| [1] Zalavras CG, Lieberman JR. Osteonecrosis of the femoral head: evaluation and treatment. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2014;22(7): 455-464.[2] Malchau H, Herberts P, Eisler T, et al. The Swedish Total Hip Replacement Register. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84-A Suppl 2:2-20.[3] Mont MA, Zywiel MG, Marker DR, et al. The natural history of untreated asymptomatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head: a systematic literature review. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92(12): 2165-2170.[4] Ha YC, Jung WH, Kim JR, et al. Prediction of collapse in femoral head osteonecrosis: a modified Kerboul method with use of magnetic resonance images. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88 Suppl 3:35-40.[5] Koo KH, Kim R, Ko GH, et al. Preventing collapse in early osteonecrosis of the femoral head. A randomised clinical trial of core decompression. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1995;77(6):870-874.[6] 孙伟,李子荣. 股骨头坏死的分期与分型[J]. 中国骨与关节杂志, 2017,6(6):465-468.[7] 李子荣,刘朝晖,孙伟,等. 基于三柱结构的股骨头坏死分型——中日友好医院分型[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2012,32(6):515-520.[8] Nishii T, Sugano N, Ohzono K, et al. Significance of lesion size and location in the prediction of collapse of osteonecrosis of the femoral head: a new three-dimensional quantification using magnetic resonance imaging. J Orthop Res. 2002;20(1):130-136.[9] Li W, Abram F, Beaudoin G, et al. Human hip joint cartilage: MRI quantitative thickness and volume measurements discriminating acetabulum and femoral head. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2008; 55(12):2731-2740.[10] 刘宏滨,赵汉青,史跃,等. 股骨头坏死区三维数字化模型建立及体积估算[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2016, 20(44): 6629-6635.[11] Singh M, Nagrath AR, Maini PS. Changes in trabecular pattern of the upper end of the femur as an index of osteoporosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1970;52(3):457-467.[12] Lian YY, Pei FX, Yoo MC, et al. Changes of the bone mineral density in proximal femur following total hip resurfacing arthroplasty in osteonecrosis of femoral head. J Orthop Res. 2008;26(4):453-459.[13] 赵海燕,夏亚一,康鹏德. 股骨头坏死病因与发病机制研究进展[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2009, 17(8): 604-607.[14] 李子荣. 股骨头坏死的早期诊断治疗及合理治疗[J]. 中华关节外科杂志:电子版, 2008, 2(1): 1-3.[15] 李子荣. 科学诊断和治疗股骨头坏死[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2005, 19(9): 685-686.[16] Liu WG, Wang SJ, Yin QF, et al. Biomechanical supporting effect of tantalum rods for the femoral head with various sized lesions: a finite-element analysis. Chin Med J (Engl). 2012;125(22): 4061-4065.[17] Floerkemeier T, Lutz A, Nackenhorst U, et al. Core decompression and osteonecrosis intervention rod in osteonecrosis of the femoral head: clinical outcome and finite element analysis. Int Orthop. 2011;35(10):1461-1466.[18] Tai CL, Chen YC, Hsieh PH. The effects of necrotic lesion size and orientation of the femoral component on stress alterations in the proximal femur in hip resurfacing - a finite element simulation. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2014;15:262.[19] Steinberg DR, Steinberg ME, Garino JP, et al. Determining lesion size in osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88 Suppl 3:27-34.[20] Kishida Y, Nishii T, Sugano N, et al. Measurement of lesion area and volume by three-dimensional spoiled gradient-echo MR imaging in osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Orthop Res. 2003; 21(5):850-858.[21] Nam KW, Kim YL, Yoo JJ, et al. Fate of untreated asymptomatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008; 90(3):477-484.[22] Lieberman JR, Engstrom SM, Meneghini RM, et al. Which factors influence preservation of the osteonecrotic femoral head. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012;470(2):525-534.[23] Nishii T, Sugano N, Ohzono K, et al. Significance of lesion size and location in the prediction of collapse of osteonecrosis of the femoral head: a new three-dimensional quantification using magnetic resonance imaging. J Orthop Res. 2002;20(1):130-136.[24] Yoshida H, Faust A, Wilckens J, et al. Three-dimensional dynamic hip contact area and pressure distribution during activities of daily living. J Biomech. 2006;39(11):1996-2004.[25] Hu LB, Huang ZG, Wei HY, et al. Osteonecrosis of the femoral head: using CT, MRI and gross specimen to characterize the location, shape and size of the lesion. Br J Radiol. 2015;88(1046): 20140508.[26] Sugano N, Takaoka K, Ohzono K, et al. Prognostication of nontraumatic avascular necrosis of the femoral head. Significance of location and size of the necrotic lesion. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994;(303):155-164.[27] Karasuyama K, Yamamoto T, Motomura G, et al. The role of sclerotic changes in the starting mechanisms of collapse: A histomorphometric and FEM study on the femoral head of osteonecrosis. Bone. 2015;81:644-648.[28] Lutz A, Nackenhorst U, von Lewinski G, et al. Numerical studies on alternative therapies for femoral head necrosis: A finite element approach and clinical experience. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2011;10(5):627-640.[29] 李孝林,吕志鹏,刘迎军. 股骨头坏死有限元模型的建立[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011, 15(30): 5522-5525. |
.jpg)
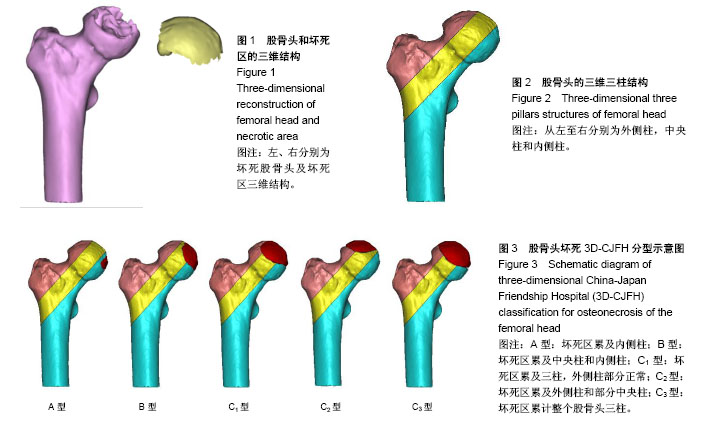
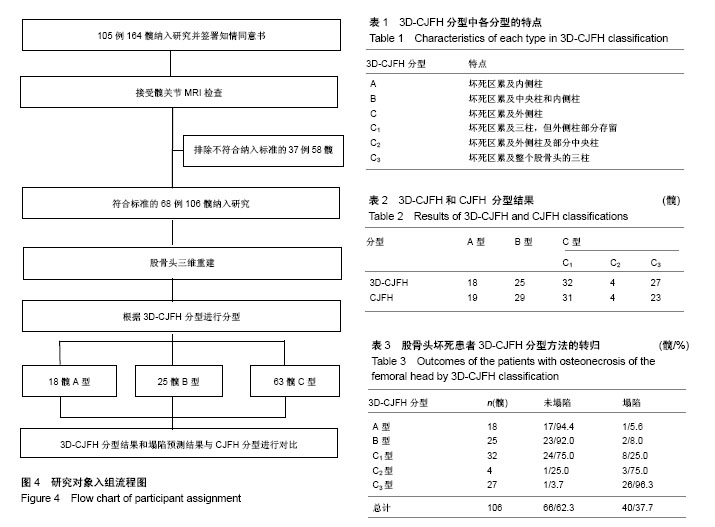
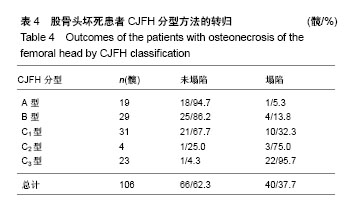
.jpg)