中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (28): 4494-4499.doi: 10.12307/2022.284
• 组织工程骨材料 tissue-engineered bone • 上一篇 下一篇
经皮椎体后凸成形与椎体成形治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折: 骨水泥渗漏与术后疼痛、伤椎Cobb角、步态恢复的关系
李友文,郑兴平,曾建洪,陈 渝
- 内江市东兴区人民医院骨科,四川省内江市 641100
Percutaneous kyphoplasty and percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: relationship of bone cement leakage with postoperative pain, Cobb angle of injured vertebrae, and gait recovery
Li Youwen, Zheng Xingping, Zeng Jianhong, Chen Yu
- Department of Orthopedics, People’s Hospital of Dongxing District, Neijiang 641100, Sichuan Province, China
摘要:

文题释义:
经皮椎体成形:是指经皮通过椎弓根或椎弓根外向椎体内注入骨泥,以达到增加椎体强度和稳定性、防止塌陷、缓解疼痛目的的手术。
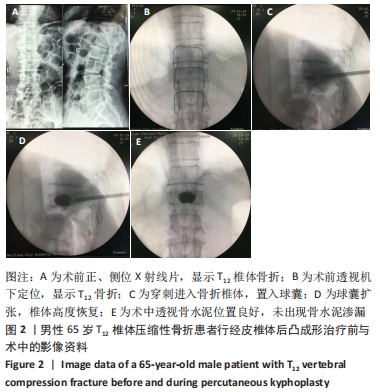
经皮椎体后凸成形:在C形臂X射线机透视指引下,经椎弓根外途径向椎体置管,插入球囊,球囊扩张恢复椎体高度,在椎体内形成空腔,骨水泥可以在低压力下注射,从而显著减少了骨水泥渗漏的风险。
背景:经皮椎体成形与经皮椎体后凸成形为治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折安全有效的手术选择,二者各有优缺点。
目的:探讨经皮椎体后凸成形与椎体成形对骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折患者早中期步态的影响。
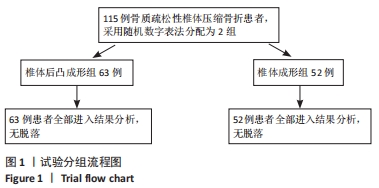
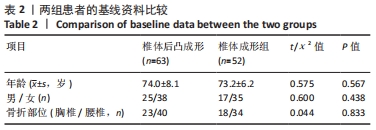
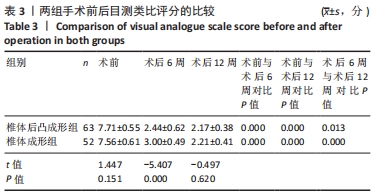
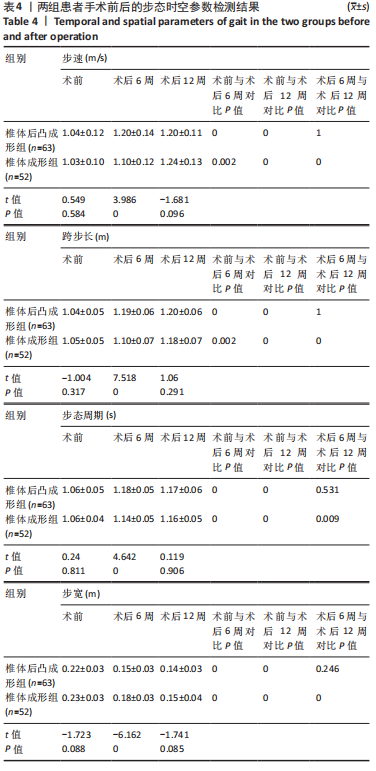
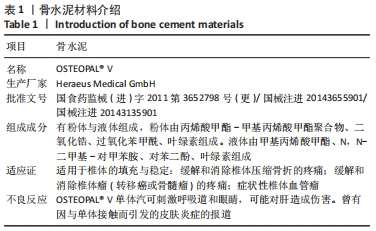
方法:选择2018年3月至2020年7月内江市东兴区人民医院脊柱外科收治的115例骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折患者,采用随机数字表法分为2组,分别进行经皮椎体后凸成形骨水泥注射治疗(63例)与经皮椎体成形骨水泥注射治疗(52例),术中记录骨折椎体骨水泥用量及骨水泥渗漏情况。术前及术后12周进行X射线片检查,测量伤椎Cobb角;术前、术后6周及术后12周对两组患者进行步态测试及疼痛评估,疼痛评估采用目测类比评分。研究得到内江市东兴区人民医院研究伦理委员会的批准。
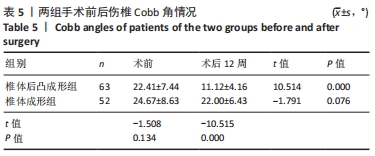
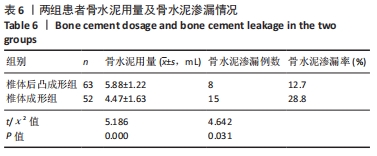
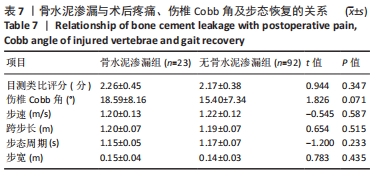
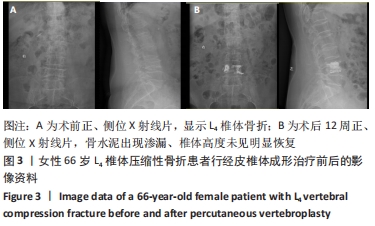
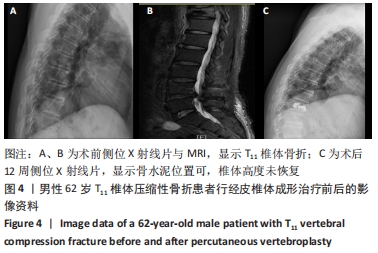
结果与结论:①椎体后凸成形组的骨水泥用量多于椎体成形组(P < 0.05),骨水泥渗漏率低于椎体成形组(12.7%,28.8%,P < 0.05);②与术前比较,椎体后凸成形组术后12周的伤椎Cobb角降低(P < 0.05),椎体成形组无明显变化(P > 0.05);椎体后凸成形组术后12周的伤椎Cobb角低于椎体成形组(P < 0.05);③两组术后的疼痛情况与步行运动功能均有明显改善,椎体后凸成形组术后6周的疼痛情况与步行运动功能改善优于椎体成形组(P < 0.05),术后12周两组疼痛情况与步行运动功能比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);④术后12周时,骨水泥渗漏组术后疼痛、伤椎Cobb角及步态参数与非骨水泥渗漏组比较差异均无显著性意义(P﹥0.05);⑤结果表明,相较于经皮椎体成形,经皮椎体后凸成形可在治疗后早期恢复骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折患者的步行运动功能,具有更好的骨折复位和镇痛效果,且较少发生骨水泥渗漏。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4522-7861 (李友文)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号: