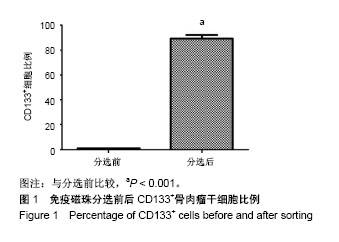
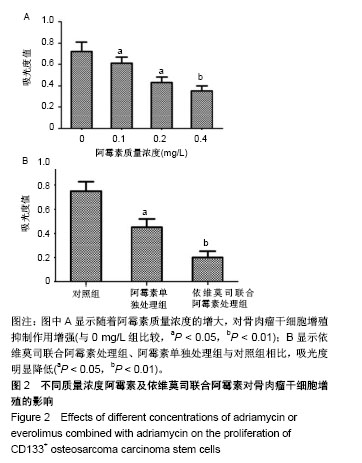
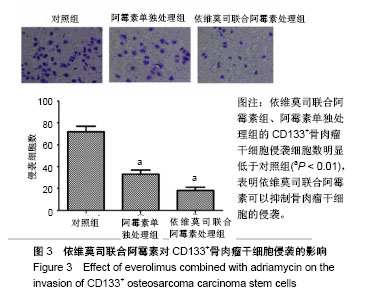
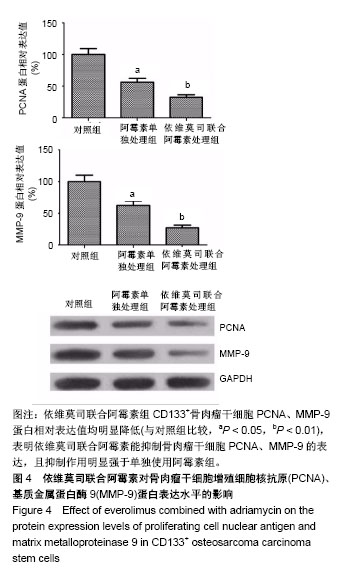
| [1] 姚阳.骨肉瘤的临床与研究现状[J]. 肿瘤,2005,25(3):201-204.[2] 燕太强,梁伟民,郭卫.骨肉瘤的诊疗和研究进展[J]. 中华临床医师杂志(电子版), 2012,6(17):4988-4990.[3] 管忠震,喻俪华,刘明镜,等.以阿霉素为主的联合化疗方案治疗恶性肿瘤227例临床观察[J].癌症,1988,7(5):349-352.[4] Kaya M. Prognostic Factors for Osteosarcoma Patients//Osteosarcoma. Tokyo: Springer. 2016:73-79.[5] Toguchida J. Genetics of Osteosarcoma//Osteosarcoma. Tokyo: Springer. 2016:3-17.[6] Mohseny AB, Szuhai K, Romeo S, et al. Osteosarcoma originates from mesenchymal stem cells in consequence of aneuploidization and genomic loss of Cdkn2. J Pathol. 2009; 219(3):294-305.[7] 邱俊骏,施鑫,赵建宁,等.骨肉瘤化疗耐药相关基因的研究进展[J]. 医学研究生学报,2005,8(2):164-166.[8] Basu-Roy U, Basilico C, Mansukhani A. Perspectives on cancer stem cells in osteosarcoma. Cancer Lett. 2013;338(1): 158-167.[9] Mutsaers AJ, Walkley CR. Cells of origin in osteosarcoma: mesenchymal stem cells or osteoblast committed cells. Bone. 2014;62:56-63.[10] Laplante M, Sabatini DM. mTOR signaling in growth control and disease. Cell. 2012;149(2):274-293.[11] Grabiner B, Wagle N, Allen EV,et al. Abstract PR04: mTOR mutations in cancer. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics. 2015; 14(7 Supplement):PR04-PR04.[12] Johnson SC, Rabinovitch PS, Kaeberlein M. mTOR is a key modulator of ageing and age-related disease. Nature. 2013; 493(7432):338-345.[13] 周荣平,廖小明,矢庆明,等.齐墩果酸通过 mTOR 信号通路促进骨肉瘤细胞凋亡[J].中华中医药杂志, 2016, 31(1): 222-225.[14] 马建辉.肾癌细胞mTOR信号通路异常与依维莫司作用机制[J].中华泌尿外科杂志, 2013, 34(3): 229-231.[15] 张旭.转移性肾细胞癌依维莫司中外研究安全性比较及不良反应管理经验[J].中华泌尿外科杂志, 2013, 34(6): 470-473.[16] 陈洪菊,屈艺,母得志. mTOR信号通路的生物学功能[J].生命的化学, 2010, 30(4): 555-561.[17] 陈豫,褚倩,郭娟,等.依维莫司对人非小细胞肺癌细胞系A549放射增敏作用[J].医药导报, 2014,33(12):1541-1544.[18] Mailand N, Gibbs-Seymour I, Bekker-Jensen S. Regulation of PCNA-protein interactions for genome stability. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013;14(5):269-282.[19] Kubota T, Nishimura K, Kanemaki MT, et al. The Elg1 replication factor C-like complex functions in PCNA unloading during DNA replication. Mol Cell. 2013;50(2):273-280.[20] 陆平,李云鹏,高岩,等.原癌基因Pim-3在胰腺癌组织中的表达及其与胰腺癌细胞增殖的相关性[J].癌变•畸变•突变,2014, 26(1): 45-48.[21] 张凤梅,李胜水,李双标,等. ILK, MMP-9在胰腺癌及其侵袭转移中的表达[J].诊断病理学杂志, 2013, 20(4): 236-238.[22] 李颖智,金海鸿,秦悦洋,等. VEGF, MMP-9 表达水平与骨巨细胞瘤侵袭性相关性[J].中国实验诊断学, 2013, 17(11): 1989-1991.[23] 孔飞飞,袁海花,王炯轶,等. Foxm1对非小细胞肺癌中MMP-2, MMP-9和迁移侵袭的影响[J].现代肿瘤医学, 2014, 22(8): 1775-1778.[24] Luetke A, Meyers PA, Lewis I, et al. Osteosarcoma treatment - where do we stand? A state of the art review. Cancer Treat Rev. 2014;40(4):523-532.[25] 陈楷,吕书军,付东,等.骨肉瘤凋亡与耐药相关机制的研究进展[J]. 中国骨与关节杂志,2015,4(1):45-49.[26] 朱忠胜,张春林.骨肉瘤干细胞研究现状[J].国际骨科学杂志, 2011,32(5): 296-299.[27] 郭卫,杨荣利,汤小东,等.成骨肉瘤新辅助化学药物治疗的疗效分析[J].中华医学杂志, 2004, 84(14): 1186-1190.[28] 司萌.骨肉瘤干细胞及其多药耐药性的体内外相关研究[D]. 济南:山东大学, 2013.[29] 杨联军,朱立新,包和婧,等.载阿霉素PLGA纳米微球的制备及其对人骨肉瘤MG63细胞的抑制作用[J].实用医学杂志, 2014, 30(4):528-531.[30] Guo Y, Wu M, Zhao J, et al. Advances in hypoxia microenvironment and chemotherapy-resistant of lung cancer. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2014;17(3):265-268.[31] 胡蓓蓓,林峰.多药耐药相关蛋白与骨肉瘤化疗耐药相关性[J]. 国际骨科学杂志, 2013, 34(1): 61-63.[32] 贺昭忠,吴承远.脑胶质瘤多药耐药基因表达及其对化疗药物敏感性[J].齐鲁医学杂志, 2002,17(2): 98-100.[33] 曹仕琼,李萍,尹太勇,等.姜黄素对人肝癌耐药细胞株Bel7402/ 5-FU多药耐药性的逆转作用[J].世界华人消化杂志,2012, 20(2): 135-139.[34] 王进,沈靖南.粉防己碱逆转骨肉瘤细胞系多药耐药性的研究[J]. 实用临床医学,2005, 6(7): 7-10.[35] 郭乔楠,陈意生.骨肉瘤多药耐药的研究进展[J].医学综述,2002, 8(8): 450-452.[36] 李杨玲,应美丹,杨波,等. Klf-4调控骨肉瘤肿瘤干细胞特性及转移能力的作用研究[C].第八届中国肿瘤学术大会暨第十三届海峡两岸肿瘤学术会议论文汇编, 2014.[37] 郑联合,张伟,韩涛,等.阿霉素可通过MAPK信号转导通路促进成骨肉瘤细胞凋亡[J].第四军医大学学报,2005,26(12): 1119-1121.[38] 许庆文,李岩松,朱荷根.大肠癌P53蛋白PCNA和CEA的表达与淋巴结转移的关系[J].华人消化杂志, 1998, 6(3): 244-246.[39] Stoimenov I, Helleday T. PCNA on the crossroad of cancer. Biochem Soc Trans. 2009;37(Pt 3):605-613.[40] Paradiso A, Rabinovich M, Vallejo C, et al. p53 and PCNA expression in advanced colorectal cancer: response to chemotherapy and long-term prognosis. Int J Cancer. 1996; 69(6):437-441.[41] Yu YL, Chou RH, Liang JH, et al. Targeting the EGFR/PCNA signaling suppresses tumor growth of triple-negative breast cancer cells with cell-penetrating PCNA peptides. PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e61362.[42] Liu Y, Bi T, Wang G, et al. Lupeol inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of human pancreatic cancer PCNA-1 cells through AKT/ERK pathways. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2015;388(3):295-304.[43] 张峻霄,王世阆,姚先莹.增殖细胞核抗原及肿瘤转移抑制基因nm23在外阴鳞状细胞癌的表达及其临床意义[J].海南医学, 2012, 23(10): 1-5.[44] 孙仁光,刘泽淼.多药耐药基因1和谷胱苷肽-S-转移酶-π在骨软组织肉瘤患者表达及其与化疗耐药关系[J].中国老年学杂志, 2015,35(20):5823-5825.[45] 孙玉满,杨俊泉,曹渤海,等.早期喉癌手术阴性切缘组织中 PCNA, COX-2表达与肿瘤局部复发的关系[J].临床与实验病理学杂志, 2014, 30(4): 408-410.[46] 高庆. MMP-2、MMP-9、TIMP-2在人脑胶质瘤中的表达及意义[D].郑州:郑州大学,2010. |
.jpg)
.jpg)