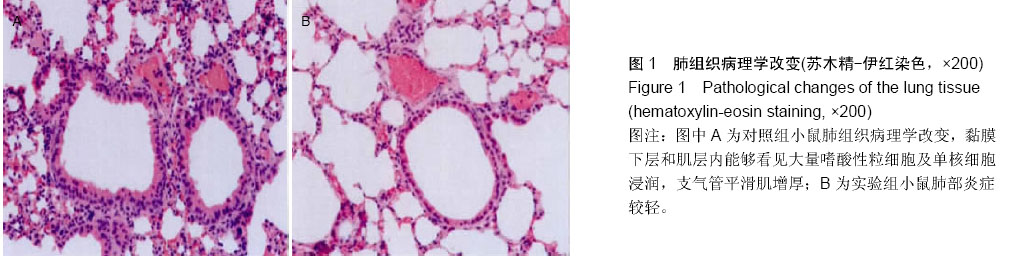
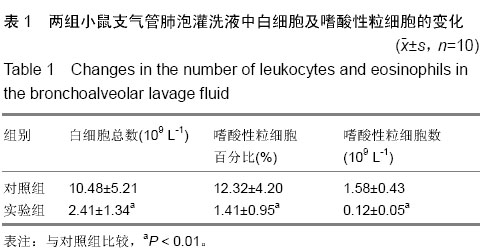
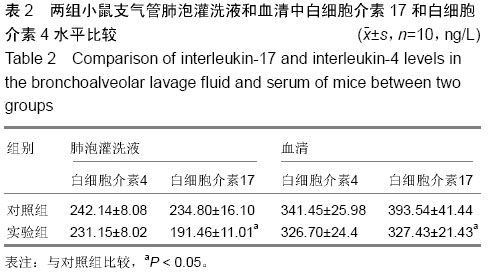
| [1] Olmez D, Babayigit A, Uzuner N, et al. Efficacy of sulphasalazine on lung histopathology in a murine model of chronic asthma. Exp Lung Res. 2008;34(8):501-511.
[2] 卢慧宇,徐虹,张亚明.雾化吸入糖皮质激素在哮喘急性发作的应用相关问题探讨[J].中华结核和呼吸杂志,2015,38(2): 158-160.
[3] Kozanoglu I, Boga C, Ozdogu H,et al. Human bone marrow mesenchymal cells express NG2: possible increase in discriminative ability of flow cytometry during mesenchymal stromal cell identification. Cytotherapy. 2009;11(5):527-533.
[4] Baskin H, Ellermann-Eriksen S. Herpes simplex virus type 2 synergizes with interferon-gamma in the induction of nitric oxide production in mouse macrophages through autocrine secretion of tumour necrosis factor-alpha. J Gen Virol. 1997; 78 ( Pt 1):195-203.
[5] Shin IS, Shin NR, Jeon CM, et al. EC-18, a synthetic monoacetyldiglyceride (1-palmitoyl-2-linoleoyl- 3-acetylglycerol), attenuates the asthmatic response in an aluminum hydroxide/ovalbumin-induced model of asthma .Int Immunopharmacol. 2014;18(1):116-123.
[6] Brightling CE, Symon FA, Birring SS, et al. TH2 cytokine expression in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid T lymphocytes and bronchial submucosa is a feature of asthma and eosinophilic bronchitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002;110(6):899-905.
[7] 黄芸,欧阳海峰,吴朔,等.外源性间充质干细胞减轻支气管哮喘小鼠气道炎症的研究[J].中华哮喘杂志:电子版,2010,4(2): 102-106.
[8] 张学敏,刘卓拉.调节性T细胞在支气管哮喘中的作用[J].国际呼吸杂志,2007,27(11):847-849.
[9] 田莹,邓宇斌,黄奕俊,等.骨髓间充质干细胞在CD4+CD25+调节性T细胞减轻实验小鼠移植物抗宿主反应中的作用[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2006,14(6):1210-1214.
[10] 陈莉娜,王颖,张艳艳,等.间充质干细胞的免疫调节作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(28): 5626-5629.
[11] 唐晓琼,赵智刚,王红祥,等.骨髓间充质干细胞免疫调节机制的实验研究[J].中国免疫学杂志,2006,22(9): 822-826.
[12] 宣旻,邱国强,谢晓宝.间充质干细胞对混合淋巴细胞反应体系中T淋巴细胞的免疫调节作用[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志, 2006,22(4):433-435.
[13] 吴涛,白海,王存邦,等.成人骨髓间充质干细胞抑制异体淋巴细胞增殖的实验研究[J].中华器官移植杂志,2006,27(2): 111-113.
[14] 祖莹,李成荣,郑跃杰,等. CD4+CD25+调节性T细胞在儿童哮喘发病机制中的作用初探[J].中华医学杂志,2006,86(1): 35-38.
[15] 郭少嘉.预防与治疗砂肺的最新研究进展[J].中国医学工程,2011, 19(7):103-106.
[16] Karaoz E, Aksoy A, Ayhan S, et al. Characterization of mesenchymal stem cells from rat bone marrow: ultrastructural properties, differentiation potential and immunophenotypic markers. Histochem Cell Biol. 2009;132(5):533-546.
[17] 高羽亭,丁国永.骨髓间充质干细胞对实验小鼠肝缺血-再灌注损伤定向促修复作用的研究[J].中外医疗,2009,28(21):25-26.
[18] Bensidhoum M, Chapel A, Francois S, et al. Homing of in vitro expanded Stro-1- or Stro-1+ human mesenchymal stem cells into the NOD/SCID mouse and their role in supporting human CD34 cell engraftment. Blood. 2004;103(9):3313-3319.
[19] 罗伟,肖恩华.骨髓间充质干细胞体外诱导分化为肝细胞的研究与进展[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(36): 7155-7158.
[20] Ji JF, He BP, Dheen ST, et al. Interactions of chemokines and chemokine receptors mediate the migration of mesenchymal stem cells to the impaired site in the brain after hypoglossal nerve injury. Stem Cells. 2004;22(3):415-427.
[21] Soleimani M, Nadri S. A protocol for isolation and culture of mesenchymal stem cells from mouse bone marrow. Nat Protoc. 2009;4(1):102-106.
[22] Zhu H, Guo ZK, Jiang XX, et al. A protocol for isolation and culture of mesenchymal stem cells from mouse compact bone. Nat Protoc. 2010;5(3):550-560.
[23] Anjos-Afonso F, Siapati EK, Bonnet D. In vivo contribution of murine mesenchymal stem cells into multiple cell-types under minimal damage conditions. J Cell Sci. 2004;117(Pt 23): 5655-5664.
[24] 唐孝青,李斌,伍小兵,等.绿色焚光蛋白及其应用的研究进展[J].陕西农业科学,2007,(1):123-124.
[25] 张雨丽,张桂征,苏红梅,等. 绿色荧光蛋白在转基因研究中的应用[J].生物技术通报,2010,(9):16-20.
[26] 胡运生,马保安,张勇,等.绿色荧光蛋白报告基因转染示踪体内骨髓间充质干细胞的分化[J].中国医师杂志,2006,8(10):1300- 1302.
[27] 吴沛桥,巴晓革,胡海,等.绿色荧光蛋白GFP的研究进展及应用[J].生物医学工程研究,2009,28(1):83-86.
[28] Lassance RM, Prota LF, Maron-Gutierrez T, et al. Intratracheal instillation of bone marrow-derived cell in an experimental model of silicosis. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2009;169(3):227-233.
[29] Xu M, Deng B, Chow YL, et al. Effects of curcumin in treatment of experimental pulmonary fibrosis: a comparison with hydrocortisone. J Ethnopharmacol. 2007;112(2):292-299.
[30] 杨霞,丁鹏,高宏生,等.肺纤维化中细胞因子网络[J].武警医学院学报,2009,18(3):245-248.
[31] 胡永斌,曾庆富. 矽肺纤维化细胞分子机制研究的进展[J].中华劳动卫生与职业病杂志,2003,21(3):219-221.
[32] 王世鑫,魏茂提,周蔚,等. 染矽尘大鼠肺匀浆TGF-β1和TNF-α的变化[J].工业卫生与职业病,2002,28(5):257-259.
[33] 李婷,曹贵文,罗莉. 干扰素-γ对染矽尘小鼠肺脏肿瘤坏死因子-α和转化生长因子-β1蛋白表达的影响[J].中国临床研究,2010, 23(1):5-7.
[34] 丁焕然,马小兵,戴丽琴.二二氧化硅对大鼠肺泡巨噬细胞和肺成纤维细胞TGF-β1表达的影响[J].工业卫生与职业病,2007,33(4): 214-217.
[35] 赵静,马小兵,王献华,等.二氧化硅对人肺泡巨噬细胞和肺成纤维细胞TGF-β1表达的影响[J].山东医药,2008,48(48):24-25.
[36] 王献华,蒋建姝.二氧化硅对人肺泡巨噬细胞和肺成纤维细胞IL-1β表达意义[J].中国职业医学,2011,38(3):213-215.
[37] 任平香,王献华,蒋建姝,等.肿瘤坏死因子-α与肺纤维化[J].中国煤炭工业医学杂志,2007,10(3):242-244.
[38] Sullivan DE, Ferris M, Pociask D, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces transforming growth factor-beta1 expression in lung fibroblasts through the extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2005;32(4):342-349.
[39] 潘雍,杨昆,刘永哲.骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗矽肺小鼠肺炎及肺纤维化[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(6):1049-1055.
[40] 韩丽红.红霉素、布地奈德联合特布他林治疗喘息性支气管炎疗效观察[J].中国现代药物应用,2010,4(21):172-173. |