中国组织工程研究 ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (50): 8168-8173.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.50.023
• 干细胞培养与分化 stem cell culture and differentiation • 上一篇 下一篇
人胚胎脑组织蛋白提取物诱导人胎盘间充质干细胞向神经细胞的分化
马丽君1,范 恒1,马晓娜1,魏 军1,2,李玉奎1,2
- 1宁夏医科大学总医院干细胞研究所,宁夏回族自治区银川市 750004;2宁夏医科大学生育力保持省部共建教育部重点实验室,宁夏回族自治区银川市 750004
Protein extracts from human embryonic brain tissue induce the neuronal differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells from human placenta
Ma Li-jun1, Fan Heng1, Ma Xiao-na1, Wei Jun1, 2, Li Yu-kui1, 2
- 1Ningxia Human Stem Cell Institute, the General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China; 2Province-Ministry Co-Constructed Key Laboratory of Fecundity Preserve, Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
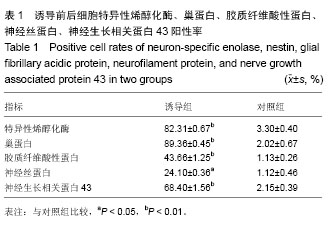
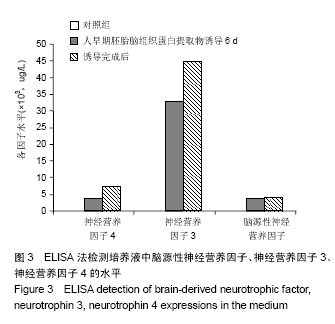
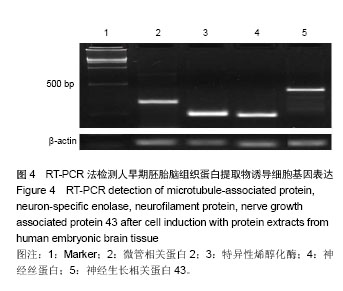
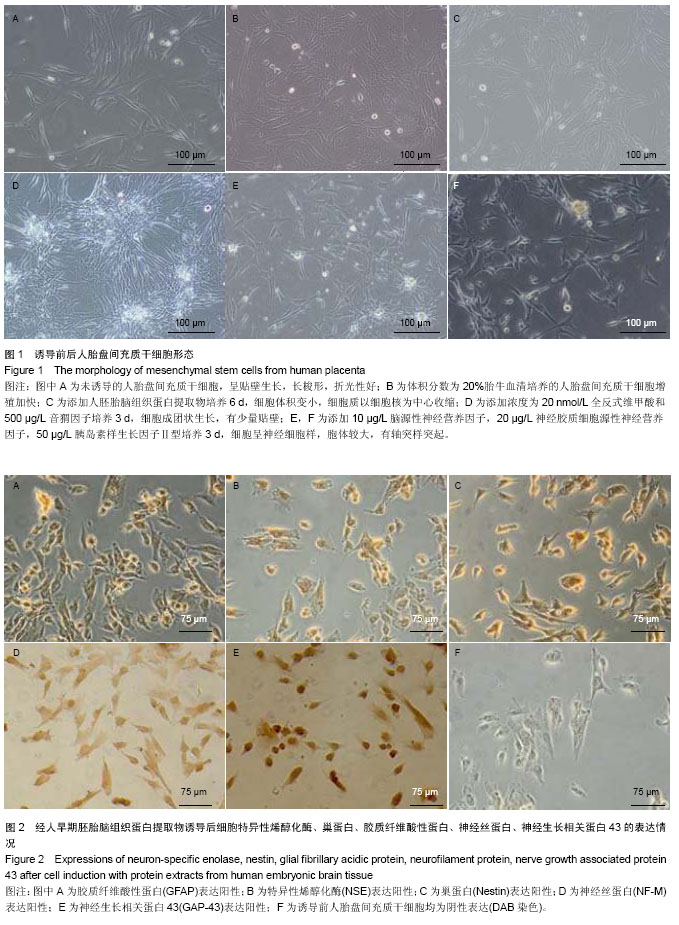
背景:选择合适的诱导方法诱导人胎盘间充质干细胞分化为神经元样细胞是临床治疗神经损伤的关键。 目的:在人胎盘间充质干细胞中加入商品化的人胚胎脑组织蛋白提取物,观察其诱导分化为神经元样细胞的可行性。 方法:采用酶消化法分离培养人胎盘间充质干细胞,传至第3代,将人早期胚胎脑组织蛋白提取物加入诱导培养基培养6 d,加入浓度为20 nmol/L全反式维甲酸和500 μg/L音猬因子培养3 d,换新的培养液,包含体积分数为10%胎牛血清,10 μg/L脑源性神经营养因子,20 μg/L神经胶质细胞源性神经营养因子,50 μg/L胰岛素样生长因子Ⅱ型继续培养3 d。 结果与结论:胎盘组织经酶消化后获得贴壁细胞,传至第2代细胞形态为梭形,成漩涡样生长,传至第3代细胞形态较均一。诱导后细胞经免疫细胞化学法检测均表达神经元特异性烯醇化酶、巢蛋白、胶质纤维酸性蛋白、神经丝蛋白、神经生长相关蛋白43;ELISA法检测细胞培养上清脑源性神经营养因子、神经营养因子3、神经营养因子4为阳性表达;RT-PCR检测细胞微管相关蛋白、神经元特异性烯醇化酶、神经丝蛋白、神经生长相关蛋白43均为阳性表达。结果表明人胚胎脑组织蛋白提取物使人胎盘间充质干细胞诱导分化为神经元样细胞。
中图分类号: