| [1]Deal C. Potential new drug targets for osteoporosis. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2009;5(1):20-27. [2]Harada S, Rodan GA. Control of osteoblast function and regulation of bone mass. Nature. 2003;423(6937):349-355.[3]Gao Y, Yang G, Weng T, et al. Disruption of Smad4 in odontoblasts causes multiple keratocystic odontogenic tumors and tooth malformation in mice. Mol Cell Biol. 2009; 29(21):5941-5951. [4]Ho JH, Ma WH, Su Y, et al. Thymosin beta-4 directs cell fate determination of human mesenchymal stem cells through biophysical effects. J Orthop Res. 2010;28(1):131-138.[5]Leskelä HV, Olkku A, Lehtonen S, et al. Estrogen receptor alpha genotype confers interindividual variability of response to estrogen and testosterone in mesenchymal-stem -cell-derived osteoblasts. Bone. 2006;39(5):1026-1034. [6]Liu Y, Wang L, Kikuiri T, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-based tissue regeneration is governed by recipient T lymphocytes via IFN-γ and TNF-α. Nat Med. 2011;17(12):1594-1601.[7]Scheller EL, Song J, Dishowitz MI, et al. Leptin functions peripherally to regulate differentiation of mesenchymal progenitor cells. Stem Cells. 2010;28(6):1071-1080. [8]Zhang X, Yang M, Lin L, et al. Runx2 overexpression enhances osteoblastic differentiation and mineralization in adipose--derived stem cells in vitro and in vivo. Calcif Tissue Int. 2006;79(3):169-178. [9]Wolffe AP, Matzke MA. Epigenetics: regulation through repression. Science. 1999;286(5439):481-486.[10]Calarco JP, Borges F, Donoghue MT, et al. Reprogramming of DNA methylation in pollen guides epigenetic inheritance via small RNA. Cell. 2012;151(1):194-205. [11]Du J, Zhong X, Bernatavichute YV, et al. Dual binding of chromomethylase domains to H3K9me2-containing nucleosomes directs DNA methylation in plants. Cell. 2012; 151(1):167-180. [12]Johnson LM, Du J, Hale CJ, et al. SRA- and SET-domain-containing proteins link RNA polymerase V occupancy to DNA methylation. Nature. 2014. in press.[13]Xie W, Barr CL, Kim A, et al. Base-resolution analyses of sequence and parent-of-origin dependent DNA methylation in the mouse genome. Cell. 2012;148(4):816-831. [14]Black JC, Manning AL, Van Rechem C, et al. KDM4A lysine demethylase induces site-specific copy gain and rereplication of regions amplified in tumors. Cell. 2013;154(3):541-555. [15]Liu W, Ma Q, Wong K, et al. Brd4 and JMJD6-associated anti-pause enhancers in regulation of transcriptional pause release. Cell. 2013;155(7):1581-1595. [16]Lyons DB, Allen WE, Goh T, et al. An epigenetic trap stabilizes singular olfactory receptor expression. Cell. 2013; 154(2):325-336. [17]Rickels R, Shilatifard A. A histone modifier's ill-gotten copy gains. Cell. 2013;154(3):477-479. [18]Zhao W, Li Q, Ayers S, et al. Jmjd3 inhibits reprogramming by upregulating expression of INK4a/Arf and targeting PHF20 for ubiquitination. Cell. 2013;152(5):1037-1050. [19]Hakim O, Misteli T. SnapShot: Chromosome confirmation capture. Cell. 2012;148(5):1068.e1-2. [20]Zhong FL, Batista LF, Freund A, et al. TPP1 OB-fold domain controls telomere maintenance by recruiting telomerase to chromosome ends. Cell. 2012;150(3):481-494. [21]Chou J, Lin JH, Brenot A, et al. GATA3 suppresses metastasis and modulates the tumour microenvironment by regulating microRNA-29b expression. Nat Cell Biol. 2013; 15(2):201-213. [22]Pencheva N, Tavazoie SF. Control of metastatic progression by microRNA regulatory networks. Nat Cell Biol. 2013;15(6): 546-554. [23]Wang D, Zhang Z, O'Loughlin E, et al. MicroRNA-205 controls neonatal expansion of skin stem cells by modulating the PI(3)K pathway. Nat Cell Biol. 2013;15(10):1153-1163. [24]Minoda A, Saitoh S, Takahashi K, et al. BAF53/Arp4 homolog Alp5 in fission yeast is required for histone H4 acetylation, kinetochore-spindle attachment, and gene silencing at centromere. Mol Biol Cell. 2005;16(1):316-327. [25]Vega RB, Matsuda K, Oh J, et al. Histone deacetylase 4 controls chondrocyte hypertrophy during skeletogenesis. Cell. 2004;119(4):555-566.[26]Schroeder TM, Kahler RA, Li X, et al. Histone deacetylase 3 interacts with runx2 to repress the osteocalcin promoter and regulate osteoblast differentiation. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(40): 41998-42007.[27]Westendorf JJ. Histone deacetylases in control of skeletogenesis. J Cell Biochem. 2007;102(2):332-340.[28]Westendorf JJ, Zaidi SK, Cascino JE, et al. Runx2 (Cbfa1, AML-3) interacts with histone deacetylase 6 and represses the p21(CIP1/WAF1) promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 2002;22(22): 7982-7992.[29]Kang JS, Alliston T, Delston R, et al. Repression of Runx2 function by TGF-beta through recruitment of class II histone deacetylases by Smad3. EMBO J. 2005;24(14):2543-2555.[30]Westendorf JJ. Transcriptional co-repressors of Runx2. J Cell Biochem. 2006;98(1):54-64.[31]Lee HW, Suh JH, Kim AY, et al. Histone deacetylase 1-mediated histone modification regulates osteoblast differentiation. Mol Endocrinol. 2006;20(10):2432-2443. [32]Thompson DD, Simmons HA, Pirie CM, et al. FDA Guidelines and animal models for osteoporosis. Bone. 1995;17(4 Suppl): 125S-133S.[33]Kim JL, Kim YH, Kang MK, et al. Antiosteoclastic activity of milk thistle extract after ovariectomy to suppress estrogen deficiency-induced osteoporosis. Biomed Res Int. 2013; 2013: 919374. [34]Ma B, Li X, Zhang Q, et al. Metabonomic profiling in studying anti-osteoporosis effects of strontium fructose 1,6-diphosphate on estrogen deficiency-induced osteoporosis in rats by GC/TOF-MS. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013;718(1-3): 524-532. [35]Miyauchi Y, Sato Y, Kobayashi T, et al. HIF1α is required for osteoclast activation by estrogen deficiency in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(41):16568-16573. [36]Rossini M, Lello S, Sblendorio I, et al. Profile of bazedoxifene/conjugated estrogens for the treatment of estrogen deficiency symptoms and osteoporosis in women at risk of fracture. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2013;7:601-610. [37]Yang N, Wang G, Hu C, et al. Tumor necrosis factor α suppresses the mesenchymal stem cell osteogenesis promoter miR-21 in estrogen deficiency-induced osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res. 2013;28(3):559-573. [38]Almeida M, Iyer S, Martin-Millan M, et al. Estrogen receptor-α signaling in osteoblast progenitors stimulates cortical bone accrual. J Clin Invest. 2013;123(1):394-404. [39]Galea GL, Meakin LB, Sugiyama T, et al. Estrogen receptor α mediates proliferation of osteoblastic cells stimulated by estrogen and mechanical strain, but their acute down-regulation of the Wnt antagonist Sost is mediated by estrogen receptor β. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(13):9035-9048.[40]Sapir-Koren R, Livshits G. Is interaction between age-dependent decline in mechanical stimulation and osteocyte-estrogen receptor levels the culprit for postmenopausal-impaired bone formation? Osteoporos Int. 2013;24(6):1771-1789. [41]Song L, Zhao J, Zhang X, et al. Icariin induces osteoblast proliferation, differentiation and mineralization through estrogen receptor-mediated ERK and JNK signal activation. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013;714(1-3):15-22. [42]Zirngibl RA, Chan JS, Aubin JE. Divergent regulation of the Osteopontin promoter by the estrogen receptor-related receptors is isoform- and cell context dependent. J Cell Biochem. 2013;114(10):2356-2362. [43]Binder NB, Niederreiter B, Hoffmann O, et al. Estrogen-dependent and C-C chemokine receptor-2- dependent pathways determine osteoclast behavior in osteoporosis. Nat Med. 2009;15(4):417-424. [44]Bonnelye E, Saltel F, Chabadel A, et al. Involvement of the orphan nuclear estrogen receptor-related receptor α in osteoclast adhesion and transmigration. J Mol Endocrinol. 2010;45(6):365-377. [45]Crusodé de Souza M, Sasso-Cerri E, Cerri PS. Immunohistochemical detection of estrogen receptor beta in alveolar bone cells of estradiol-treated female rats: possible direct action of estrogen on osteoclast life span. J Anat. 2009;215(6):673-681. [46]Pederson L, Kremer M, Foged NT, et al. Evidence of a correlation of estrogen receptor level and avian osteoclast estrogen responsiveness. J Bone Miner Res. 1997;12(5): 742-752.[47]Taranta A, Brama M, Teti A, et al. The selective estrogen receptor modulator raloxifene regulates osteoclast and osteoblast activity in vitro. Bone. 2002;30(2):368-376.[48]Almeida M, Iyer S, Martin-Millan M, et al. Estrogen receptor-α signaling in osteoblast progenitors stimulates cortical bone accrual. J Clin Invest. 2013;123(1):394-404. [49]Bonnelye E, Aubin JE. An energetic orphan in an endocrine tissue: a revised perspective of the function of estrogen receptor-related receptor alpha in bone and cartilage. J Bone Miner Res. 2013;28(2):225-233. [50]Ming LG, Chen KM, Xian CJ. Functions and action mechanisms of flavonoids genistein and icariin in regulating bone remodeling. J Cell Physiol. 2013;228(3):513-521. [51]Chen JD, Evans RM. A transcriptional co-repressor that interacts with nuclear hormone receptors. Nature. 1995;377 (6548):454-457.[52]Sevetson B, Taylor S, Pan Y. Cbfa1/RUNX2 directs specific expression of the sclerosteosis gene (SOST). J Biol Chem. 2004;279(14):13849-13858.[53]Lamour V, Detry C, Sanchez C, et al. Runx2- and histone deacetylase 3-mediated repression is relieved in differentiating human osteoblast cells to allow high bone sialoprotein expression. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(50):36240- 36249. [54]Nam HK, Liu J, Li Y, et al. Ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/ phosphodiesterase-1 (ENPP1) protein regulates osteoblast differentiation. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(45):39059-39071.[55]Marulanda J, Gao C, Roman H, et al. Prevention of arterial calcification corrects the low bone mass phenotype in MGP-deficient mice. Bone. 2013;57(2):499-508. [56]Lie DC, Colamarino SA, Song HJ, et al. Wnt signalling regulates adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Nature. 2005; 437(7063):1370-1375.[57]Anastas JN, Moon RT. WNT signalling pathways as therapeutic targets in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013;13(1): 11-26. [58]Baron R, Kneissel M. WNT signaling in bone homeostasis and disease: from human mutations to treatments. Nat Med. 2013;19(2):179-192. [59]Bennett CN, Longo KA, Wright WS, et al. Regulation of osteoblastogenesis and bone mass by Wnt10b. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(9):3324-3329.[60]Wahli W, Michalik L. PPARs at the crossroads of lipid signaling and inflammation. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2012;23(7):351-363. [61]Maroni P, Brini AT, Arrigoni E, et al. Chemical and genetic blockade of HDACs enhances osteogenic differentiation of human adipose tissue-derived stem cells by oppositely affecting osteogenic and adipogenic transcription factors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;428(2):271-277. |
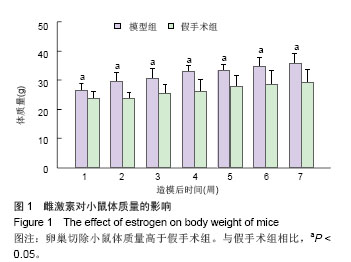
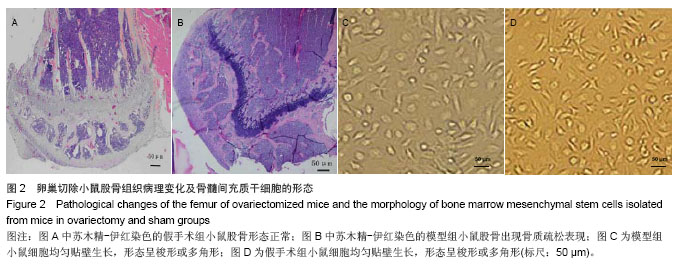
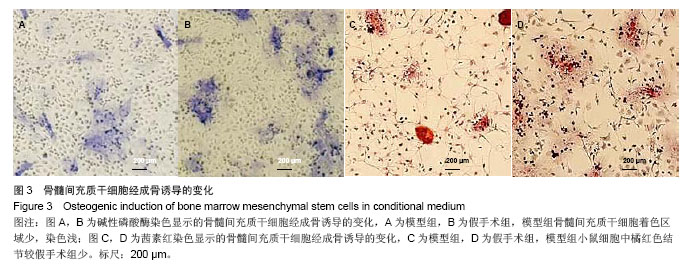
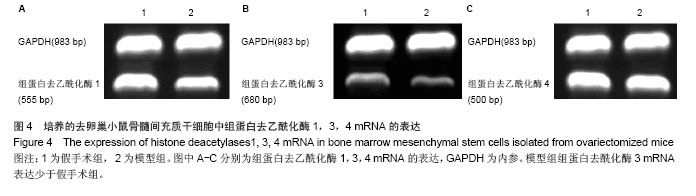
.jpg)