| [1] Teeple E, Jay GD, Elsaid KA, et al. Animal models of osteoarthritis: challenges of model selection and analysis. AAPS J. 2013; 15(2):438-446.[2] Xing D, Xu Y, Liu Q, et al. Osteoarthritis and all-cause mortality in worldwide populations: grading the evidence from a meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2016; 6:24393.[3] Yelin E, Weinstein S, King T. The burden of musculoskeletal diseases in the United States. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2016; 46(3):259-260.[4] Roos H, Lauren M, Adalberth T, et al. Knee osteoarthritis after meniscectomy: prevalence of radiographic changes after twenty-one years, compared with matched controls. Arthritis Rheum. 1998; 41(4):687-693.[5] Anetzberger H, Mayer A, Glaser C, et al. Meniscectomy leads to early changes in the mineralization distribution of subchondral bone plate. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014; 22(1):112-119.[6] E X, Cao Y, Meng H, et al. Dendritic cells of synovium in experimental model of osteoarthritis of rabbits. Cell Physiol Biochem.2012; 30(1):23-32.[7] Zhang ZZ, Wang SJ, Zhang JY, et al. 3D-Printed Poly(epsilon-caprolactone) scaffold augmented with mesenchymal stem cells for total meniscal substitution: a 12- and 24-week animal study in a rabbit model. The American journal of sports medicine 2017; 45(7):1497-1511.[8] Lampropoulou-Adamidou K, Lelovas P, Karadimas EV, et al. Useful animal models for the research of osteoarthritis. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2014; 24(3):263-271.[9] Colombo C, Butler M, O'Byrne E, et al. A new model of osteoarthritis in rabbits. I. Development of knee joint pathology following lateral meniscectomy and section of the fibular collateral and sesamoid ligaments. Arthritis Rheum. 1983; 26(7):875-886.[10] 黄媛霞,徐海斌,郭春. IL-1β和MMP-13在兔骨关节炎模型软骨和滑液中的表达[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版) 2017,38(4): 507-511+528.[11] Arunakul M, Tochigi Y, Goetz JE, et al. Replication of chronic abnormal cartilage loading by medial meniscus destabilization for modeling osteoarthritis in the rabbit knee in vivo. J Orthop Res. 2013; 31(10):1555-1560.[12] Steineman BD, LaPrade RF, Santangelo KS, et al. Early osteoarthritis after untreated anterior meniscal root tears: an in vivo animal study. Orthop J Sports Med.2017; 5(4): 2325967117702452.[13] Sweigart MA, Zhu CF, Burt DM, et al. Intraspecies and interspecies comparison of the compressive properties of the medial meniscus. Ann Biomed Eng. 2004; 32(11):1569-1579.[14] Kraus VB, Feng S, Wang S, et al. Subchondral bone trabecular integrity predicts and changes concurrently with radiographic and magnetic resonance imaging-determined knee osteoarthritis progression. Arthritis Rheum. 2013; 65(7): 1812-1821.[15] Hutchinson ID, Moran CJ, Potter HG, et al. Restoration of the meniscus: form and function. Am J Sports Med. 2014; 42(4): 987-998.[16] Oiestad BE, Engebretsen L, Storheim K, et al. Knee osteoarthritis after anterior cruciate ligament injury: a systematic review. Am J Sports Med. 2009; 37(7):1434-1443.[17] Roman-Blas JA, Mediero A, Tardio L, et al. The combined therapy with chondroitin sulfate plus glucosamine sulfate or chondroitin sulfate plus glucosamine hydrochloride does not improve joint damage in an experimental model of knee osteoarthritis in rabbits. Eur J Pharmacol. 2017; 794:8-14.[18] Chang NJ, Shie MY, Lee KW, et al. Can Early Rehabilitation Prevent Posttraumatic Osteoarthritis in the Patellofemoral Joint after Anterior Cruciate Ligament Rupture? Understanding the Pathological Features. Int J Mol Sci. 2017; 18(4):5.[19] Papaioannou NA, Triantafillopoulos IK, Khaldi L, et al. Effect of calcitonin in early and late stages of experimentally induced osteoarthritis. A histomorphometric study. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2007; 15(4):386-395.[20] Kaderli S, Viguier E, Watrelot-Virieux D, et al. Efficacy study of two novel hyaluronic acid-based formulations for viscosupplementation therapy in an early osteoarthrosic rabbit model. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015; 96:388-395.[21] Desando G, Cavallo C, Sartoni F, et al. Intra-articular delivery of adipose derived stromal cells attenuates osteoarthritis progression in an experimental rabbit model. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013; 15(1):R22.[22] Laverty S, Girard CA, Williams JM, et al. The OARSI histopathology initiative - recommendations for histological assessments of osteoarthritis in the rabbit. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010; 18:S53-65.[23] Bao JP, Chen WP, Wu LD. Lubricin: a novel potential biotherapeutic approaches for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Mol Biol Rep. 2011; 38(5):2879-2885.[24] Chen WP, Bao JP, Hu PF, et al. Alleviation of osteoarthritis by Trichostatin A, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, in experimental osteoarthritis. Mol Biol Rep.2010; 37(8):3967-3972.[25] 杨松滨,刘益杰,冯伟,等.基于关节力学失稳方法建立兔膝骨关节炎模型[J].上海中医药杂志,2015,49(4):11-15.[26] 朱鸿飞,冯伟,刘益杰,等.髌韧带内侧缺损构建兔膝骨关节炎模型初探[J].上海中医药杂志,2012, 46(1):11-14+18.[27] Wang J, Gao JS, Chen JW, et al. Effect of resveratrol on cartilage protection and apoptosis inhibition in experimental osteoarthritis of rabbit. Rheumatol Int. 2012; 32(6): 1541-1548.[28] 咸杰,何本祥,吴骁,等.自体富血小板血浆对兔膝关节骨性关节炎的治疗效果观察[J].重庆医学, 2017, 46(20):2747-2750.[29] Kyrkos MJ, Papavasiliou KA, Kenanidis E, et al.Calcitonin delays the progress of early-stage mechanically induced osteoarthritis. In vivo, prospective study. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013; 21(7):973-980.[30] Pauly HM, Larson BE, Coatney GA, et al. Assessment of cortical and trabecular bone changes in two models of post-traumatic osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res. 2015; 33(12): 1835-1845.[31] Bellido M, Lugo L, Roman-Blas JA, et al. Subchondral bone microstructural damage by increased remodelling aggravates experimental osteoarthritis preceded by osteoporosis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010; 12(4):R152.[32] Buckland-Wright C. Subchondral bone changes in hand and knee osteoarthritis detected by radiography. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2004; 12:S10-19.[33] Chappard C, Peyrin F, Bonnassie A, et al. Subchondral bone micro-architectural alterations in osteoarthritis: a synchrotron micro-computed tomography study. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2006; 14(3):215-223.[34] Pastoureau P, Leduc S, Chomel A, et al. Quantitative assessment of articular cartilage and subchondral bone histology in the meniscectomized guinea pig model of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2003; 11(6):412-423.[35] Bellido M, Lugo L, Roman-Blas JA, et al. Improving subchondral bone integrity reduces progression of cartilage damage in experimental osteoarthritis preceded by osteoporosis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2011; 19(10): 1228-1236.[36] Wu CC, Sheu SY, Hsu LH, et al. Intra-articular Injection of platelet-rich fibrin releasates in combination with bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of articular cartilage defects: An in vivo study in rabbits. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2017; 105(6):1536-1543.[37] Vaseenon T, Tochigi Y, Heiner AD, et al. Organ-level histological and biomechanical responses from localized osteoarticular injury in the rabbit knee. J Orthop Res. 2011; 29(3):340-346.[38] Freisinger GM, Schmitt LC, Wanamaker AB, et al. Tibiofemoral Osteoarthritis and Varus-Valgus Laxity. J Knee Surg. 2017; 30(5):440-451.[39] Jansen EJ, Emans PJ, Van Rhijn LW, et al. Development of partial-thickness articular cartilage injury in a rabbit model. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008; 466(2):487-494.[40] Mizuta H, Kudo S, Nakamura E, et al. Expression of the PTH/PTHrP receptor in chondrogenic cells during the repair of full-thickness defects of articular cartilage. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2006; 14(9):944-952.[41] Hunt N, Sanchez-Ballester J, Pandit R, et al. Chondral lesions of the knee: A new localization method and correlation with associated pathology. Arthroscopy. 2001; 17(5):481-490.[42] Fischenich K, Pauly H, Button K, et al. A study of acute and chronic tissue changes in surgical and traumatically-induced experimental models of knee joint injury using magnetic resonance imaging and micro-computed tomography. Osteoarthr Cartil.2017; 25(4):561-569.[43] Rehan Youssef A, Longino D, Seerattan R, et al. Muscle weakness causes joint degeneration in rabbits. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2009; 17(9):1228-1235.[44] 戴七一,覃学流,韩杰,等.基于1HNMR平台探讨揉髌手法对兔膝关节骨关节炎模型血清代谢组学的影响[J].广西中医药大学学报, 2017, 20(1):1-5.[45] Lu W, Wang L, Wo C, et al. Ketamine attenuates osteoarthritis of the knee via modulation of inflammatory responses in a rabbit model. Mol Med Rep. 2016; 13(6):5013-5020.[46] Zhou Q, Wei B, Liu S, et al. Cartilage matrix changes in contralateral mobile knees in a rabbit model of osteoarthritis induced by immobilization. BMC Musculoskelet Disord.2015; 16:224.[47] Hermeto LC, DeRossi R, Oliveira RJ, et al. Effects of intra-articular injection of mesenchymal stem cells associated with platelet-rich plasma in a rabbit model of osteoarthritis. Genet Mol Res. 2016; 15(3). doi: 10.4238/gmr.15038569.[48] Iannitti T, Elhensheri M, Bingol AO, et al. Preliminary histopathological study of intra-articular injection of a novel highly cross-linked hyaluronic acid in a rabbit model of knee osteoarthritis. J Mol Histol. 2013; 44(2):191-201.[49] Kim SB, Kwon DR, Kwak H, et al. Additive effects of intra-articular injection of growth hormone and hyaluronic acid in rabbit model of collagenase-induced osteoarthritis. J Korean Med Sci. 2010; 25(5):776-780.[50] Shen S, Wang H, Zhang J, et al. T1rho magnetic resonance imaging quantification of early articular cartilage degeneration in a rabbit model. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015; 16:361.[51] 陈达,彭力平,廖州伟,等.木瓜蛋白酶与石膏制动建立兔膝骨关节炎模型的比较[J].广东医学,2017,14(38):2114-2118.[52] 王维山,史晨辉,周卓浩,等. 一侧兔膝关节注射外源性尿激酶型纤溶酶原激活物引起双侧膝关节软骨降解的实验[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2007,11(19):3738-3741. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
Hulth法:为经典骨关节炎造模方式,手术需切除前、后交叉韧带、内侧副韧带及内侧半月板,造成关节的极度不稳定,从而诱发骨关节炎改变,该方法诱导率高,稳定性好,但创伤大,感染风险较高,产生的炎症因子对早期骨关节炎软骨及滑膜的生化变化影响较大。
改良Hulth法:是在传统Hulth法的基础上进行改良,是在切除前交叉韧带及基础上进一步破坏关节内的稳定结构,如再全部或部分切除内外侧半月板、再切断内侧副韧带等,具有创伤较小,稳定好,重复性好的特点。
文题释义:
Hulth法:为经典骨关节炎造模方式,手术需切除前、后交叉韧带、内侧副韧带及内侧半月板,造成关节的极度不稳定,从而诱发骨关节炎改变,该方法诱导率高,稳定性好,但创伤大,感染风险较高,产生的炎症因子对早期骨关节炎软骨及滑膜的生化变化影响较大。
改良Hulth法:是在传统Hulth法的基础上进行改良,是在切除前交叉韧带及基础上进一步破坏关节内的稳定结构,如再全部或部分切除内外侧半月板、再切断内侧副韧带等,具有创伤较小,稳定好,重复性好的特点。.jpg) 文题释义:
Hulth法:为经典骨关节炎造模方式,手术需切除前、后交叉韧带、内侧副韧带及内侧半月板,造成关节的极度不稳定,从而诱发骨关节炎改变,该方法诱导率高,稳定性好,但创伤大,感染风险较高,产生的炎症因子对早期骨关节炎软骨及滑膜的生化变化影响较大。
改良Hulth法:是在传统Hulth法的基础上进行改良,是在切除前交叉韧带及基础上进一步破坏关节内的稳定结构,如再全部或部分切除内外侧半月板、再切断内侧副韧带等,具有创伤较小,稳定好,重复性好的特点。
文题释义:
Hulth法:为经典骨关节炎造模方式,手术需切除前、后交叉韧带、内侧副韧带及内侧半月板,造成关节的极度不稳定,从而诱发骨关节炎改变,该方法诱导率高,稳定性好,但创伤大,感染风险较高,产生的炎症因子对早期骨关节炎软骨及滑膜的生化变化影响较大。
改良Hulth法:是在传统Hulth法的基础上进行改良,是在切除前交叉韧带及基础上进一步破坏关节内的稳定结构,如再全部或部分切除内外侧半月板、再切断内侧副韧带等,具有创伤较小,稳定好,重复性好的特点。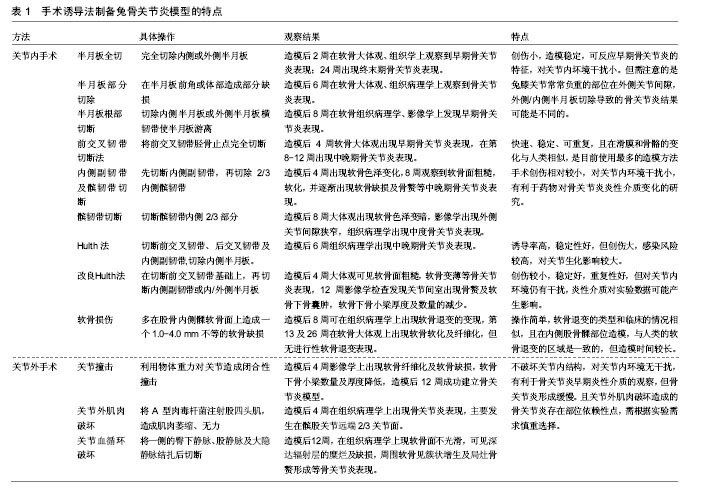
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
Hulth法:为经典骨关节炎造模方式,手术需切除前、后交叉韧带、内侧副韧带及内侧半月板,造成关节的极度不稳定,从而诱发骨关节炎改变,该方法诱导率高,稳定性好,但创伤大,感染风险较高,产生的炎症因子对早期骨关节炎软骨及滑膜的生化变化影响较大。
改良Hulth法:是在传统Hulth法的基础上进行改良,是在切除前交叉韧带及基础上进一步破坏关节内的稳定结构,如再全部或部分切除内外侧半月板、再切断内侧副韧带等,具有创伤较小,稳定好,重复性好的特点。
文题释义:
Hulth法:为经典骨关节炎造模方式,手术需切除前、后交叉韧带、内侧副韧带及内侧半月板,造成关节的极度不稳定,从而诱发骨关节炎改变,该方法诱导率高,稳定性好,但创伤大,感染风险较高,产生的炎症因子对早期骨关节炎软骨及滑膜的生化变化影响较大。
改良Hulth法:是在传统Hulth法的基础上进行改良,是在切除前交叉韧带及基础上进一步破坏关节内的稳定结构,如再全部或部分切除内外侧半月板、再切断内侧副韧带等,具有创伤较小,稳定好,重复性好的特点。