[2] Payne JB, Reinhardt RA, Nummikoski PV, et al. Longitudinal alveolar bone loss in postmenopausal osteoporotic/osteopenic women. Osteoporos Int. 1999; 10(1):34-40.
[3] Darcey J, Horner K, Walsh T, et al. Tooth loss and osteoporosis: to assess the association between osteoporosis status and tooth number. Br Dent J. 2013;214(4):E10.
[4] Xie H, Yang F, Deng L, et al. The performance of a bone-derived scaffold material in the repair of critical bone defects in a rhesus monkey model. Biomaterials. 2007;28(22):3314-3324.
[5] Yang ZH, Zhang XJ, Dang NN, et al. Apical tooth germ cell-conditioned medium enhances the differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells into cementum/ periodontal ligament-like tissues.J Periodontal Res. 2009;44(2):199-210.
[6] Wang L, Shen H, Zheng W, et al. Characterization of stem cells from alveolar periodontal ligament. Tissue Eng Part A. 2011;17(7-8):1015-1026.
[7] Kunz GA, Liang G, Cuculi F, et al. Circulating endothelial progenitor cells predict coronary artery disease severity.Am Heart J. 2006;152(1):190-195.
[8] Henrich D, Seebach C, Kaehling C, et al. Simultaneous cultivation of human endothelial-like differentiated precursor cells and human marrow stromal cells on beta-tricalcium phosphate. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2009;15(4):551-560.
[9] Henrich D, Seebach C, Kaehling C, et al. Simultaneous cultivation of human endothelial-like differentiated precursor cells and human marrow stromal cells on beta-tricalcium phosphate. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2009;15(4):551-560.
[10] Peng H, Wright V, Usas A, et al. Synergistic enhancement of bone formation and healing by stem cell-expressed VEGF and bone morphogenetic protein-4. J Clin Invest. 2002;110(6):751-759.
[11] Yang ZH, Zhang XJ, Dang NN, et al. Apical tooth germ cell-conditioned medium enhances the differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells into cementum/ periodontal ligament-like tissues. J Periodontal Res. 2009;44(2):199-210.
[12] Wang L, Shen H, Zheng W, et al. Characterization of stem cells from alveolar periodontal ligament. Tissue Eng Part A. 2011;17(7-8):1015-1026.
[13] Cheng ML, Gupta V. Premenopausal osteoporosis. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2013;17(2):240-244.
[14] Darcey J, Horner K, Walsh T, et al. Tooth loss and osteoporosis: to assess the association between osteoporosis status and tooth number. Br Dent J. 2013;214(4):E10.
[15] Cao L, Liu G, Gan Y, et al. The use of autologous enriched bone marrow MSCs to enhance osteoporotic bone defect repair in long-term estrogen deficient goats. Biomaterials. 2012;33(20):5076-5084.
[16] Murphy WL, Simmons CA, Kaigler D, et al. Bone regeneration via a mineral substrate and induced angiogenesis. J Dent Res. 2004;83(3):204-210.
[17] Faugere MC, Okamoto S, DeLuca HF, et al. Calcitriol corrects bone loss induced by oophorectomy in rats. Am J Physiol. 1986;250(1 Pt 1):E35-38.
[18] Kalu DN. The ovariectomized rat model of postmenopausal bone loss. Bone Miner. 1991;15(3): 175-191.
[19] Jee WS, Yao W. Overview: animal models of osteopenia and osteoporosis. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2001;1(3):193-207.
[20] Wronski TJ, Cintrón M, Dann LM. Temporal relationship between bone loss and increased bone turnover in ovariectomized rats. Calcif Tissue Int. 1988; 43(3):179-183.
[21] Li M, Shen Y, Wronski TJ. Time course of femoral neck osteopenia in ovariectomized rats. Bone. 1997;20(1): 55-61.
[22] Ingram DA, Caplice NM, Yoder MC. Unresolved questions, changing definitions, and novel paradigms for defining endothelial progenitor cells. Blood. 2005; 106(5):1525-1531.
[23] Urbich C, Dimmeler S. Endothelial progenitor cells: characterization and role in vascular biology. Circ Res. 2004;95(4):343-353.
[24] Rafii S, Lyden D. Therapeutic stem and progenitor cell transplantation for organ vascularization and regeneration. Nat Med. 2003;9(6):702-712.
[25] Asahara T, Murohara T, Sullivan A, et al. Isolation of putative progenitor endothelial cells for angiogenesis. Science. 1997;275(5302):964-967.
[26] Marsboom G, Janssens S. Endothelial progenitor cells: new perspectives and applications in cardiovascular therapies. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2008;6(5): 687-701.
[27] Lévesque JP, Winkler IG, Hendy J, et al. Hematopoietic progenitor cell mobilization results in hypoxia with increased hypoxia-inducible transcription factor-1 alpha and vascular endothelial growth factor A in bone marrow. Stem Cells. 2007;25(8):1954-1965.
[28] Xu J, Liu X, Chen J, et al. Cell-cell interaction promotes rat marrow stromal cell differentiation into endothelial cell via activation of TACE/TNF-alpha signaling. Cell Transplant. 2010;19(1):43-53.
[29] Loibl M, Binder A, Herrmann M, et al. Direct cell-cell contact between mesenchymal stem cells and endothelial progenitor cells induces a pericyte-like phenotype in vitro. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:395781.
.jpg)
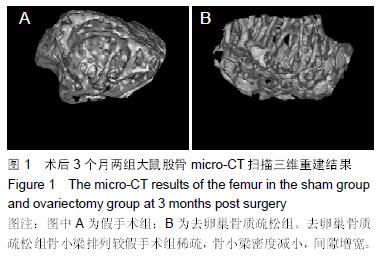
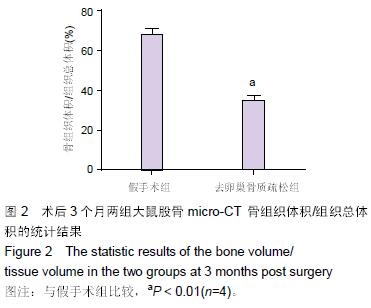
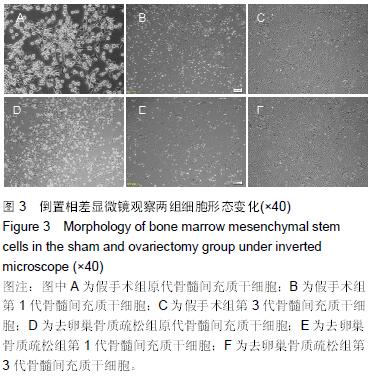
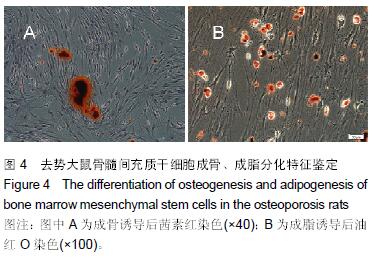

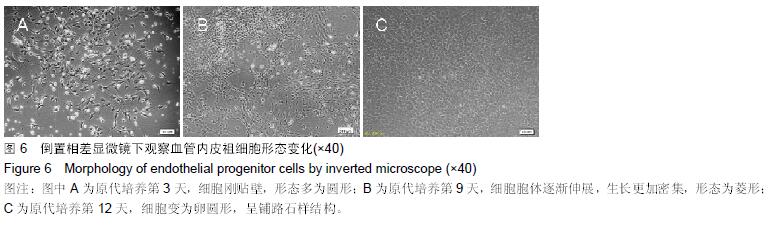
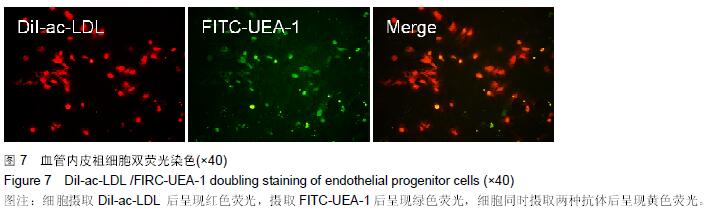
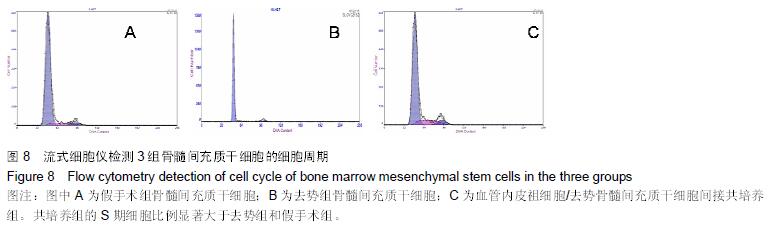
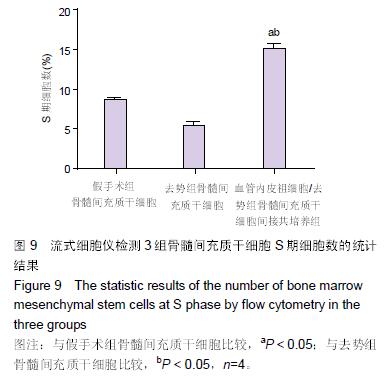
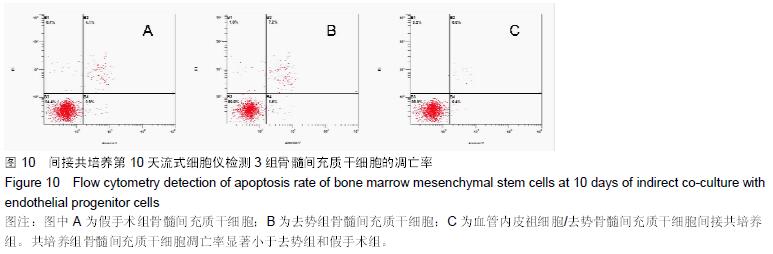
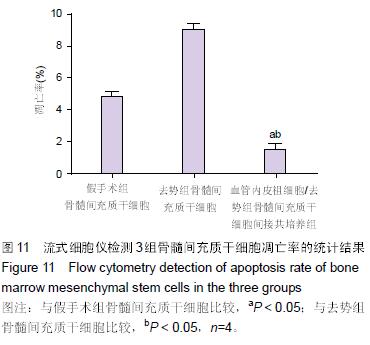
.jpg) 文题释义:
血管内皮祖细胞:1997年Asahara首次报道由外周血获得能分化为血管内皮细胞的前体细胞,此细胞表达CD34和血管内皮细胞生长因子受体2,在体外培养呈典型的长梭形,可形成管腔样结构,能够表达内皮细胞的特异性抗原,在缺血性动物模型中可观察到它们参与血管的生成,故命名为血管内皮祖细胞。研究发现,血管内皮祖细胞在组织工程骨中参与了血管的再生和修复。
Transwell间接共培养:此项技术的特点在于运用一种特殊的共培养工具进行细胞共培养,观察两种细胞的相互作用。该技术关键部分在于杯子底层有一张有通透性的聚碳酸酯膜,这层膜带有微孔,孔径最大为12.0 μm,最小为0.1 μm,使得培养的两细胞不能相互接触,实现非接触性共培养。
文题释义:
血管内皮祖细胞:1997年Asahara首次报道由外周血获得能分化为血管内皮细胞的前体细胞,此细胞表达CD34和血管内皮细胞生长因子受体2,在体外培养呈典型的长梭形,可形成管腔样结构,能够表达内皮细胞的特异性抗原,在缺血性动物模型中可观察到它们参与血管的生成,故命名为血管内皮祖细胞。研究发现,血管内皮祖细胞在组织工程骨中参与了血管的再生和修复。
Transwell间接共培养:此项技术的特点在于运用一种特殊的共培养工具进行细胞共培养,观察两种细胞的相互作用。该技术关键部分在于杯子底层有一张有通透性的聚碳酸酯膜,这层膜带有微孔,孔径最大为12.0 μm,最小为0.1 μm,使得培养的两细胞不能相互接触,实现非接触性共培养。