| [1] Zuk PA, Zhu M, Mizuno H,et al. Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies.Tissue Eng. 2001;7(2):211-228.
[2] Ferrari G, Cusella-De Angelis G, Coletta M, et al. Muscle regeneration by bone marrow-derived myogenic progenitors.Science. 1998;279(5356):1528-1530.
[3] Dennis JE, Merriam A, Awadallah A, et al. A quadripotential mesenchymal progenitor cell isolated from the marrow of an adult mouse.J Bone Miner Res. 1999;14(5):700-709.
[4] Li W, Ren G, Huang Y, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells: a double-edged sword in regulating immune responses. Cell Death Differ. 2012;19(9):1505-1513.
[5] Mahmood A, Lu D, Chopp M. Marrow stromal cell transplantation after traumatic brain injury promotes cellular proliferation within the brain.Neurosurgery. 2004;55(5): 1185-1193.
[6] Ding W, Bai J, Zhang J, et al. In vivo tracking of implanted stem cells using radio-labeled transferrin scintigraphy.Nucl Med Biol. 2004;31(6):719-725.
[7] Zhao DC, Lei JX, Chen R, et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells protect against experimental liver fibrosis in rats.World J Gastroenterol. 2005;11(22):3431-3340.
[8] He R, You XG, Shao J, et al. Core/shell fluorescent magnetic silica-coated composite nanoparticles for bioconjugation. Nanotechnology. 2007;18(31): 1-7.
[9] 吉佳佳,阮静,崔大祥.荧光磁性纳米粒子体外标记骨髓间充质干细胞研究[J].东南大学学报:医学版,2011,30(1): 43-47.
[10] 吉佳佳,阮静,崔大祥.荧光磁性纳米粒子标记间充质干细胞靶向胃癌研究[J].生物技术, 2011,21(1):66-68.
[11] 周婷婷,卫超,陈晓东,等.无血清培养体系原代培养脐带间充质干细胞[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(27): 4980-4987.
[12] Nishida S, Endo N, Yamagiwa H, et al. Number of osteoprogenitor cells in human bone marrow markedly decreases after skeletal maturation.J Bone Miner Metab. 1999;17(3):171-177.
[13] Mueller SM, Glowacki J.Age-related decline in the osteogenic potential of human bone marrow cells cultured in three- dimensional collagen sponges.J Cell Biochem. 2001;82(4): 583-590.
[14] Stenderup K, Justesen J, Clausen C, et al. Aging is associated with decreased maximal life span and accelerated senescence of bone marrow stromal cells.Bone. 2003;33(6):919-926.
[15] Jiang Y, Lee A, Chen J ,et al. The open pore conformation of potassium channels.Nature. 2002;417(6888):523-526.
[16] Oswald J, Boxberger S, Jørgensen B, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells can be differentiated into endothelial cells in vitro.Stem Cells. 2004;22(3):377-384.
[17] 苏约翰,卫超,吕品雷,等.利用细胞外基质大规模扩增临床级人脂肪间充质干细胞[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(10): 1521-1531.
[18] Prockop DJ.Repair of tissues by adult stem/progenitor cells (MSCs): controversies, myths, and changing paradigms.Mol Ther. 2009;17(6):939-946. |

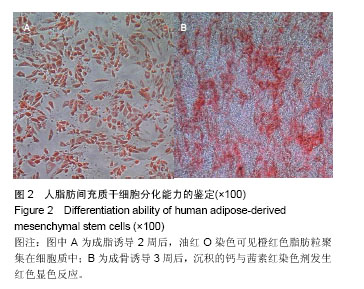
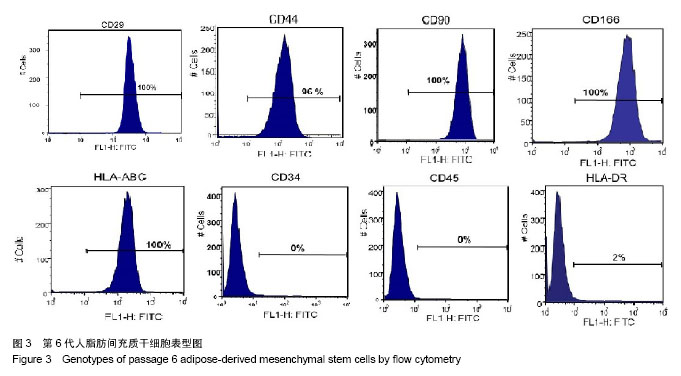
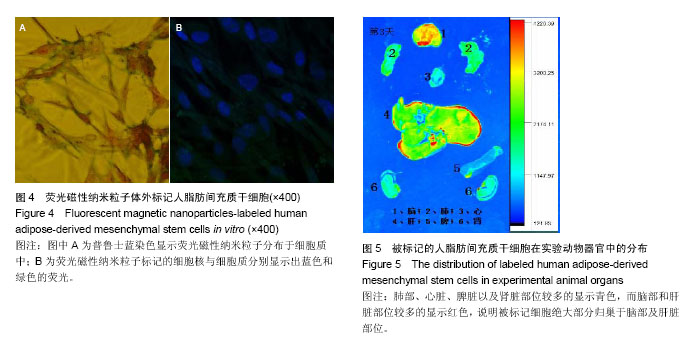
.jpg)