J Neurosurg. 2021;35(2):166-169.
[48] LEE MJ, DUMONSKI M, CAHILL P, et al. Percutaneous treatment of vertebral compression fractures: a meta-analysis of complications. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34(11):1228-1232.
[49] MISHRA PK, DWIVEDI R, DHILLON CS. Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture and Single Balloon Extrapedicular Kyphoplasty: Findings and Technical Considerations. Bull Emerg Trauma. 2020; 8(1):34-40.
[50] DERAMOND H, MATHIS JM. Vertebroplasty in osteoporosis. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2002;6(3):263-268.
|