| [1] Ahmed S.The culture of neural stem cells.J Cell Biochem. 2009;106(1):1-6.
[2] Lee GY, Kim JA, Oh IH. Stem cell niche as a prognostic factor in leukemia. BMB Rep. 2015;48(8):427-428.
[3] Allazetta S, Lutolf MP. Stem cell niche engineering through droplet microfluidics. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2015;35:86-93.
[4] DeCarolis NA, Kirby ED, Wyss-Coray T, et al. The Role of the Microenvironmental Niche in Declining Stem-Cell Functions Associated with Biological Aging.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2015;5(12). pii: a025874.
[5] Polisetti N, Zenkel M, Menzel-Severing J, et al. Cell Adhesion Molecules and Stem Cell-Niche-Interactions in the Limbal Stem Cell Niche.Stem Cells. 2015 Sep 9. doi: 10.1002/stem. 2191. [Epub ahead of print]
[6] Feng JF, Liu J, Zhang XZ, et al. Guided migration of neural stem cells derived from human embryonic stem cells by an electric field. Stem Cells. 2012;30(2):349-355.
[7] Li Q, Brus-Ramer M, Martin JH, et al. Electrical stimulation of the medullary pyramid promotes proliferation and differentiation of oligodendrocyte progenitor cells in the corticospinal tract of the adult rat. Neurosci Lett. 2010;479(2): 128-133.
[8] Koppes AN, Nordberg AL, Paolillo GM, et al. Electrical stimulation of schwann cells promotes sustained increases in neurite outgrowth. Tissue Eng Part A. 2014;20(3-4):494-506.
[9] Adams DS, Levin M. Endogenous voltage gradients as mediators of cell-cell communication: strategies for investigating bioelectrical signals during pattern formation. Cell Tissue Res. 2013;352(1):95-122.
[10] Sütterlin P, Williams EJ, Chambers D, et al. The molecular basis of the cooperation between EGF, FGF and eCB receptors in the regulation of neural stem cell function. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2013;52:20-30.
[11] Dupin E, Sommer L. Neural crest progenitors and stem cells: from early development to adulthood. Dev Biol. 2012;366(1): 83-95.
[12] Stemple DL, Anderson DJ. Isolation of a stem cell for neurons and glia from the mammalian neural crest. Cell. 1992; 71(6): 973-985.
[13] Mokrý J, Karbanová J. Foetal mouse neural stem cells give rise to ependymal cells in vitro. Folia Biol (Praha). 2006;52(5): 149-155.
[14] Deleyrolle LP, Reynolds BA. Identifying and enumerating neural stem cells: application to aging and cancer. Prog Brain Res. 2009;175:43-51.
[15] Zhang P, Wu X, Hu C, et al. Rho kinase inhibitor Y-27632 and Accutase dramatically increase mouse embryonic stem cell derivation. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2012;48(1):30-36.
[16] Bajpai R, Lesperance J, Kim M, et al. Efficient propagation of single cells Accutase-dissociated human embryonic stem cells. Mol Reprod Dev. 2008;75(5):818-827.
[17] Taha MF, Javeri A, Kheirkhah O, et al. Neural differentiation of mouse embryonic and mesenchymal stem cells in a simple medium containing synthetic serum replacement. J Biotechnol. 2014;172:1-10.
[18] Chojnacki A, Weiss S. Production of neurons, astrocytes and oligodendrocytes from mammalian CNS stem cells. Nat Protoc. 2008;3(6):935-940.
[19] Remaud S, López-Juárez SA, Bolcato-Bellemin AL, et al. Inhibition of Sox2 Expression in the Adult Neural Stem Cell Niche In Vivo by Monocationic-based siRNA Delivery. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2013;2:e89.
[20] Kim SM, Flaßkamp H, Hermann A, et al. Direct conversion of mouse fibroblasts into induced neural stem cells. Nat Protoc. 2014;9(4):871-881.
[21] De Filippis L, Binda E. Concise review: self-renewal in the central nervous system: neural stem cells from embryo to adult. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2012;1(4):298-308.
[22] Yaqubi M, Mohammadnia A, Fallahi H. Predicting involvement of polycomb repressive complex 2 in direct conversion of mouse fibroblasts into induced neural stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;6:42.
[23] Nout YS, Rosenzweig ES, Brock JH, et al. Animal models of neurologic disorders: a nonhuman primate model of spinal cord injury. Neurotherapeutics. 2012;9(2):380-392.
[24] Conover JC, Notti RQ. The neural stem cell niche. Cell Tissue Res. 2008;331(1):211-224.
[25] Haubenwallner S, Katschnig M, Fasching U, et al. Effects of the polymeric niche on neural stem cell characteristics during primary culturing. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2014;25(5): 1339-1355.
[26] Kerever A, Mercier F, Nonaka R, et al. Perlecan is required for FGF-2 signaling in the neural stem cell niche. Stem Cell Res. 2014;12(2):492-505.
[27] Belmadani A, Tran PB, Ren D, et al. Chemokines regulate the migration of neural progenitors to sites of neuroinflammation. J Neurosci. 2006;26(12):3182-3191.
[28] Illes S, Theiss S, Hartung HP, et al. Niche-dependent development of functional neuronal networks from embryonic stem cell-derived neural populations. BMC Neurosci. 2009; 10:93.
[29] Garcion E, Halilagic A, Faissner A, et al. Generation of an environmental niche for neural stem cell development by the extracellular matrix molecule tenascin C. Development. 2004; 131(14):3423-3432.
[30] Musienko P, van den Brand R, Maerzendorfer O, et al. Combinatory electrical and pharmacological neuroprosthetic interfaces to regain motor function after spinal cord injury. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2009;56(11 Pt 2):2707-2711. |
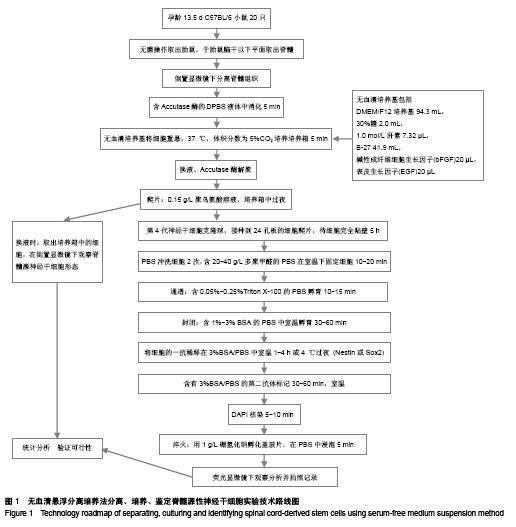
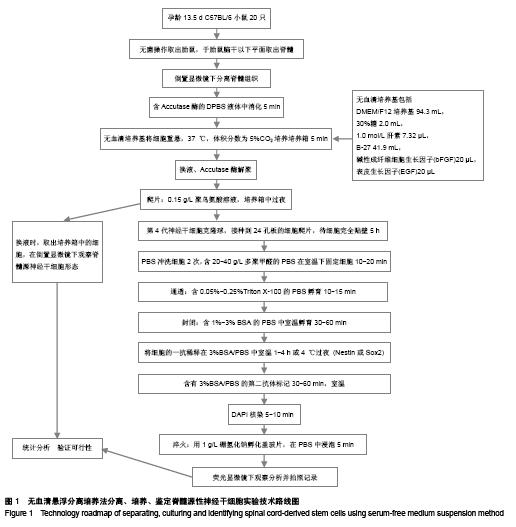
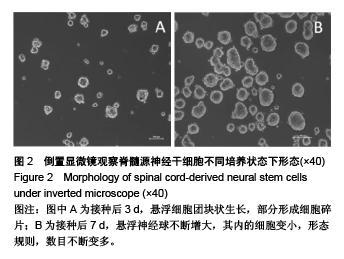
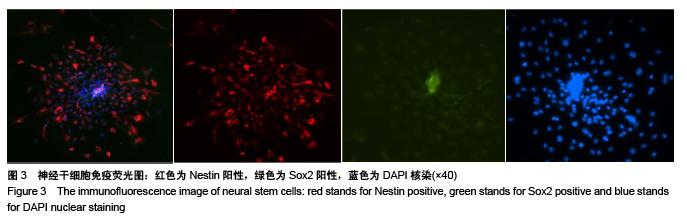
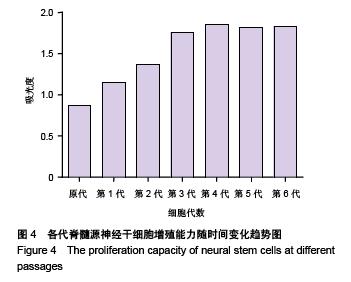
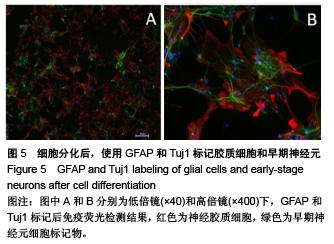
.jpg)