| [1] 杨红,廉翔,樊晶.成人正畸的临床特点及治疗方法分析[J].中国实用医药,2015,10(27):87-88.[2] 罗尚叠.单颌与双颌拔牙矫治成人安氏Ⅱ类1分类的疗效对比研究[D].暨南大学, 2014.[3] Kalha AS. Early orthodontic treatment reduced incisal trauma in children with class II malocchsions. Evid Based Dent, 2014, 15(1):18-20.[4] 奉晓斌.安氏Ⅱ1错(牙合)上颌单颌拔牙矫治前后咀嚼效率对比研究[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2012,5(8):495-497.[5] 黄红亮,安爱群,卢红飞,等.上颌单颌拔牙矫治成人安氏Ⅱ错(牙合)的头影测量研究[J].北京口腔医学,2012,19(6):346-348.[6] 陆盛.不同拔牙矫治模式矫治安氏Ⅱ类伴下切牙缺失错合畸形疗效的PAR指数评价[J].浙江医学,2014,26(10):857-862.[7] 闫阔.Tip-Edge矫治技术中尖牙外展弯相对位置对尖牙移动趋势影响的有限元分析[D].吉林大学,2012.[8] Kim KN, Cha BK, Choi DS, et al. A finite element study on the effects of midsymphyseal distraction osteogenesis on the mandibule and articular disc. Angle Orthod, 2012,82(3): 464-471.[9] 周子凌,张渊,石利强,等.咬合接触对颞下颌关节应力分布影响的三维有限元分析[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2015,50(5):302-306.[10] Koolstra JH, vanEijden TM. Three-dimensional dynamical capabilities of the human masticatory muscles. J Biomech. 1999;32(2):145-152.[11] 刘梦超. 颞下颌关节骨骼肌肉系统三维有限元模型的建立[D]. 温州医科大学, 2014.[12] 王杰睿,潘旭,米丛波.维吾尔族错颌畸形患者髁突位置及颞下颌关节形态的锥形束CT研究[J].上海口腔医学,2016,25(4): 461-464.[13] 车蓓,张昊,钱才梅,等.不同垂直骨面型安氏Ⅱ类1分类错合患者颞下颌关节三维形态结构的比计较[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2014, 49(7):399-402.[14] Fang HJ, Tao L. Evaluation of sagittal temporomandibular condyle position in adolescent Angle Class II division 1 patients by cone-beam CT. Shanghai Kouqiang Yixue. 2014; 23(6):740-743.[15] 赖晓宇,林雪峰,吴夏怡.青年安氏Ⅱ类1分类错合患者下颌咀嚼运动轨迹特征的研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2016,32(1): 115-119.[16] 葛胜将.不同骨性错(牙合)患者髁突形态及位置的CBCT研究[D].青岛大学,2015.[17] Savoldelli C, Bouchard PO, Maniere-Ezvan A, et al. Comparison of stress distribution in the temporomandibular joint during jaw closing before and after symphyseal distraction:a finite element study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012;41(12): 1474-1482.[18] Meloto CB, Serrano PO, Ribeiro-DaSilva MC, et a1.Genomics and the new Perspectives for temporomandibular disorders. Arch Oral Biol. 2011;56(11):1181-1191.[19] Papageorgiou SN, Keilig L, Vandevska-Radunovic V, et al. Torque differences due to the material variation of the orthodontic appliance: a finite element study. Prog Orthod. 2017;18(1):6.[20] Jo AR, Mo SS, Lee KJ, et al. Finite-element analysis of resistance of the mandibular dentition. Korean J Orthod. 2017;47(1):21-30.[21] Mathew A, Nagachandran KS, Vijayalakshmi D. Stress and displacement pattern evaluation using two different palatal expanders in unilateral cleft lip and palate: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. Prog Orthod. 2016;17(1):2-10.[22] Savoldelli C, Bouchard PO, Loudad R, et al.Stress distribution in the temporomandibular joint discs during jaw closing:a high-resolution three-dimensional finite-element model analysis. Surg Radiol Anat. 2012;4(5):404-413.[23] Mori H, Horiuchi S, Nishimura S,et al. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of cartilaginous tissues in human temporomandibular joint during prolonged clenching. Arch Oral Biol. 2010;55(11):879-886.[24] 邓潇,万哲,何姝姝,等.成人安氏II类错合正畸人群正中关系位与最大牙尖交错位你不调的研究[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2011, 29(1):48-52.[25] Vitral RWF, Telles CS. Computed tomography evaluation of temporomandibular joint alterations in ClassⅡDivisioon 1subdivision patients:condylar symmetry. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2002;121(4):369-374.[26] Vitral RW, Telles Cde S, Fraga MR, et al. Computed tomography evaluation of temporomandibular joint alterations in patients with class II division 1 subdivision malocclusions:condyle-fossa relationship. Am J Oahod Dentofacial Oahop. 2004;126(1): 48-52.[27] 孙岩.安氏Ⅱ类1分类错合患者颞下颌关节CBCT测量值分析[D].中山大学,2010.[28] 方海军,陶列.青春期安氏Ⅱ类1分类患者髁突矢状向位置的锥形束CT测量分析[J].上海口腔医学,2014,23(6):740-743.[29] 张亚楠,雷勇华,邹双双,等.双合垫矫治器治疗青少年安氏Ⅱ1错合患者颞下颌关节变化的初步研究[J].中华口腔正畸学杂志, 2016,23(1):12-16.[30] 顾永佳,陆胜男,高美琴,等.青少年安氏I、II类错合畸形患者髁突位置的比较[J].上海口腔医学,2016,25(6):694-696.[31] 刘展,钱英莉,张远理,等.关节盘移位对颞下颌关节内应力分布的影响[J].医用生物力学,2013,28(5):528-532.[32] 王晓宇,厉松.安氏II1类青少年髁突运动轨迹与颞下颌关节形态的研究[J].北京口腔医学,2011,19(3):164-166.[33] Piehslinger E, Celar A,Celar RM, et al. Orthopetic jaw movement observations, Part V: Transversal condylar shift in protrusive and retrusive movement. Cranio.1994;12(4): 247-251.[34] Tomonari H, Kubota T, Yagi T, et al. Posterior scissorsbite: Masticatory jaw movement and muscle activity. J Oral Rehabil. 2014;41(4):257-265.[35] Nakamura A, Zeredo JL, Utsumi D, et al. Influence of malocclusion on the development of masticatory function and mandibular growth. Angle Orthod. 2013;83(5):749-757.[36] 方颖,孙雯,施洁珺,等.安氏Ⅱ1类下颌后缩颞下颌关节结构与垂直骨面型、覆牙合覆盖的相关性研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志, 2008,24(6):886-889.[37] 王天丛,闫翔,何冬梅,等.安氏Ⅱ类1分类错殆上牙列单颌拔牙矫治后颞下颌关节间隙变化的研究[J].实用临床医药杂志,2016, 20(15):198-199.[38] 张学军,周传丽,白玉兴,等.安氏Ⅱ类1分类错合髁突运动轨迹与关节盘位置的相关性研究[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2010,45(1): 16-19.[39] Aoun M, Mesnard M, Monede-Hocquard L, et al. Stress analysis of temporpm-andibular joint disc during maintained clenching using a viscohyperelastic finite element model. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2014;72(6):1070-1077.[40] 唐顼晶,刘月华,王冬梅,等.两种加载方式前牙闭锁性深覆合颞下颌关节的三维有限元分析[J].中国美容医学,2012,21(6): 982-985. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
颞下颌关节:是人体内可左右联动的负重关节,其结构形态与颅面结构及咬合状态存在较大的相关性,正常生理状态下颞下颌关节的关节窝及髁突位置协调而平衡,然而其相对位置并不是稳定不变的,能够根据其所承受的力学环境不同而做出相对应的改建,当异常咬合产生的应力超出其适应性改建的范围时,则存在颞下颌关节紊乱病的危险。
三维有限元分析:通过单元格划分将连续的模型划分为有限个单元,后期根据研究的需要赋予其不同的材料性能,模拟生物力学环境,计算其所受应力。自1980年运用于口腔医学研究以来,有限元法已涉及正畸的各个领域,如对下颌牙列阻抗中心的有限元分析及不同扩弓矫治器在腭中缝及其他骨缝处产生的应力分布等,且经过国内外学者的大量研究,建模过程简便快捷的同时其模型的精确度也已得到很大提升。
文题释义:
颞下颌关节:是人体内可左右联动的负重关节,其结构形态与颅面结构及咬合状态存在较大的相关性,正常生理状态下颞下颌关节的关节窝及髁突位置协调而平衡,然而其相对位置并不是稳定不变的,能够根据其所承受的力学环境不同而做出相对应的改建,当异常咬合产生的应力超出其适应性改建的范围时,则存在颞下颌关节紊乱病的危险。
三维有限元分析:通过单元格划分将连续的模型划分为有限个单元,后期根据研究的需要赋予其不同的材料性能,模拟生物力学环境,计算其所受应力。自1980年运用于口腔医学研究以来,有限元法已涉及正畸的各个领域,如对下颌牙列阻抗中心的有限元分析及不同扩弓矫治器在腭中缝及其他骨缝处产生的应力分布等,且经过国内外学者的大量研究,建模过程简便快捷的同时其模型的精确度也已得到很大提升。.jpg) 文题释义:
颞下颌关节:是人体内可左右联动的负重关节,其结构形态与颅面结构及咬合状态存在较大的相关性,正常生理状态下颞下颌关节的关节窝及髁突位置协调而平衡,然而其相对位置并不是稳定不变的,能够根据其所承受的力学环境不同而做出相对应的改建,当异常咬合产生的应力超出其适应性改建的范围时,则存在颞下颌关节紊乱病的危险。
三维有限元分析:通过单元格划分将连续的模型划分为有限个单元,后期根据研究的需要赋予其不同的材料性能,模拟生物力学环境,计算其所受应力。自1980年运用于口腔医学研究以来,有限元法已涉及正畸的各个领域,如对下颌牙列阻抗中心的有限元分析及不同扩弓矫治器在腭中缝及其他骨缝处产生的应力分布等,且经过国内外学者的大量研究,建模过程简便快捷的同时其模型的精确度也已得到很大提升。
文题释义:
颞下颌关节:是人体内可左右联动的负重关节,其结构形态与颅面结构及咬合状态存在较大的相关性,正常生理状态下颞下颌关节的关节窝及髁突位置协调而平衡,然而其相对位置并不是稳定不变的,能够根据其所承受的力学环境不同而做出相对应的改建,当异常咬合产生的应力超出其适应性改建的范围时,则存在颞下颌关节紊乱病的危险。
三维有限元分析:通过单元格划分将连续的模型划分为有限个单元,后期根据研究的需要赋予其不同的材料性能,模拟生物力学环境,计算其所受应力。自1980年运用于口腔医学研究以来,有限元法已涉及正畸的各个领域,如对下颌牙列阻抗中心的有限元分析及不同扩弓矫治器在腭中缝及其他骨缝处产生的应力分布等,且经过国内外学者的大量研究,建模过程简便快捷的同时其模型的精确度也已得到很大提升。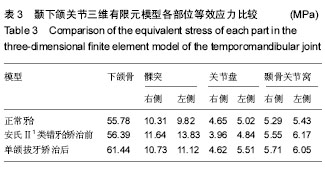
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
颞下颌关节:是人体内可左右联动的负重关节,其结构形态与颅面结构及咬合状态存在较大的相关性,正常生理状态下颞下颌关节的关节窝及髁突位置协调而平衡,然而其相对位置并不是稳定不变的,能够根据其所承受的力学环境不同而做出相对应的改建,当异常咬合产生的应力超出其适应性改建的范围时,则存在颞下颌关节紊乱病的危险。
三维有限元分析:通过单元格划分将连续的模型划分为有限个单元,后期根据研究的需要赋予其不同的材料性能,模拟生物力学环境,计算其所受应力。自1980年运用于口腔医学研究以来,有限元法已涉及正畸的各个领域,如对下颌牙列阻抗中心的有限元分析及不同扩弓矫治器在腭中缝及其他骨缝处产生的应力分布等,且经过国内外学者的大量研究,建模过程简便快捷的同时其模型的精确度也已得到很大提升。
文题释义:
颞下颌关节:是人体内可左右联动的负重关节,其结构形态与颅面结构及咬合状态存在较大的相关性,正常生理状态下颞下颌关节的关节窝及髁突位置协调而平衡,然而其相对位置并不是稳定不变的,能够根据其所承受的力学环境不同而做出相对应的改建,当异常咬合产生的应力超出其适应性改建的范围时,则存在颞下颌关节紊乱病的危险。
三维有限元分析:通过单元格划分将连续的模型划分为有限个单元,后期根据研究的需要赋予其不同的材料性能,模拟生物力学环境,计算其所受应力。自1980年运用于口腔医学研究以来,有限元法已涉及正畸的各个领域,如对下颌牙列阻抗中心的有限元分析及不同扩弓矫治器在腭中缝及其他骨缝处产生的应力分布等,且经过国内外学者的大量研究,建模过程简便快捷的同时其模型的精确度也已得到很大提升。