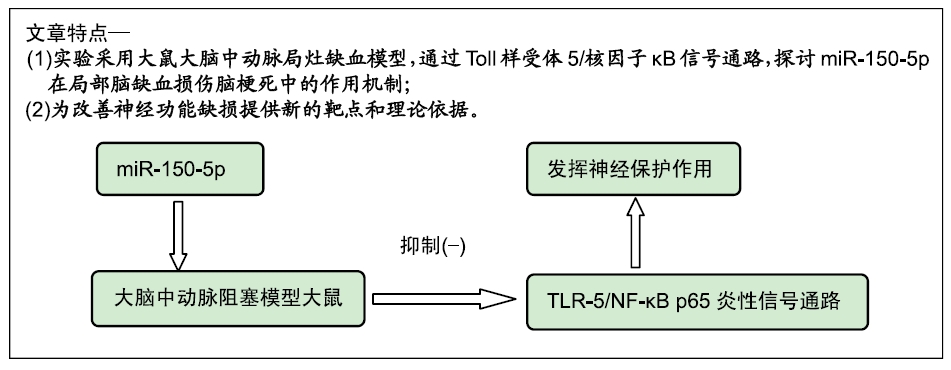
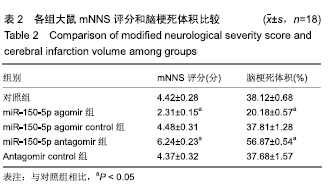
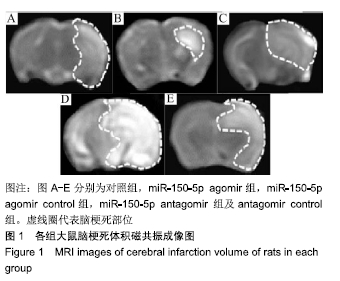
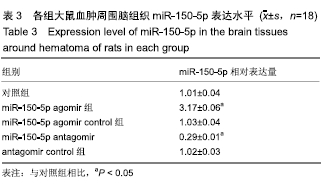
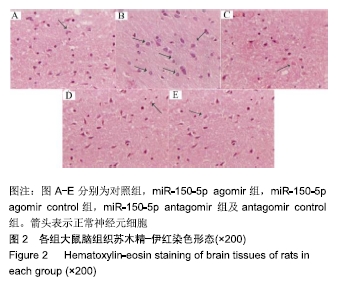
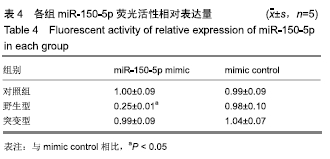
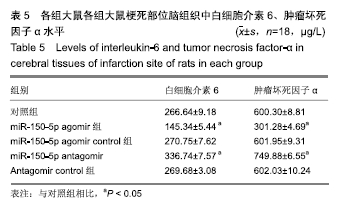
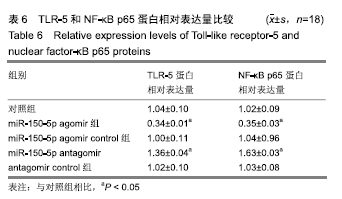
[1] 王立新,李惠平.人脐带间充质干细胞不同移植途径治疗缺血性脑损伤以及生物发光技术示踪的研究及进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(33):5407-5412.
[2] YOU S, SAXENA A, WANG X, et al. Efficacy and safety of intravenous recombinant tissue plasminogen activator in mild ischaemic stroke: a meta-analysis. Stroke Vasc Neurol. 2018; 3(1):22-27.
[3] 姜敏,王继先,余波,等.丰富环境对小鼠缺血性脑损伤后运动、社交功能的作用[J].中国康复理论与实践,2017,23(1):32-36.
[4] 荆利娜,高培毅,林燕,等.急性缺血性脑卒中病人FLAIR血管高信号与预后的相关性研究[J].国际医学放射学杂志,2017,40(6): 647-655.
[5] DROMMELSCHMIDT K, SERDAR M, BENDIX I, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles ameliorate inflammation-induced preterm brain injury. Brain Behav Immunr. 2017;2(60):220-232.
[6] XU S, ZHONG A, MA H, et al. Neuroprotective effect of salvianolic acid b against cerebral ischemic injury in rats via the CD40/NF-κB pathway associated with suppression of platelets activation and neuroinflammation. Brain Res. 2017; 8(1661):37-48.
[7] ELLOUMI N, FAKHFAKH R, ABIDA O, et al. Relevant genetic polymorphisms and kidney expression of Toll-like receptor (TLR)-5 and TLR-9 in lupus nephritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 2017; 190(3):328-339.
[8] 杨元,袁正洲,吕志宇,等.血管活性肠肽(VIP)对实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎(EAE)大鼠脑组织IL-17A含量的影响[J].中国比较医学杂志,2016,26(10):32-35.
[9] BAI L, SHI W, LIU J, et al. Protective effect of pilose antler peptide on cerebral ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury through Nrf-2/OH-1/NF-κB pathway. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017;9(102): 741-748.
[10] 邹燕,肖凯强,何雪梅,等.miRNAs 与血管新生关系的研究进展[J].山东医药,2018,58(10):106-109.
[11] 易朝晖,黄素丽,张艳炜,等.外周血miR-200c-3p、miR-99b-5p和miR-150-5p作为缺血性脑卒中生物标记物的研究[J].中华神经医学杂志,2015,14(6):597-603.
[12] 叶涛,朱路文,唐强,等.电针预处理对大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤后脑梗死体积及血清TNF-α、IL-10含量的影响[J].中国针灸,2017, 37(10):1093-1098.
[13] 何霞,崔璨,陈敏.骨髓间充质干细胞移植对实验性大鼠缺血性脑梗死免疫炎性反应的影响研究[J].中国免疫学杂志,2018,34(5): 13-18.
[14] 武晓灵,喻莉,龙鼎.suPAR及D-二聚体对创伤性颅脑损伤患者病情严重程度及预后的判断价值[J].实用医学杂志,2017,33(2): 234-237.
[15] HASANVAND A, ABBASZADEH A, DARABI S, et al. Evaluation of selenium on kidney function following ischemic injury in rats; protective effects and antioxidant activity. J Renal Inj Prev. 2017;6(2):93-98.
[16] RICE RA, PHAM J, LEE R J, et al. Microglial repopulation resolves inflammation and promotes brain recovery after injury. Glia. 2017;65(6):931-944.
[17] ZHU LH, ZHANG ZP, WANG FN, et al.Diffusion kurtosis imaging of microstructural changes in brain tissue affected by acute ischemic stroke in different locations.Neural Regen Res. 2019;14(2):272-279.
[18] 林泽明,何池忠,刘新通,等.miR-150与缺血性脑卒中患者二级预防预后的关系[J].广东医学,2016,37(22):3381-3384.
[19] BATAH J, DENÈVELARRAZET C, JOLIVOT PA, et al. Clostridium difficile flagella predominantly activate TLR5-linked NF-κB pathway in epithelial cells. Anaerobe. 2016;8(38):116-124.
[20] XIA B, HOU Y, CHEN H, et al. Long non-coding RNA ZFAS1 interacts with miR-150-5p to regulate Sp1 expression and ovarian cancer cell malignancy. Oncotarget. 2017;8(12): 19534.
[21] PENG L, CHEN G, ZHU Z, et al. Circular RNA ZNF609 functions as a competitive endogenous NA to regulate AKT3 expression by sponging miR-150-5p in Hirschsprung's disease. Oncotarget. 2017;8(1):808.
[22] YU J, FENG Y, WANG Y, et al. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor enhances the expression of miR-150-5p to suppress in prostate cancer progression by regulating MAP3K12. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2018;654(15):47-54.
[23] OKATO A, ARAI T, KOJIMA S, et al. Dual strands of pre-miR 150 (miR 150 5p and miR 150 3p) act as antitumor miRNAs targeting SPOCK1 in naïve and castration-resistant prostate cancer. Int J Oncol. 2017;51(1):245-256.
[24] 张友平,占大钱,陈华文,等.丹参酮ⅡA对脓毒症小鼠脑软膜微血流速度和脑组织炎性介质水平的干预作用[J].微循环学杂志, 2017,27(3):1-4.
[25] LIN Z, LIN H, LI W, et al. Complement Component C3 Promotes Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Mediated by TLR2/NFκB Activation in Diabetic Mice. Neurochem Res. 2018;43(8):1599-1607.
[26] VAEZ H, NAJAFI M, RAMESHRAD M, et al. AMPK activation by metformin inhibits local innate immune responses in the isolated rat heart by suppression of TLR 4-related pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2016;40:501-507.
[27] LEE RHC, LEE MHH, WU CYC, et al.Cerebral ischemia and neuroregeneration.Neural Regen Res. 2018;13(3):373-385.
[28] SHEN H, WU N, WANG Y, et al. Chloroquine attenuates paraquat-induced lung injury in mice by altering inflammation, oxidative stress and fibrosis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017; 46(Complete):16-22.
[29] SAMBANDAN S, AKBALIK G, KOCHEN L, et al. Activity-dependent spatially localized miRNA maturation in neuronal dendrites. Science. 2017;355(6325):634-637.
[30] TOSHKOV IA, GLEIBERMAN AS, METT VL, et al. Mitigation of Radiation-Induced Epithelial Damage by the TLR5 agonist entolimod in a mouse model of fractionated head and neck irradiation. Radiat Res. 2017;187(5):570.
[31] CHAICHANA P, CHANTRATITA N, BROD F, et al. A nonsense mutation in TLR5 is associated with survival and reduced IL-10 and TNF-α levels in human Melioidosis. PLoS Neglect Trop D. 2017;11(5):e0005587.
[32] 常洁,夏中元,罗兴均.丹皮酚对心肌缺血再灌注损伤大鼠模型肿瘤坏死因子-α和Toll样受体4表达的影响[J].中国老年学杂志, 2017,37(21):12-14.
[33] ZHENG Y, BU J, YU L, et al. Nobiletin improves propofol- induced neuroprotection via regulating Akt/mTOR and TLR 4/NF-κB signaling in ischemic brain injury in rats. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;7(91):494-503.
|