中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (19): 3051-3056.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.19.016
• 骨与关节图像与影像 bone and joint imaging • 上一篇 下一篇
腰椎QCT与骨质疏松性胸腰椎骨折伤椎骨造影弥散度的关联性
宋泉生1,唐福波1,王晓琥1,张家立1,李智斐1,饶远森2,伍 亮1,邰志洪2,覃海飚1,许建文3
- 1广西中医药大学第一附属医院骨科,广西壮族自治区南宁市 530023;2广西中医药大学,广西壮族自治区南宁市 530200;3广西医科大学第一附属医院康复医学科,广西壮族自治区南宁市 530021
Relationship between the lumbar quantitative computed tomography values and contrast agent dispersion in osteoporotic thoracolumbar fractures
Song Quan-sheng1, Tang Fu-bo1, Wang Xiao-hu1, Zhang Jia-li1, Li Zhi-fei1, Rao Yuan-sen2, Wu Liang1, Tai Zhi-hong2, Qin Hai-biao1, Xu Jian-wen3
- 1Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530023, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 3Department of Rehabilitation, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
椎体成形术:临床研究证明椎体成形术是治疗骨质疏松性胸腰椎骨折的有效方法,采用双侧穿刺椎体成形术骨水泥填充较充分,且可以减少每侧骨水泥注入量,从而可以减少骨水泥的渗漏。采用单侧穿刺术,与双侧穿刺术比较,单侧穿刺术减少了穿刺次数、治疗时间、射线暴露时间、患者痛苦及并发症发生概率。单侧或双侧穿刺椎体成形术两者之间手术效果无显著性差异。
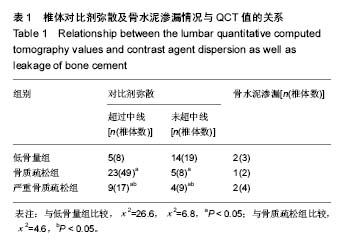
伤椎骨造影:伤椎骨静脉造影,能够准确观察到病变椎体的形态和位置,掌握其至体内的弥散分布情况,有助于选择单侧或双侧穿刺椎体成形术,降低手术穿刺的风险;能提示骨水泥有可能的弥散路径,降低骨水泥渗漏并发症的发生率,提高椎体成形术的安全性。
摘要
背景:骨质疏松性胸腰椎骨折目前临床通常采用经皮穿刺椎体成形术治疗,该术式具有操作难度不大,手术时间短,创伤较小,康复快,止痛疗效确切等多项优点,但其存在骨水泥渗漏而引起的神经压迫症状甚至肺栓塞等并发症,制约其发展。如何降低骨水泥的渗漏,是目前研究的热点。
目的:分析腰椎QCT值与骨质疏松性胸腰椎骨折伤椎对比剂的弥散分布的关联性。
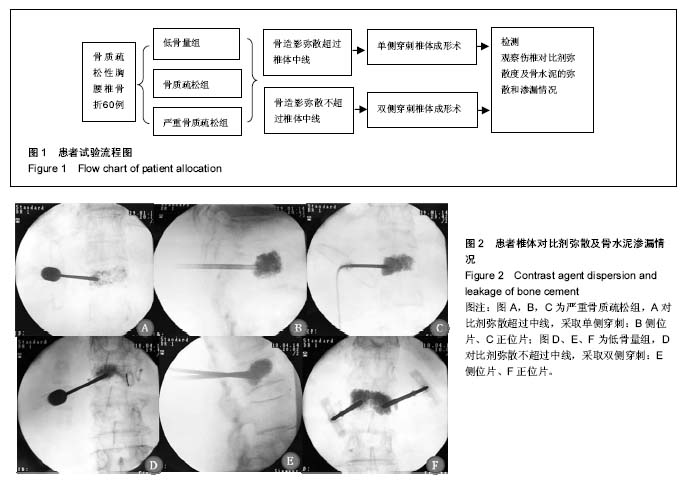
方法:选取60例行经皮穿刺椎体成形术治疗的骨质疏松性胸腰椎骨折患者,术前行腰椎QCT检查,术中往椎体内注射对比剂,正侧位C臂X光机透视,了解不同骨密度值患者对比剂弥散分布情况以及骨水泥在椎体内弥散分布及渗漏等情况,分析腰椎QCT值与伤椎对比剂弥散分布及骨水泥渗漏的关联性。
结果与结论:①60例共110个伤椎中对比剂弥散超过椎体中线74椎,占67.3%。低骨量组、骨质疏松组、严重骨质疏松组各组间对比剂弥散度比较差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);②经单侧或双侧入路椎体成形式注入骨水泥,不同骨密度患者组间骨水泥渗漏情况比较无显著差异(P > 0.05)。③结果显示,对比剂在骨质疏松性胸腰椎骨折伤椎中的弥散分布与腰椎QCT值有一定关系,QCT值低的患者比QCT值较高的患者伤椎对比剂弥漫分布更充分,但骨水泥渗漏的发生与QCT值高低无明显相关,说明根据QCT值结合对比剂分布选择不同穿刺术式伤椎注入骨水泥可减少其渗漏,提高椎体成形术的安全性。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0003-4500-5959(宋泉生)
中图分类号:
.jpg)