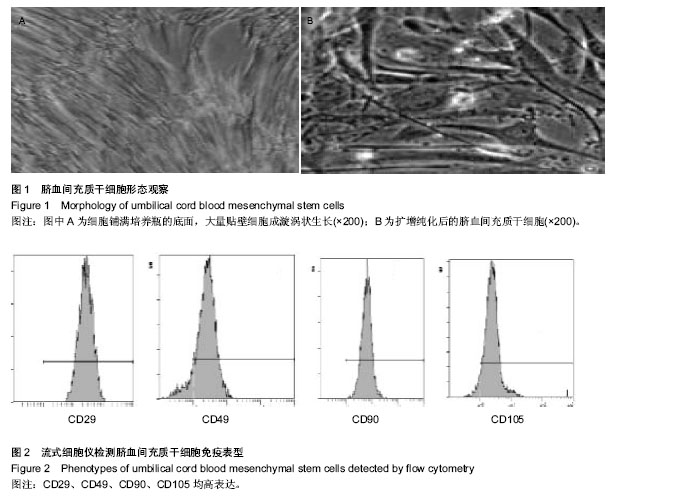
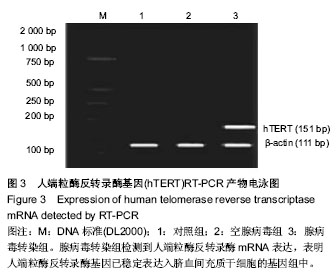
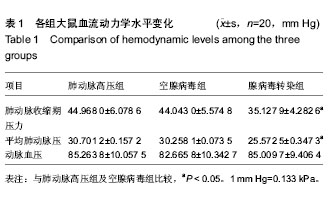
| [1] 王秋芬,廖玉华.欧洲心脏病协会 2004 年肺动脉高压诊断和治疗指南简介[J].临床心血管病杂志,2005, 21(7):385-386.
[2] 王俊东,杨达宽,李治纲,等.野百合碱诱导大鼠肺动脉高压模型的建立[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(28): 5237- 5240.
[3] 尚峰,何志旭,汪浩文,等.骨髓间充质干细胞治疗实验性肺动脉高压大鼠的疗效观察[J].贵阳医学院学报,2008,33(6):567-572.
[4] 胡建明,高占成. 骨髓间充质干细胞治疗肺动脉高压的研究进展[J].国际呼吸杂志,2013,33(5):385-388.
[5] 赵科研,王辉山,侯明晓,等. 不同数目骨髓间充质干细胞移植对大鼠肺动脉高压的作用及内皮素-1表达的影响[J].中国胸心血管外科临床杂志,2012,19(3):298-303.
[6] 何志旭,汪浩文,尚峰,等. 骨髓间充质干细胞治疗实验性肺动脉高压后肺组织结构的变化[J].中国病理生理杂志,2009, 25(10): 1907-1911.
[7] 卢艳,孔令彩,张兆华. 移植骨髓间充质干细胞预防野百合碱诱导的肺动脉高压[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(36): 6468- 6473.
[8] 张春曦,黄达德,陈敏东,等.间充质干细胞联合辛伐他汀对动力性肺动脉高压的影响[J].广州医药,2012,43(6):1-3.
[9] 李建斌,焦红亮,单泓,等. 脐血间充质干细胞在脑卒中小鼠模型主要器官分布研究[J].中国输血杂志, 2010, 23(10):870-871.
[10] Farber HW, Loscalzo J. Pulmonary arterial hypertension. N Engl J Med. 2004;351(16):1655-1665.
[11] Passier R, Mummery C. Origin and use of embryonic and adult stem cells in differentiation and tissue repair. Cardiovasc Res. 2003;58(2):324-335.
[12] Goodwin HS, Bicknese AR, Chien SN, et al. Multilineage differentiation activity by cells isolated from umbilical cord blood: expression of bone, fat, and neural markers. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2001;7(11):581-588.
[13] Tsuda H, Wada T, Yamashita T, et al. Enhanced osteoinduction by mesenchymal stem cells transfected with a fiber-mutant adenoviral BMP2 gene. J Gene Med. 2005;7(10): 1322-1334.
[14] 赵科研,王辉山,侯明晓,等.不同数目骨髓间充质干细胞移植对大鼠肺损伤的抑制作用[J].中国比较医学杂志,2012,22(1):34-38.
[15] Alviano F, Fossati V, Marchionni C, et al. Term Amniotic membrane is a high throughput source for multipotent Mesenchymal Stem Cells with the ability to differentiate into endothelial cells in vitro. BMC Dev Biol. 2007;7:11.
[16] Toyama K, Honmou O, Harada K, et al. Therapeutic benefits of angiogenetic gene-modified human mesenchymal stem cells after cerebral ischemia. Exp Neurol. 2009;216(1):47-55.
[17] Brevetti G, Schiano V, Chiariello M. Endothelial dysfunction: a key to the pathophysiology and natural history of peripheral arterial disease. Atherosclerosis. 2008;197(1):1-11.
[18] Avogaro A, Fadini GP, Gallo A, et al. Endothelial dysfunction in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2006; 16 Suppl 1:S39-45.
[19] 赵科研,王辉山,侯明晓,等. 骨髓间充质干细胞移植肺动脉高压大鼠内皮素-1的变化[J].中华实验外科杂志,2012,29(8): 1460-1462.
[20] 齐建光,杜军保, 魏冰,等. 左向右分流所致肺动脉高压大鼠模型的建立及其肺血管结构的变化[J].中华实验外科杂志,2002, 19(3):199-200.
[21] 曲素萍,牛丽丽.经气管注射骨髓间充质干细胞治疗早期血管炎性作用所致肺动脉高压的实验研究[J].安徽医科大学学报,2012, 47(10):1169-1173.
[22] 吴德全,高峰,金光鑫,等.足月胎儿脐血间充质干细胞体外培养方法的比较[J].哈尔滨医科大学学报,2007,41(5):429-433,436.
[23] Gang EJ, Hong SH, Jeong JA, et al. In vitro mesengenic potential of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;321(1):102-108.
[24] 迟作华,张洹,何冬梅,等.脐血间充质干细胞培养条件的优化[J].中国实用内科杂志:临床版,2006,26(5):372-375.
[25] 李建斌,焦红亮,单泓,等.脐血间充质干细胞在脑卒中小鼠模型主要器官分布研究[J].中国输血杂志, 2010, 23(10):870-871.
[26] Park H, Temenoff JS, Tabata Y, et al. Injectable biodegradable hydrogel composites for rabbit marrow mesenchymal stem cell and growth factor delivery for cartilage tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2007;28(21):3217-3227.
[27] Park Y, Chen Y, Ordovas L, et al. Hepatic differentiation of human embryonic stem cells on microcarriers. J Biotechnol. 2014;174:39-48.
[28] Kidd SA. Congenital heart disease: a 10 year cohort. J Paediatr Child Health. 1995;31(4):362.
[29] Bieback K, Kern S, Klüter H, et al. Critical parameters for the isolation of mesenchymal stem cells from umbilical cord blood. Stem Cells. 2004;22(4):625-634.
[30] 刘素芳,鄢文海,韩雪飞,等.人脐血间充质细胞体外分离培养方法及培养基特性[J].中国临床康复,2005,9(46):34-35.
[31] 王屹,季凤清,孙海梅,等.人脐血非造血干细胞的基本特性[J].中国临床康复,2006,10(29): 50-52.
[32] 孙海梅,季凤清,李荣平,等.不同培养条件下人脐血间充质干细胞的差异[J].中国临床康复,2006, 10(45):51-53.
[33] 金玮,杨安怀,邢怡桥.人脐血间充质干细胞的体外培养及生物学特性[J].武汉大学学报:医学版,2007,28(4):488-491.
[34] 常相萍,马艳,毕晓娟,等.冷冻前后脐带间充质干细胞造血支持能力的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(32):5765-5771.
[35] Yao LQ,He C,Zhang Y,et al.Human umbilical cord blood stem cell transplantation for the treatment of chronic spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2013;8 (5): 397-403.
[36] 陈镭,苗宗宁,张东强,等.人脐血源性间充质干细胞的体外培养及生物学鉴定[J].江苏医药,2005,31(7):481-483 |