中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (29): 4681-4686.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0627
• 干细胞培养与分化 stem cell culture and differentiation • 上一篇 下一篇
3D培养体系下人来源诱导性多能干细胞向肝细胞的转化
李嘉晋1,2,王荣丽1,李婷婷2,何 东3,石 伟2
- 1西南医科大学临床医学院,四川省泸州市 646000;绵阳市人民医院,2重症医学科,3肾病内科,四川省绵阳市 621000
Transformation of human induced pluripotent stem cells into hepatocytes in 3D culture system
Li Jia-jin1, 2, Wang Rong-li1, Li Ting-ting2, He Dong3, Shi Wei2
- 1School of Clinical Medicine, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; 2Department of Critical Care Medicine, 3Department of Nephropathy, Mianyang People’s Hospital, Mianyang 621000, Sichuan Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义: 生物型人工肝的构建:将人工培养的有生物活性的肝细胞填充在生物反应器内,构建体外生物反应装置模拟正常人体肝脏,以代替受损肝脏发挥解毒、合成与代谢功能。 诱导性多能干细胞:对完全分化的体细胞的多个基因进行重新编程,使其逆向分化为与胚胎干细胞类似的具有自我更新能力和多向分化潜能的多能干细胞,理论上可以转化为人体内任何类型的细胞。
摘要
背景:生物型人工肝的构建有望成为治疗急性肝衰竭的有效方法,但构建人工肝的种子细胞来源、培养模式、营养获取等方面仍存在较多难题,制约血液净化-人工肝的发展与临床应用。
目的:探讨在不添加外源血清等异种来源物质的条件下将人诱导性多能干细胞诱导分化为肝细胞样细胞的可行性。
方法:应用含Transwell小室的6孔板构建3D培养体系,外源添加丙戊酸和尼克酰胺对人诱导性多能干细胞进行诱导分化,并将分化的肝细胞样细胞与生物补片共培养。实验分为5组:人诱导性多能干细胞为A组、正常肝细胞为B组、不添加尼克酰胺诱导分化的肝细胞样细胞为C组、添加尼克酰胺诱导分化的肝细胞样细胞为D组、在生物外科补片上培养的肝细胞样细胞为E组。倒置相差显微镜下观察D组肝细胞样细胞的形态;免疫荧光检测D组细胞中肝细胞核因子4α和甲胎蛋白的表达;荧光实时定量PCR和Western blot检测A、B、C、D组细胞中甲胎蛋白与白蛋白的mRNA和蛋白表达;流式细胞术检测A、C、D组细胞的分化效率;免疫细胞化学检测B组和E组细胞中胆盐输出泵蛋白的表达;ELISA检测D组和E组上清液中乳酸脱氢酶活性、白蛋白和尿素氮含量。
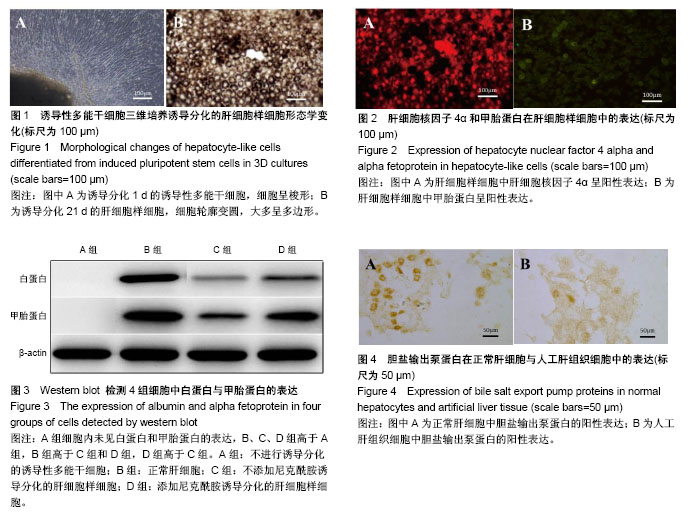
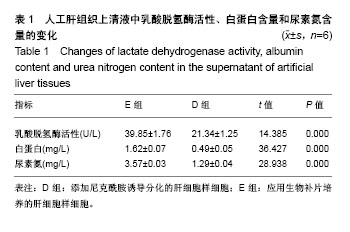
结果与结论:①D组细胞由梭形逐渐转变成多边形;②D组细胞中肝细胞核因子4α和甲胎蛋白呈阳性表达;③D组细胞中甲胎蛋白、白蛋白的基因和蛋白表达明显高于A组和C组(P < 0.01);④B组和E组细胞中胆盐输出泵蛋白呈明显阳性表达;⑤E组细胞乳酸脱氢酶活性、白蛋白和尿素氮的含量明显高于D组(P < 0.01);⑥结果表明,外源添加小分子化合物的三维培养体系和生物外科补片联合应用有助于促进诱导性多能干细胞在体外诱导分化为功能性肝细胞样细胞。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-8103-3116(李嘉晋)
中图分类号:
.jpg)