中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (5): 689-693.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1910
• 肌肉肌腱韧带组织构建 tissue construction of the muscle, tendon and ligament • 上一篇 下一篇
桑黄粗多糖对被动吸烟模型小鼠运动能力和骨骼肌自由基代谢的影响
万华喆1,柴广新2,肖晓玲3,黄文英4
- 1南昌航空大学科技学院,江西省南昌市 332020;2华东师范大学体育与健康学院,上海市 200241;3江西科技职业学院,江西省南昌市 330200;4江西师范大学体育学院,江西省南昌市 330022
Effects of phellinus igniarius crude polysaccharides on sporting ability and free radical metabolism of skeletal muscle in mice suffering passive smoking
Wan Huazhe1, Chai Guangxin2, Xiao Xiaoling3, Huang Wenying4
- 1Science and Technology College of Nanchang Hangkong University; 2Physical Education and Health School of East China Normal University; 3Jiangxi University of Science and Technology; 4Sports College of Jiangxi Normal University, Nanchang 330022, Jiangxi Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
脂质过氧化反应:氧自由基反应和脂质过氧化反应在机体的新陈代谢过程中起着重要的作用,正常情况下两者处于协调与动态平衡状态,维持着体内许多生理生化反应和免疫反应。一旦这种协调与动态平衡产生紊乱与失调,就会引起一系列的新陈代谢失常和免疫功能降低,形成氧自由基连锁反应,损害生物膜及其功能,以致形成细胞透明性病变、纤维化,大面积细胞损伤造成进神经、组织、器官等损伤。这种反应就叫脂质过氧化。
自由基:自由基又称游离基,是指外层轨道上具有未配对电子的原子、分子、离子或原子团。自由基具有非常强的化学性,易反应形成新自由基,从而呈现明显连续反应趋势。自由基可来源于机体自身,也可来源于侵犯机体的外源化合物或物理因子。外源性自由基是指由体外物理因子(如:运动及辐射等)产生的。
背景:香烟烟雾中含有大量多种类型氧自由基和细胞毒性成分,被动吸烟会损害呼吸、心血管系统功能,导致骨骼肌氧化损伤和运动能力下降。
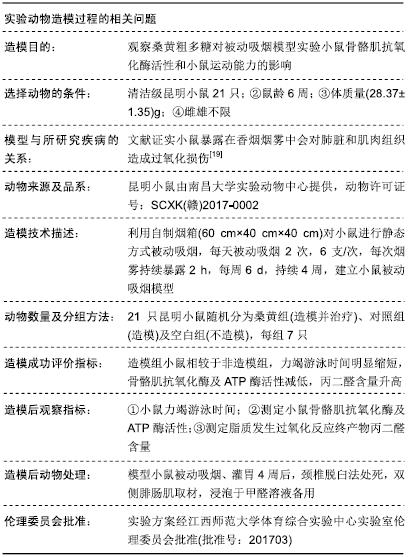
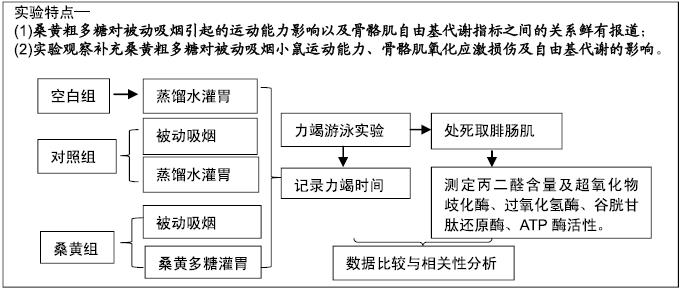
目的:观察具有抗氧化应激作用的桑黄粗多糖对被动吸烟模型小鼠运动能力和骨骼肌氧化应激的影响,为被动吸烟小鼠骨骼肌过氧化损伤和运动能力下降的防治提供思路。
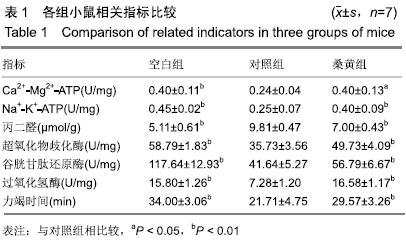
方法:将21只雄性昆明小鼠随机分为3组:桑黄组采用桑黄粗多糖灌胃然后被动吸烟,对照组采用蒸馏水灌胃然后被动吸烟,空白组单纯蒸馏水灌胃。各组干预持续4周,然后进行1次力竭游泳运动,记录各组小鼠游泳力竭时间。运动结束后检测小鼠双侧腓肠肌超氧化物歧化酶、过氧化氢酶、谷胱甘肽还原酶与Ca2+-Mg2+-ATP、Na+-K+-ATP酶活性及丙二醛含量。
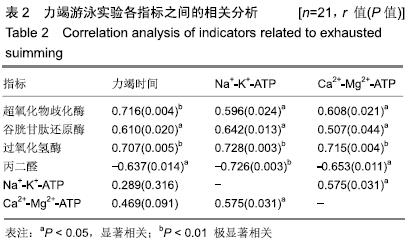
结果与结论:①与空白组相比,对照组小鼠力竭游泳时间缩短(P < 0.01);与对照组相比,桑黄组小鼠力竭游泳时间延长(P < 0.01);②与空白组相比,对照组小鼠超氧化物歧化酶、谷胱甘肽还原酶、过氧化氢酶活性和Ca2+-Mg2+-ATP、Na+-K+-ATP酶活性显著降低(P < 0.01),丙二醛含量显著升高(P < 0.01);③与对照组相比,桑黄组小鼠超氧化物歧化酶、谷胱甘肽还原酶、过氧化氢酶活性和Ca2+-Mg2+-ATP、Na+-K+-ATP活性升高(P < 0.05,P < 0.01),丙二醛含量显著降低(P < 0.01);④相关性分析显示:力竭游泳时间与谷胱甘肽还原酶、过氧化氢酶、超氧化物歧化酶活性呈正相关(r > 0.6,P < 0.05),与丙二醛呈负相关(r = -0.637,P < 0.05);Ca2+-Mg2+-ATP、Na+-K+-ATP酶活性与谷胱甘肽还原酶、过氧化氢酶及超氧化物歧化酶活性呈正相关(r > 0.6,P < 0.05),与丙二醛呈负相关(r < -0.6,P < 0.05);⑤结果提示:桑黄粗多糖可以提高被动吸烟模型小鼠骨骼肌抗氧化酶活性,减轻脂质过氧化反应,提高运动能力。实验方案经江西师范大学体育综合实验中心实验室伦理委员会批准(批准号:201703)。
ORCID: 0000-0002-1367-3656(万华喆)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: