| [1] Otsuka T, Imura T, Nakagawa K, et al. Simulated microgravity culture enhances the neuroprotective effects of human cranial bone-derived mesenchymal stem cells in traumatic brain injury. Stem Cells Dev. 2018. doi: 10.1089/scd.2017.0299.[2] Monfrini M, Ravasi M, Maggioni D, et al. Comparing the different response of PNS and CNS injured neurons to mesenchymal stem cell treatment. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2018;86:16-24. [3] Tsui YP, Mung AK, Chan YS, et al. Hypoxic preconditioning of marrow-derived progenitor cells as a source for the generation of mature Schwann cells. J Vis Exp. 2017(124). [4] Ali EHA, Ahmed-Farid OA, Osman AAE. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate sodium nitrite-induced hypoxic brain injury in a rat model. Neural Regen Res. 2017;12(12):1990-1999.[5] Sakai K, Shimba K, Kotani K et al. A co-culture microtunnel technique demonstrating a significant contribution of unmyelinated Schwann cells to the acceleration of axonal conduction in Schwann cell-regulated peripheral nerve development. Integr Biol (Camb). 2017;9(8):678-686. [6] Li G, Yu F, Lei T,et al.Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell therapy in ischemic stroke: mechanisms of action and treatment optimization strategies. Neural Regen Res. 2016;11(6):1015-1024.[7] Bonilla-Porras AR, Velez-Pardo C, Jimenez-Del-Rio M. Fast transdifferentiation of human Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cells into neurospheres and nerve-like cells. J Neurosci Methods. 2017;282:52-60. [8] Enomoto M.The future of bone marrow stromal cell transplantation for the treatment of spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2015;10(3):383-384.[9] Qian JY, Chopp M, Liu Z. Mesenchymal stromal cells promote axonal outgrowth alone and synergistically with astrocytes via tPA. PLoS One. 2016;11(12):e0168345.[10] Park HJ, Oh SH, Kim HN, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells enhance α-synuclein clearance via M2 microglia polarization in experimental and human parkinsonian disorder. Acta Neuropathol. 2016;132(5):685-701.[11] Kong D, Zhu J, Liu Q, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells protect neurons against hypoxic-ischemic injury via inhibiting parthanatos, necroptosis, and apoptosis, but not autophagy. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2017;37(2):303-313.[12] Lopez-Verrilli MA, Caviedes A, Cabrera A, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes from different sources selectively promote neuritic outgrowth. Neuroscience. 2016;320:129-139.[13] Gu Y, Zhang Y, Bi Y, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells suppress neuronal apoptosis and decrease IL-10 release via the TLR2/NFκB pathway in rats with hypoxic-ischemic brain damage. Mol Brain. 2015;8(1):65. [14] Okolicsanyi RK, Camilleri ET, Oikari LE, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells retain multilineage differentiation capacity including neural marker expression after extended in vitro expansion. PLoS One. 2015;10(9):e0137255.[15] Stucky EC, Schloss RS, Yarmush ML, et al. Alginate micro-encapsulation of mesenchymal stromal cells enhances modulation of the neuro-inflammatory response. Cytotherapy. 2015;17(10):1353-1364. [16] Redondo J, Hares K, Wilkins A, et al. Reductions in kinesin expression are associated with nitric oxide-induced axonal damage. J Neurosci Res. 2015;93(6):882-892. [17] Donega V, Nijboer CH, Braccioli L, et al. Intranasal administration of human MSC for ischemic brain injury in the mouse: in vitro and in vivo neuroregenerative functions. PLoS One. 2014;9(11):e112339. [18] Donega V, Nijboer CH, van Tilborg G, et al. Intranasally administered mesenchymal stem cells promote a regenerative niche for repair of neonatal ischemic brain injury. Exp Neurol. 2014;261:53-64. [19] Cui X, Liu J, Bai L, et al. Interleukin-6 induces malignant transformation of rat mesenchymal stem cells in association with enhanced signaling of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3. Cancer Sci. 2014;105(1): 64-71.[20] Ravasi M, Scuteri A, Pasini S, et al. Undifferentiated MSCs are able to myelinate DRG neuron processes through p75. Exp Cell Res. 2013;319(19):2989-2999. [21] Xu X, Chen C, Akiyama K, et al. Gingivae contain neural-crest- and mesoderm-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Dent Res. 2013;92(9):825-832. [22] Xin H, Chopp M, Shen LH, et al. Multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells decrease transforming growth factor β1 expression in microglia/macrophages and down-regulate plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 expression in astrocytes after stroke. Neurosci Lett. 2013;542:81-86. [23] Mukhamedshina YO, Rizvanov AA.Genetically modified human umbilical cord blood cells as a promising strategy for treatment of spinal cord injury.Neural Regen Res. 2016;11(9):1420-1421.[24] Phetfong J, Tawonsawatruk T, Seenprachawong K, et al. Re-using blood products as an alternative supplement in the optimisation of clinical-grade adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell culture. Bone Joint Res. 2017;6(7):414-422. [25] Ordóñez-Vásquez A, Jaramillo-Gómez L, Duran-Correa C, et al. A reliable and reproducible model for assessing the effect of different concentrations of α-solanine on rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Bone Marrow Res. 2017;2017:2170306.[26] Monfrini M, Ravasi M, Maggioni D, et al. Comparing the different response of PNS and CNS injured neurons to mesenchymal stem cell treatment. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2018;86:16-24. [27] Namestnikova D, Gubskiy I, Kholodenko I, et al. Methodological aspects of MRI of transplanted superparamagnetic iron oxide-labeled mesenchymal stem cells in live rat brain. PLoS One. 2017;12(10):e0186717. [28] Namestnikova D, Gubskiy I, Kholodenko I, et al. Methodological aspects of MRI of transplanted superparamagnetic iron oxide-labeled mesenchymal stem cells in live rat brain. PLoS One. 2017;12(10):e0186717. [29] Fu Q, Liu Y, Liu X, et al. Engrafted peripheral blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote locomotive recovery in adult rats after spinal cord injury. Am J Transl Res. 2017; 9(9):3950-3966.[30] Dahbour S, Jamali F, Alhattab D, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells and conditioned media in the treatment of multiple sclerosis patients: Clinical, ophthalmological and radiological assessments of safety and efficacy. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2017;23(11):866-874.[31] WenBo W, Fei Z, YiHeng D, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing nerve growth factor ameliorate diabetic cystopathy in rats. Neurochem Res. 2017;42(12):3537-3547. [32] Centeno C, Markle J, Dodson E, et al. Treatment of lumbar degenerative disc disease-associated radicular pain with culture-expanded autologous mesenchymal stem cells: a pilot study on safety and efficacy. J Transl Med. 2017;15(1): 197. [33] Walsh DP, Heise A, O'Brien FJ, et al. An efficient, non-viral dendritic vector for gene delivery in tissue engineering. Gene Ther. 2017;24(11):681-691. [34] Kim HS, Lee NK, Yoo D, et al. Lowering the concentration affects the migration and viability of intracerebroventricular-delivered human mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;493(1): 751-757. [35] Shwartz A, Betzer O, Kronfeld N, et al. Therapeutic effect of astroglia-like mesenchymal stem cells expressing glutamate transporter in a genetic rat model of depression. Theranostics. 2017;7(10):2690-2703. [36] Ravanidis S, Bogie JFJ, Donders R, et al. Crosstalk with inflammatory macrophages shapes the regulatory properties of multipotent adult progenitor cells. Stem Cells Int. 2017;2017:2353240.[37] Chen X, Wang S, Cao W. Mesenchymal stem cell-mediated immunomodulation in cell therapy of neurodegenerative diseases. Cell Immunol. 2018;326:8-14.[38] Vanacker J, Viswanath A, De Berdt P, et al. Hypoxia modulates the differentiation potential of stem cells of the apical papilla. J Endod. 2014;40(9):1410-1418. [39] Lupatov AY, Poltavtseva RA, Bystrykh OA, et al. Neural stem/progenitor cells maintained in vitro under different culture conditions alter differentiation capacity of monocytes to generate dendritic cells. J Stem Cells Regen Med. 2017;13(2):54-61. |
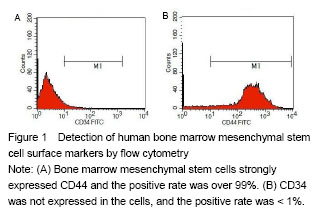
.jpg)
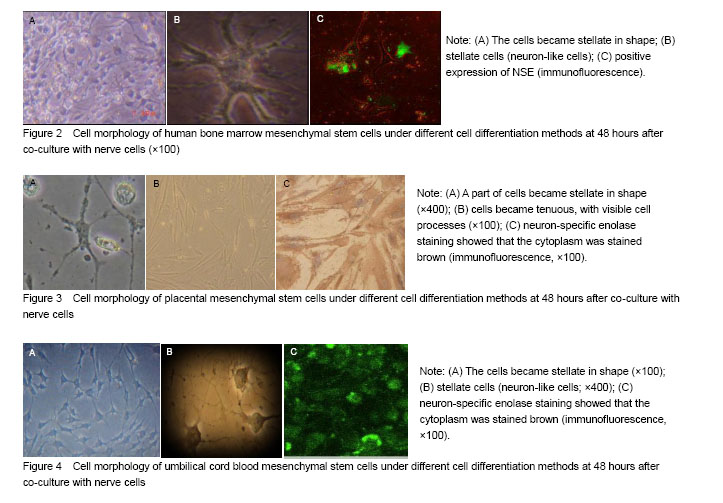
.jpg)