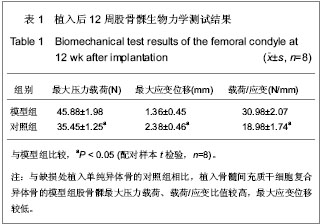
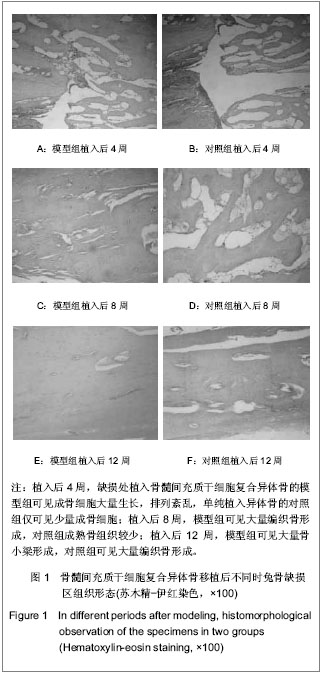
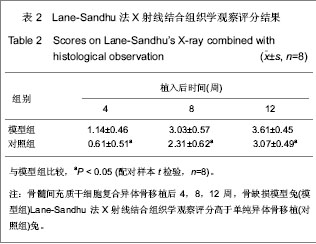
| [1] Niederauer GG, Lee DR, Sankaran S. Bone grafting in arthroscopy and sports medicine. sports Med Arthrosc. 2006; 14(3):163-168.[2] Garcia-Maya M, Anderson AA, Kendal CE, et al. Ligand concen-trafion is a driver of divergent signaling and pleiotropic cellular responses to FGF. J Cell Physiol. 2006;206(2):386-393.[3] 胡金龙,王静成,颜连启.组织工程学技术治疗骨缺损的最新研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2013,21(2):150-153.[4] Endres S, Kratz M. Gamma irradiation. An effective procedure for bone banks, but does it make sense from an osteobiological perspective. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2009;9(1):25-31.[5] Dawn B, Bolli R. Adult bone marrow-derived cells: regenerative potential, plasticity, and tissuecommitment. Basic Res Cardiol. 2005;100(6):494-503.[6] Korda M, Blunn G, Phipps K, et al. Can mesenchymal stem cells survive under normal impaction force in revision total hip replacements? Tissue Eng. 2006;12(3):625-630.[7] The Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China. Guidance Suggestions for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 2006-09-30.[8] Romanov YA, Darevskaya AN, Merzlikina NV, et al. Mesenchymalstem cells from human bone marrow and adipose tissue:isolation, characterization, and differentiation potentialities. Cell Technol Biol Med. 2005;140(1):138-143.[9] Yao J, Radin S, Reilly G, et al. Solution-mediated effect of bioactive glass in poly(lactic-coglyclic acid)-bioactive glass composites on osteogenesis of marrow stromal cells. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2005;75(4):794-801.[10] 付志厚,王爱民.假体与组织工程骨界面骨整合的生物学特征[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(44):8852-8856.[11] 周健,戴尅戎,汤亭亭.BMSCs胶原刮膜对松质骨缺损的修复[J].上海第二医科大学学报,2004,24(8):627-631.[12] 窦强兵,孔荣,朱六龙,等.同种异体间充质干细胞复合纤维蛋白修复骨缺损[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2006,14(10):766-768.[13] Bostrom M, Lane JM, Tomin E, et al. Use of bone morphogenetic protein-2 in the rabbit ulnar nonunion model. Clin Orthop. 1996;327:272-282. [14] 刘阳,曹延林,朱立新,等.新型可注射性nHA/CS骨修复材料修复兔股骨髁骨缺损的X 线评估[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2011,19(17): 1472-1475.[15] 阳懿,赵承初,孙勇,等.两种骨修复材料修复兔颅骨骨缺损:X射线评估效果[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(34): 6283-6286.[16] Khan SN, Cammisa FP, Sandhu HS, et al. The biology of bonegrafting. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2005;13(1):77-86.[17] 胡忠洲,孟凡丁,王韶进.颗粒骨打压植骨治疗全髋关节翻修中髋臼侧骨缺损[J].医学与哲学,2012,33(3):35-37.[18] Olivier V, Hivart P, Descamps M, et al. In vitro culture of large bone substitutes in a new bioreactor:importance of the flow direction. Biomed Mat. 2007;2(3):174-180.[19] 胥少汀,葛宝丰,许印坎.实用骨科学[M]. 3版.北京:人民军医出版社,2005.[20] Devine SM. Mesenehymal stem cells:will they have a role in the clinic. J Cell Biochem Suppl. 2002;38:73-79.[21] Niemeyer P, Kornacker M, Mehlhorn A, et al. Comparison of immunological properties of bone marrow stromal cells and adipose tissue-derived stem cells before and after osteogenic differentiation in vitro. Tissue Eng. 2007;13(1): 111-121.[22] Ohgushi H, Dohi Y, Tamai S, et al. Osteogenic differentiation of marrow stromal stem cells in porous hydroxyapatite ceramics. J Biomed Mater Res. 1993;27(11):1401-1407.[23] Matsushima A, Kotobuki N, Tadokoro M, et al. In vivo osteogenic capability of human mesenchymal cells cultured on hydroxyapatite and on beta-tricalcium phosphate. Artif Organs. 2009;33(6):474-481.[24] Park SH, Tofighi A, Wang X, et al. Calcium phosphate combination biomaterials as human mesenchymal stem cell delivery vehicles for bone repair. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2011;97(2):235-244.[25] Mauney JR, Jaquiery C, Volloch V, et al. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of differentially demineralized cancellous bone scaffolds combined with human bone marrow stromal cells for tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2005;26(16):3173- 3185.[26] Tsiridis E, Ali Z, Bhalla A, et al. In vitro proliferation and differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells on hydroxyapatite versus human demineralised bone matrix with and without osteogenic protein-1. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2009; 9(1):9-19.[27] Okamoto M, Dohi Y, Ohgushi H, et al. Influence of the porosity of hydroxyapatite ceramics on in vitro and in vivo bone formation by cultured rat bone marrow stromal cells. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2006;17(4):327-336.[28] Hing KA, Revell PA, Smith N, et al. Effect of silicon level on rate, quality and progression of bone healing within silicate-substituted porous hydroxyapatite scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2006;27(29):5014-5026.[29] Hing KA, Wilson LF, Buckland T. Comparative performance of three ceramic bone graft substitutes. Spine J. 2007;7(4): 475-490.[30] Mankani MH, Kuznetsov SA, Wolfe RM, et al. In vivo bone formation by human bone marrow stromal cells: reconstruction of the mouse calvarium and mandible. Stem Cells. 2006;24(9):2140-2149.[31] Mankani MH, Kuznetsov SA, Shannon B, et al. Canine cranial reconstruction using autologous bone marrow stromal cells. Am J Pathol. 2006;168(2):542-550.[32] Quarto R, Mastrogiacomo M,Cancedda R, et al. Repair of large bone defects with the use of autologous bone marrow stromal cells. N Engl J Med. 2001;344(5):385-386.[33] Marcacci M, Kon E, Moukhachev V, et al. Stem cells associated with macroporous bioceramics for long bone repair: 6- to 7-year outcome of a pilot clinical study. Tissue Eng. 2007;13(5):947-955.[34] Bolland BJ, Partridge K, Tilley S, et al. Biological and mechanical enhancement of impacted allograft seeded with human bone marrow stromal cells: potential clinical role in impaction bone grafting. Regen Med. 2006;1(4):457-467.[35] Korda M, Blunn G, Goodship A, et al. Use of mesenchymal stem cells to enhance bone formation around revision hip replacements. J Orthop Res. 2008;26(6):880-885.[36] Casabona F, Martin I, Muraglia A, et al. Prefabricated engineered bone flaps: an experimental model of tissue reconstruction in plastic surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1998; 101(3):577-581.[37] Mankani MH, Kuznetsov SA, Robey PG. Formation of hematopoietic territories and bone by transplanted human bone marrow stromal cells requires a critical cell density. Exp Hematol. 2007;35(6):995-1004.[38] 田志逢,秦书俭,张小玲,等.不同接种密度骨髓间充质干细胞/骨基质明胶复合体修复大鼠桡骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(49):9126-9130. |
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)