| [1] Rao Kondapally Seshasai S, Kaptoge S, Thompson A, et al. Diabetes mellitus, fasting glucose, and risk of cause-specific death. N Engl J Med. 2011;364(9):829-841.[2] Bo S, Ciccone G, Gancia R, et al. Mortality within the first 10 years of the disease in type 2 diabetic patients. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2006;16(1):8-12.[3] Lombardo MF, Iacopino P, Cuzzola M, et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus impairs the maturation of endothelial progenitor cells and increases the number of circulating endothelial cells in peripheral blood. Cytometry A. 2012;81(10):856-864.[4] Russell JS, Brown JM. Circulating mouse Flk1+/c-Kit+/CD45- cells function as endothelial progenitors cells (EPCs) and stimulate the growth of human tumor xenografts. Mol Cancer. 2014;13:177.[5] Pías-Peleteiro J, Campos F, Castillo J, et al.Endothelial progenitor cells as a therapeutic option in intracerebral hemorrhage.Neural Regen Res. 2017;12(4):558-561.[6] Hamed S, Brenner B, Roguin A. Nitric oxide: a key factor behind the dysfunctionality of endothelial progenitor cells in diabetes mellitus type-2. Cardiovasc Res. 2011;91(1):9-15.[7] 陈树春,宋光耀,孙阳,等. 初诊2型糖尿病患者外周血内皮祖细胞的研究[J]. 天津医药, 2010, 38(7): 549-551.[8] 夏文华,饶玉霞. 2型糖尿病患者内皮祖细胞数量和功能研究[J]. 咸宁学院学报(医学版), 2012, 26(1): 12-14.[9] Asahara T, Masuda H, Takahashi T, et al. Bone marrow origin of endothelial progenitor cells responsible for postnatal vasculogenesis in physiological and pathological neovascularization. Circ Res. 1999;85(3):221-228.[10] Hristov M, Schmitz S, Nauwelaers F, et al. A flow cytometric protocol for enumeration of endothelial progenitor cells and monocyte subsets in human blood. J Immunol Methods. 2012;381(1-2):9-13.[11] Ma XL, Sun XL, Wan CY, et al. Significance of circulating endothelial progenitor cells in patients with fracture healing process. J Orthop Res. 2012;30(11):1860-1866.[12] Sen S, McDonald SP, Coates PT, et al. Endothelial progenitor cells: novel biomarker and promising cell therapy for cardiovascular disease. Clin Sci (Lond). 2011;120(7): 263-283.[13] Zhou X, Patel D, Sen S, et al. Poly-ADP-ribose polymerase inhibition enhances ischemic and diabetic wound healing by promoting angiogenesis. J Vasc Surg. 2017;65(4):1161-1169.[14] Lin CP, Lin FY, Huang PH, et al. Endothelial progenitor cell dysfunction in cardiovascular diseases: role of reactive oxygen species and inflammation. Biomed Res Int. 2013; 2013:845037.[15] Barton M. Prevention and endothelial therapy of coronary artery disease. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2013;13(2):226-241.[16] Chen S, Sun L, Gao H, et al. Visfatin and oxidative stress influence endothelial progenitor cells in obese populations. Endocr Res. 2015;40(2):83-87.[17] 陈树春,宋光耀,孙阳,等. 2型糖尿病一级亲属内皮祖细胞与氧化应激[J].中华内科杂志,2012,51(3):197-200.[18] 陈树春,宋光耀.内皮祖细胞与氧化应激研究进展[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(6): 1119-1122.[19] Chen DD, Dong YG, Yuan H, et al. Endothelin 1 activation of endothelin A receptor/NADPH oxidase pathway and diminished antioxidants critically contribute to endothelial progenitor cell reduction and dysfunction in salt-sensitive hypertension. Hypertension. 2012;59(5):1037-1043.[20] Kulikowska-Karpińska E, Czerw K. Estimation of 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) concentration in the urine of cigarette smokers. Wiad Lek. 2015;68(1):32-38.[21] Tabur S, Aksoy ?N, Korkmaz H, et al. Investigation of the role of 8-OHdG and oxidative stress in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2015;36(4):2667-2674.[22] Liu JT, Chen YL, Chen WC, et al. Role of pigment epithelium-derived factor in stem/progenitor cell-associated neovascularization. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012;2012:871272.[23] Zaragoza C, Gomez-Guerrero C, Martin-Ventura JL, et al. Animal models of cardiovascular diseases. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011;2011:497841.[24] Tousoulis D, Andreou I, Antoniades C, et al. Role of inflammation and oxidative stress in endothelial progenitor cell function and mobilization: therapeutic implications for cardiovascular diseases. Atherosclerosis. 2008;201(2): 236-247.[25] Carracedo J, Merino A, Briceño C, et al. Carbamylated low-density lipoprotein induces oxidative stress and accelerated senescence in human endothelial progenitor cells. FASEB J. 2011;25(4):1314-1322.[26] Pickering RJ, Rosado CJ, Sharma A, et al. Recent novel approaches to limit oxidative stress and inflammation in diabetic complications. Clin Transl Immunology. 2018;7(4): e1016.[27] Sasaki S, Inoguchi T. The role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of diabetic vascular complications. Diabetes Metab J. 2012;36(4):255-261.[28] Ceretta LB, Réus GZ, Abelaira HM, et al. Increased oxidative stress and imbalance in antioxidant enzymes in the brains of alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Exp Diabetes Res. 2012;2012: 302682.[29] Hernández-Beltrán N, Moreno CB, Gutiérrez-Álvarez AM. Contribution of mitochondria to pain in diabetic neuropathy. Endocrinol Nutr. 2013;60(1):25-32.[30] Rochette L, Ghibu S, Muresan A, et al. Alpha-lipoic acid: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential in diabetes. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2015;93(12):1021-1027.[31] 陈树春,宋光耀,章冬梅,等. α-硫辛酸对高糖状态下内皮祖细胞的影响[J]. 细胞与分子免疫学杂志, 2012,28(3): 240-243.[32] Zhao M, Chen JY, Chu YD, et al.Efficacy of epalrestat plus α-lipoic acid combination therapy versus monotherapy in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a meta-analysis of 20 randomized controlled trials.Neural Regen Res. 2018; 13(6):1087-1095.[33] 王景尚,孙明月,黄烨,等. α-硫辛酸对血糖波动状态下2型糖尿病大鼠血管内皮细胞功能及PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β通路的影响[J]. 中国全科医学, 2017,20(24): 2965-2971. |
.jpg)
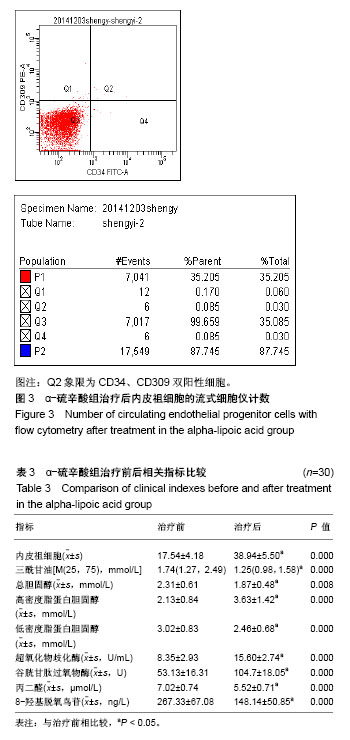

.jpg)