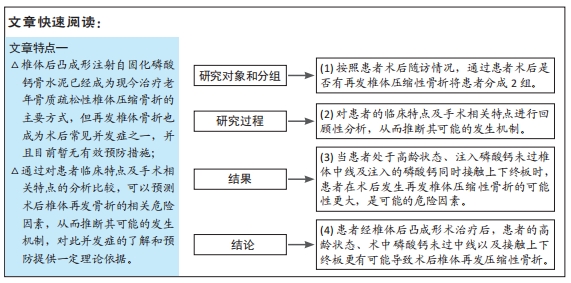
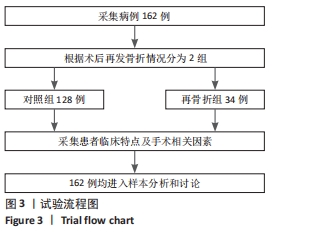
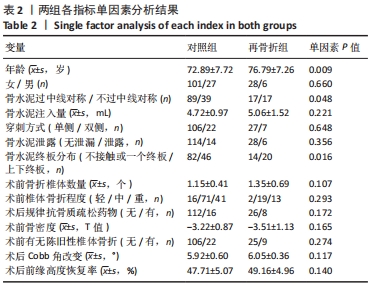
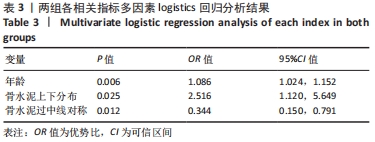
[1] LIU J, TANG J, ZHANG Y, et al. Percutaneous Vertebral Augmentation for Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture in the Midthoracic Vertebrae (T5-8): A Retrospective Study of 101 Patients with 111 Fractured Segments. World Neurosurg. 2019;122:e1381-e1387.
[2] POURTAHERI S, LUO W, CUI C, et al. Vertebral Augmentation is Superior to Nonoperative Care at Reducing Lower Back Pain for Symptomatic Osteoporotic Compression Fractures: A Meta-Analysis. Clin Spine Surg. 2018;31(8):339-344.
[3] MAZZANTINI M, FIGLIOMENI A, BOTTAI V, et al. High rate of vertebral refracture after vertebroplasty in patients taking glucocorticoids: a prospective two-year study. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2020;38(4):649-653.
[4] WANG WF, LIN CW, XIE CN, et al. The association between sarcopenia and osteoporotic vertebral compression refractures. Osteoporos Int. 2019;30(12):2459-2467.
[5] 贾小林,谭祖键,杨阜滨,等.磷酸钙骨水泥与传统骨水泥后凸成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体骨折的比较[J].中国骨与关节杂志, 2016,5(5):391-394.
[6] RHO YJ, CHOE WJ, CHUN YI. Risk factors predicting the new symptomatic vertebral compression fractures after percutaneous vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty. Eur Spine J. 2012;21(5):905-911.
[7] LIU H, ZHANG J, LIANG X, et al. Distribution Pattern Making Sense: Patients Achieve Rapider Pain Relief with Confluent Rather Than Separated Bilateral Cement in Percutaneous Kyphoplasty for Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures. World Neurosurg. 2019;126:e1190-e1196.
[8] SUN HB, JING XS, LIU YZ, et al. The Optimal Volume Fraction in Percutaneous Vertebroplasty Evaluated by Pain Relief, Cement Dispersion, and Cement Leakage: A Prospective Cohort Study of 130 Patients with Painful Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture in the Thoracolumbar Vertebra. World Neurosurg. 2018; 114:e677-e688.
[9] YU W, LIANG D, YAO Z, et al. Risk factors for recollapse of the augmented vertebrae after percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral fractures with intravertebral vacuum cleft. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(2):e5675.
[10] KOLANU N, SILVERSTONE EJ, HO BH, et al. Clinical Utility of Computer-Aided Diagnosis of Vertebral Fractures From Computed Tomography Images. J Bone Miner Res. 2020;35(12):2307-2312.
[11] LI Y, YAN L, CAI S, et al. The prevalence and under-diagnosis of vertebral fractures on chest radiograph. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018;19(1): 235.
[12] JAEBLON T. Polymethylmethacrylate: properties and contemporary uses in orthopaedics. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2010;18(5):297-305.
[13] PATEL H, CM RK, AA P, et al. The Effect of Primer on Bond Strength of Silicone Prosthetic Elastomer to Polymethylmethacrylate: An in vitro Study. J Clin Diagn Res. 2015;9(3):ZC38-ZC42.
[14] 杨中华,崔青,魏华,等.经皮椎体成形术磷酸钙骨水泥治疗老年骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2010,16(6): 439-441.
[15] HU L, SUN H, WANG H, et al. Cement injection and postoperative vertebral fractures during vertebroplasty. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019; 14(1):228.
[16] KIM YY, RHYU KW. Recompression of vertebral body after balloon kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture. Eur Spine J. 2010;19(11):1907-1912.
[17] ZHU J, ZHANG K, LUO K, et al. Mineralized Collagen Modified Polymethyl Methacrylate Bone Cement for Osteoporotic Compression Vertebral Fracture at 1-Year Follow-up. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2019; 44(12):827-838.
[18] DENG D, LIAN Z, CUI W, et al. Function of low back muscle exercise: Preventive effect of refracture analysis of postoperative vertebral fractures. Orthopade. 2019;48(4):337-342.
[19] ZHANG J, FAN Y, HE X, et al. Bracing after percutaneous vertebroplasty for thoracolumbar osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures was not effective. Clin Interv Aging. 2019;14:265-270.
[20] HUANG ZF, XIA P, LIU K, et al. Analysis of Risk Factors of New Fracture of Vertebral Body After Percutaneous Kyphoplasty in Patients with Primary Osteoporotic Fracture of Thoracic and Lumbar Spine. J Biomater Tiss Eng. 2018,8(5):756-759.
[21] LUO J, ANNESLEY-WILLIAMS DJ, ADAMS MA, et al. How are adjacent spinal levels affected by vertebral fracture and by vertebroplasty? A biomechanical study on cadaveric spines. Spine J. 2017;17(6):863-874.
[22] XIE L, ZHAO ZG, ZHANG SJ, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty versus conservative treatment for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: An updated meta-analysis of prospective randomized controlled trials. Int J Surg. 2017;47:25-32.
[23] PENG Y, DU X, HUANG L, et al. Optimizing bone cement stiffness for vertebroplasty through biomechanical effects analysis based on patient-specific three-dimensional finite element modeling. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2018;56(11):2137-2150.
[24] ROTTER R, PFLUGMACHER R, KANDZIORA F, et al. Biomechanical in vitro testing of human osteoporotic lumbar vertebrae following prophylactic kyphoplasty with different candidate materials. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32(13):1400-1405.
[25] SIRIS ES, MILLER PD, BARRETT-CONNOR E, et al. Identification and fracture outcomes of undiagnosed low bone mineral density in postmenopausal women: results from the National Osteoporosis Risk Assessment. JAMA. 2001;286(22):2815-2822.
[26] 黄天霁,寇玉辉,殷晓峰,等.椎体强化术后再发椎体骨折的临床特点和危险因素[J].北京大学学报(医学版),2015,47(2):237-241.
[27] 黄何平,宁亮生,温志宏.跟骨骨密度及骨强度与运动的关系[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(46):9134-9137.
[28] TSENG YY, SU CH, LUI TN, et al. Prospective comparison of the therapeutic effect of teriparatide with that of combined vertebroplasty with antiresorptive agents for the treatment of new-onset adjacent vertebral compression fracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty. Osteoporos Int. 2012;23(5):1613-1622.
[29] GERTZ BJ, CLEMENS JD, HOLLAND SD, et al. Application of a new serum assay for type I collagen cross-linked N-telopeptides: assessment of diurnal changes in bone turnover with and without alendronate treatment. Calcif Tissue Int. 1998;63(2):102-106.
[30] CHEN CH, FAN P, XIE XH, et al. Risk Factors for Cement Leakage and Adjacent Vertebral Fractures in Kyphoplasty for Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures. Clin Spine Surg. 2020;33(6):E251-E255.
[31] YAMAUCHI K, ADACHI A, KAMEYAMA M, et al. A risk factor associated with subsequent new vertebral compression fracture after conservative therapy for patients with vertebral compression fracture: a retrospective observational study. Arch Osteoporos. 2020;15(1):9.
[32] TAKAHASHI S, HOSHINO M, YASUDA H, et al. Development of a scoring system for predicting adjacent vertebral fracture after balloon kyphoplasty. Spine J. 2019;19(7):1194-1201.
[33] ZHANG L, WANG Q, WANG L, et al. Bone cement distribution in the vertebral body affects chances of recompression after percutaneous vertebroplasty treatment in elderly patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Clin Interv Aging. 2017;12:431-436.
[34] XU K, LI YL, SONG F, et al. Influence of the distribution of bone cement along the fracture line on the curative effect of vertebral augmentation. J Int Med Res. 2019;47(9):4505-4513.
[35] YU W, XU W, JIANG X, et al. Risk Factors for Recollapse of the Augmented Vertebrae After Percutaneous Vertebral Augmentation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2018;111: 119-129.
[36] 张大鹏,毛克亚,强晓军,等.椎体增强术后骨水泥分布形态分型及其临床意义[J].中华创伤杂志,2018,34(2):130-137.
[37] WANG DG, LI Y, YIN HL, et al. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of optimal distribution model of vertebroplasty. Ann Palliat Med. 2020; 9(3):1062-1072.
[38] LI YX, MO GY, ZHANG SC, et al. Cement for Treating Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures: Finite Element Study and Clinical Outcomes. J Biomater Tiss eng. 2018;8(12):1652-1657.
[39] BOGER A, HEINI P, WINDOLF M, et al. Adjacent vertebral failure after vertebroplasty: a biomechanical study of low-modulus PMMA cement. Eur Spine J. 2007;16(12):2118-2125.
[40] STEINMANN J, TINGEY CT, CRUZ G, et al. Biomechanical comparison of unipedicular versus bipedicular kyphoplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(2):201-205.
[41] SUN HL, LI CD. Comparison of unilateral and bilateral percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2016;11(1): 156.
[42] ZHU SQ, SU QJ, ZHANG YS, et al. Risk factors of cemented vertebral refracture after percutaneous vertebral augmentation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neuroradiology. 2020;62(11):1353-1360.
|