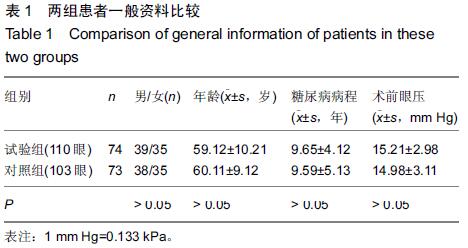
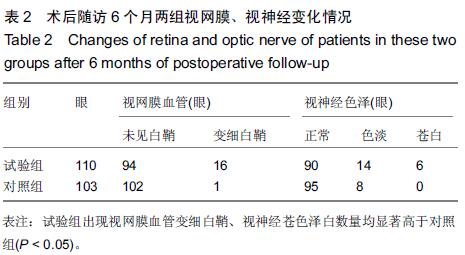
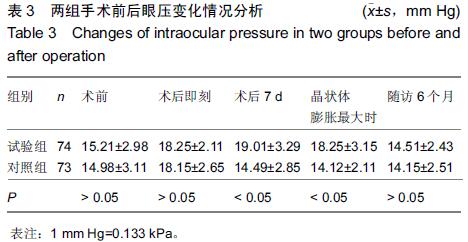
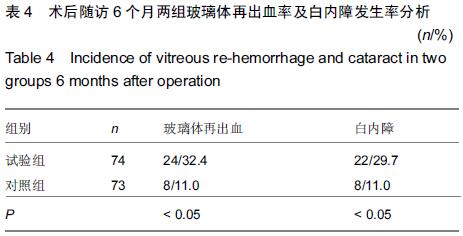
|
[1] 勾明宝.糖尿病病人硅油填充术后视网膜、视神经改变的临床研究[D].内蒙古民族大学,2012.
[2] 周兰新,李建荣,刘虹,等.无眼内气体或硅油填充的玻璃体切割手术治疗糖尿病视网膜病变并发牵拉性视网膜脱离的疗效观察[J].中华眼底病杂志,2012,28(2):168-169.
[3] 黄黎黎,宋愈,吴莹,等.早期硅油填充联合曲安奈德治疗增生性糖尿病视网膜病变[J].中华眼外伤职业眼病杂志,2011,33(10): 750-752.
[4] 周晓芳,付汛安,赵芳,等.玻璃体切割联合硅油填充术治疗晚期增殖性糖尿病视网膜病变疗效观察[J].山东医药,2010,50(24): 86-87.
[5] 范传峰,王玉,舒相汶,等.玻璃体切除联合不同眼内填充物治疗增性糖尿病视网膜病变的效果分析[J].中国实用眼科杂志,2009, 27(9):989-992.
[6] 张海江,李铮,苏陆青,等.糖尿病视网膜病变玻璃体切割手术联合硅油填充术后激光治疗的现状与进展[J].河北医药,2012,34(15): 2357-2358.
[7] 李云环.眼内气体填充和硅油填充治疗增殖型糖尿病视网膜病变[J].医学临床研究,2013,30(8):1531-1532,1535.
[8] 李闻思,张风,卢海,等.增生陛糖尿病视网膜病变硅油填充眼白内障摘出人工晶状体植入的手术效果分析[J].眼科,2008,17(4): 239-241,249.
[9] 田锁成,李慧俐,罗翠平,等.玻璃体视网膜手术联合全氟丙烷气体与硅油填充治疗增殖性糖尿病视网膜病变疗效观察[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志,2011,25(8):810-812.
[10] 勾明宝,佟艳秋.糖尿病病人硅油填充术后视网膜、视神经改变的研究进展[J].中国伤残医学,2012,20(4):123-124.
[11] 李蕙.糖尿病视网膜病变的玻切联合不同填充物治疗的并发症分析[D].中国协和医科大学,2006.
[12] 赵全良,张春香,勾明宝,等.PDR患者硅油填充术后视网膜功能评价[J].国际眼科杂志,2013,13(4):756-758.
[13] 王叶楠,卢海,刘大川,等.2型糖尿病患者增生性糖尿病视网膜病变玻璃体切割术后玻璃体再积血原因分析[J].中华实验眼科杂志,2014,32(11):1021-1024.
[14] 狄浩浩,陈松,王昀,等.保留晶状体的玻璃体视网膜术治疗严重增殖型糖尿病视网膜病变观察[J].中国实用眼科杂志,2013,31(2): 124-127.
[15] Cilenšek I,Manko? S,Globo?nik Petrovi? M,et al.The 4a/4a genotype of the VNTR polymorphism for endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) gene predicts risk for proliferative diabetic retinopathy in Slovenian patients (Caucasians) with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Mol Biol Rep.2012;39(6): 7061-7067.
[16] 王颖,江枫,韩金栋,等.玻璃体腔硅油或C3F8填充对增生型糖尿病视网膜病变并发单纯玻璃体积血玻璃体切割手术疗效的影响[J].中华眼底病杂志,2014,30(2):148-151.
[17] 刘大川,吴航,郭丽,等.玻璃体切除联合白内障手术治疗增生性糖尿病视网膜病变的临床效果[J].中华眼科杂志,2007,43(4): 346-349.
[18] 王瑞峰,高雪霞.玻璃体切割联合硅油填充治疗增殖性糖尿病视网膜病变玻璃体积血的临床观察[J].河南医学研究,2008,17(1): 53-54.
[19] 张静琳,吕林,李永浩,等.玻璃体腔注射Avastin在晚期增生性糖尿病视网膜病变术中应用分析[J].中国实用眼科杂志,2010, 28(3):223-225.
[20] Charles BA,Conley YP,Chen G,et al.Variants of the adenosine A(2A) receptor gene are protective against proliferative diabetic retinopathy in patients with type 1 diabetes. Ophthalmic Res.2011;46(1):1-8.
[21] Oloumi F,Rangayyan RM,Ells AL.Computer-aided diagnosis of proliferative diabetic retinopathy via modeling of the major temporal arcade in retinal fundus images.J Digit Imaging. 2013; 26(6):1124-1130.
[22] 刘海芸,宋正宇,刘堃,等.23G和20G玻璃体切割手术治疗糖尿病视网膜病变的有效性和安全性比较[J].中华眼底病杂志,2012, 28(2):138-141.
[23] 王丁丁,陈子林,周慧兰,等.重硅油填充治疗增生性糖尿病视网膜病变的临床研究[J].眼科新进展,2013,33(1):74-76.
[24] 高朋芬,陈梅珠,杨丽霞,等.玻璃体切除联合白内障手术治疗增殖性糖尿病视网膜病变52眼分析[J].局解手术学杂志,2010,19(5): 387-389.
[25] 王敏.不同填充物在糖尿病视网膜病变玻璃体手术中的对比研究[J].当代医学,2013,19(30):59-60,61.
[26] 陶勇,姜燕荣,黎晓新,等.增生性糖尿病视网膜病变患者玻璃体手术不同眼内填充物的效果分析[J].眼科新进展,2008,28(2): 119-121, 124.
[27] 江枫,韩金栋,颜华,等.糖尿病视网膜病变合并视网膜中央静脉阻塞的临床特征及玻璃体切割手术治疗效果观察[J].中华眼底病杂志,2013,29(6):567-570.
[28] 佟艳秋,孙刚,马慧蕾,等.玻璃体切除联合眼内光凝治疗增生性糖尿病视网膜病变[J].眼外伤职业眼病杂志,2010,32(6):435-437.
[29] 陶勇,姜燕荣,黎晓新,等.无眼内填充的玻璃体视网膜手术治疗糖尿病视网膜病变牵引性视网膜脱离疗效观察[J].中华眼底病杂志, 2009,25(1):14-17.
[30] 彭超,王立,陈惠莉,等.玻璃体切除治疗增生性糖尿病视网膜病变[J].国际眼科杂志,2013,13(10):2122-2123.
[31] Welikala RA,Dehmeshki J,Hoppe A,et al.Automated detection of proliferative diabetic retinopathy using a modified line operator and dual classification.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2014;114(3):247-261.
[32] 颜华,崔靖,于金国,等.增生性糖尿病视网膜病变患者玻璃体内血管内皮生长因子的表达[J].中华眼科杂志,2009,45(3):206-209.
[33] 李松涛,张红鸽,周占宇,等.玻璃体术后硅油界面前纤维膜对Ⅵ期糖尿病视网膜病变疗效影响[J].中国实用眼科杂志,2014,32(6): 742-745.
[34] 曹金峰,刘早霞,赵劲松等.增殖性糖尿病视网膜病变102例手术治疗的临床分析[J].中国实用眼科杂志,2012,30(5):532-536.
[35] 陈松,王莹,赵秉水,等.糖尿病性视网膜病变与其他眼底血管性疾病的玻璃体视网膜手术治疗研究[J].临床眼科杂志,2005, 13(1):3-8.
[36] 胡恩海,吴法华.微创玻璃体切割联合白内障超声乳化术治疗增生性糖尿病视网膜病变的临床疗效[J].实用防盲技术, 2014,(3): 104-106. |